Structure
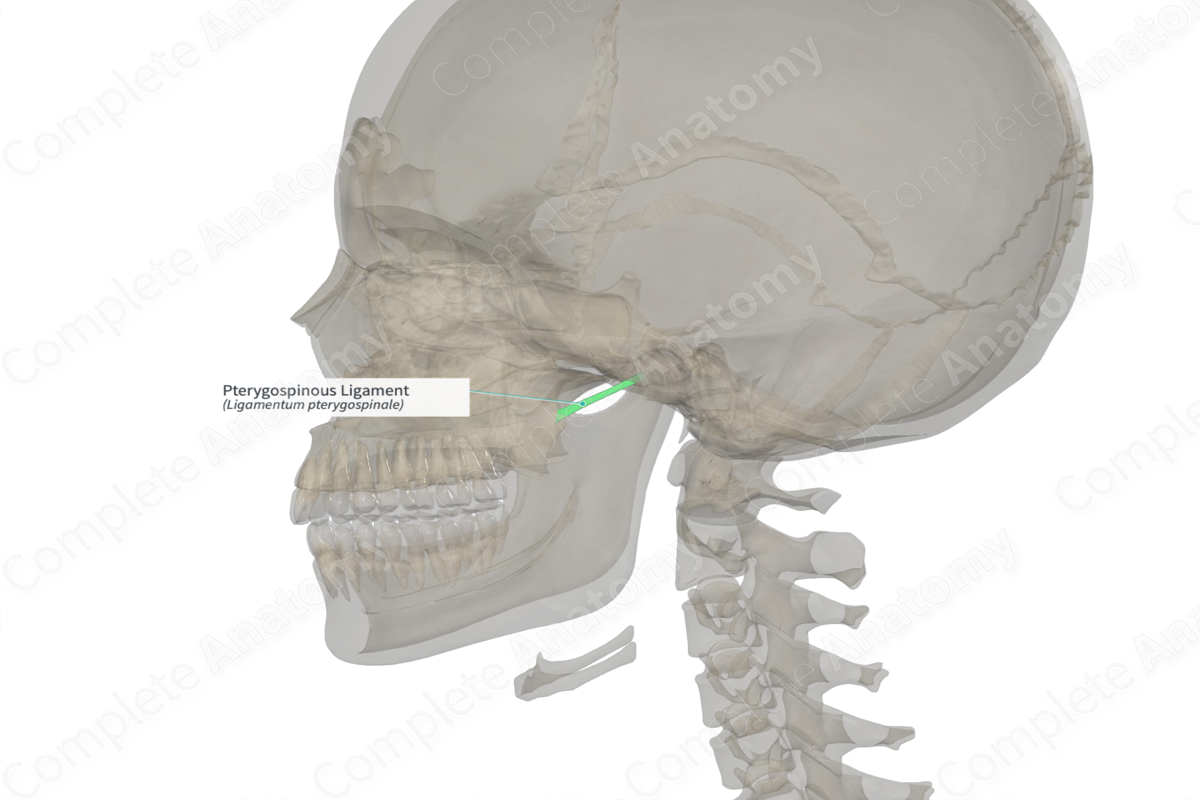
The pterygospinous ligament is a band of fibers that connects one part of the sphenoid bone to another. In some instances, it may be replaced with muscle fibers or may be ossified.
Related parts of the anatomy
Anatomical Relations
The pterygospinous ligament extends between the spine of the sphenoid bone and the pterygospinous process on the posterior margin of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Function
If ossified, this ligament may form a foramen, the pterygospinous foramen, that transmits the muscular branches of the mandibular nerve to the temporalis, masseter, and the lateral pterygoid muscles.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Mandibular neuralgia
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Joint Ligament

Entheseal structures are widely located throughout the body and are represented by the interface between bone and several tissues including tendon, joint capsules and ligaments.



