Description
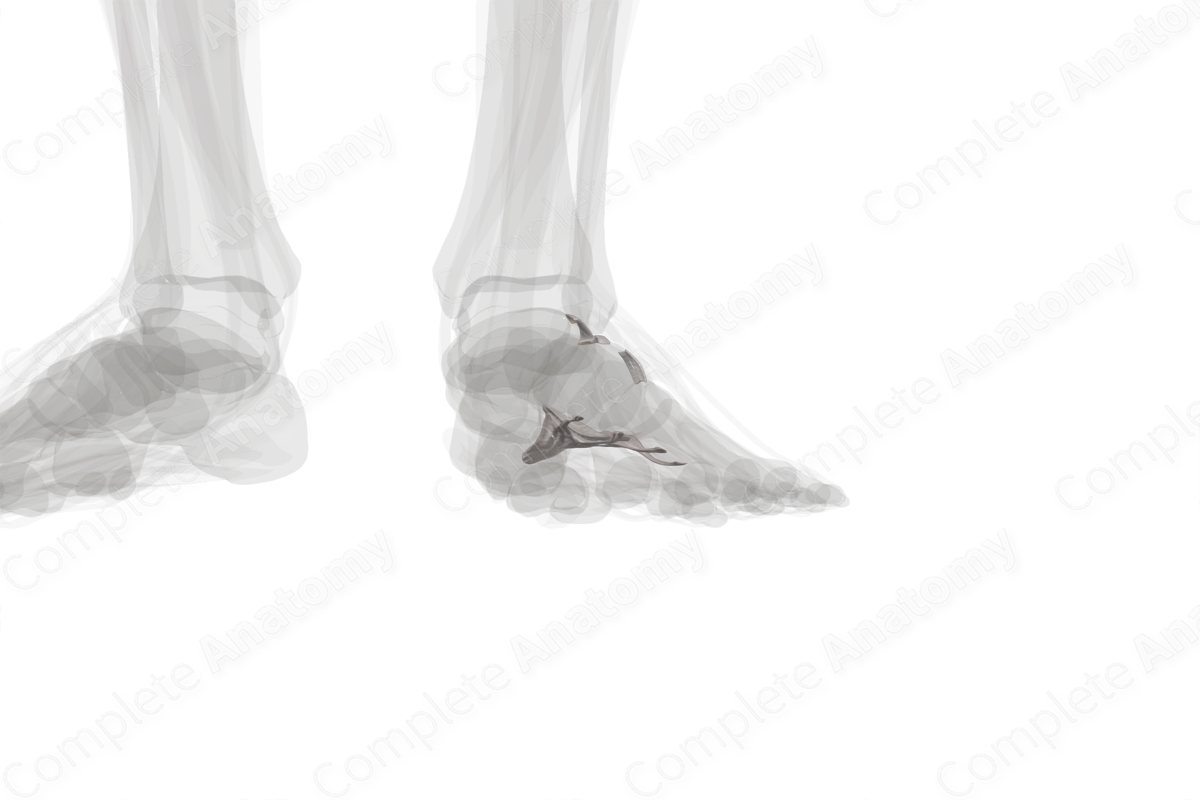
The calcaneocuboid joint is formed by the articulation of the calcaneus and cuboid bones. This joint is located at the same level as the articulation of the talus and navicular bone, thus, collectively, they are known as the transverse tarsal joint.
The calcaneocuboid joint is a saddle joint and plays a role in movements such as inversion, eversion, and circumduction of the foot. The bones are held together by a fibrous capsule, strengthened by the dorsal and plantar calcaneocuboid ligaments and the long plantar ligament. Additionally, the bifurcate ligament also contributes to the stability of this joint.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Foot Joint

The plantar vault is an architectural structure which blends all the elements of the foot – joints, ligaments and muscles – into a unified system.




