Quick Facts
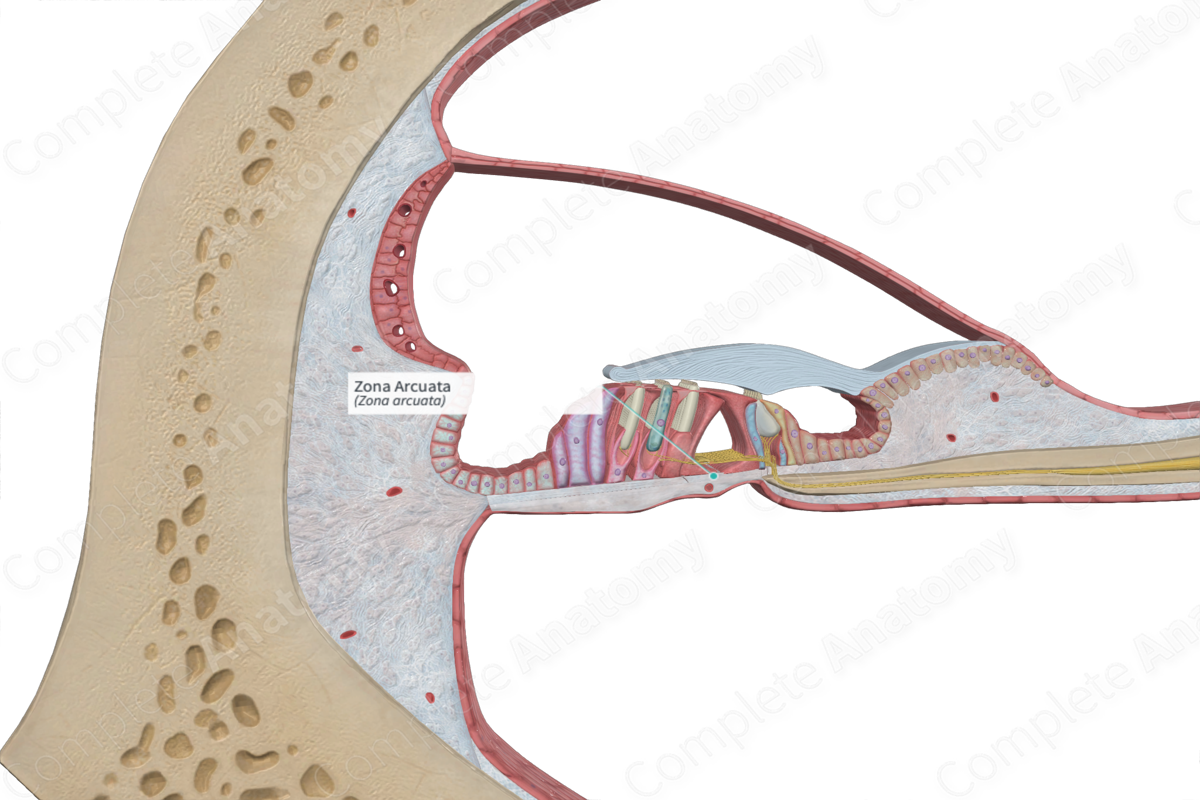
The zona arcuata is the inner third of the basilar membrane of the cochlear duct; it is roughly equivalent to the floor of the inner tunnel (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
The zona arcuata is one of two regions of the basilar membrane, the other being the zona pectinata. The zona arcuata is the innermost part of the basilar membrane and it is notably thinner than its outer counterpart. The zona arcuata attaches from the base of the outer pillar cells and inserts into the spiral limbus.
Structurally, it is comprised of bundles of collagenous filaments that are organized radially rather than longitudinally (Standring, 2016).
Anatomical Relations
The zona arcuata forms the inner part of the basilar membrane, while the zona pectinata forms the outer part. The zona arcuata lies inferior to the epithelial cells of the organ of Corti.
Function
The zona arcuata supports the epithelial cells of the organ of Corti and enable the transduction process to be carried without interfering factors. The zona arcuata, along with the zona pectinata, comprise a barrier which separates the cochlear duct and the scala tympani, as well as the endolymph and the perilymph occupying these canals. These two fluids have different ion concentrations involved in the transmission of vibrations. However, the zona arcuata is permeable to the perilymph of the scala tympani to an extent, thus allowing the spiral organ (of Corti) to bathe in perilymph (also referred to cortilymph in this region due to some minor alterations of its composition) (Standring, 2016).
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice., 41st edition. Elsevier Limited.
