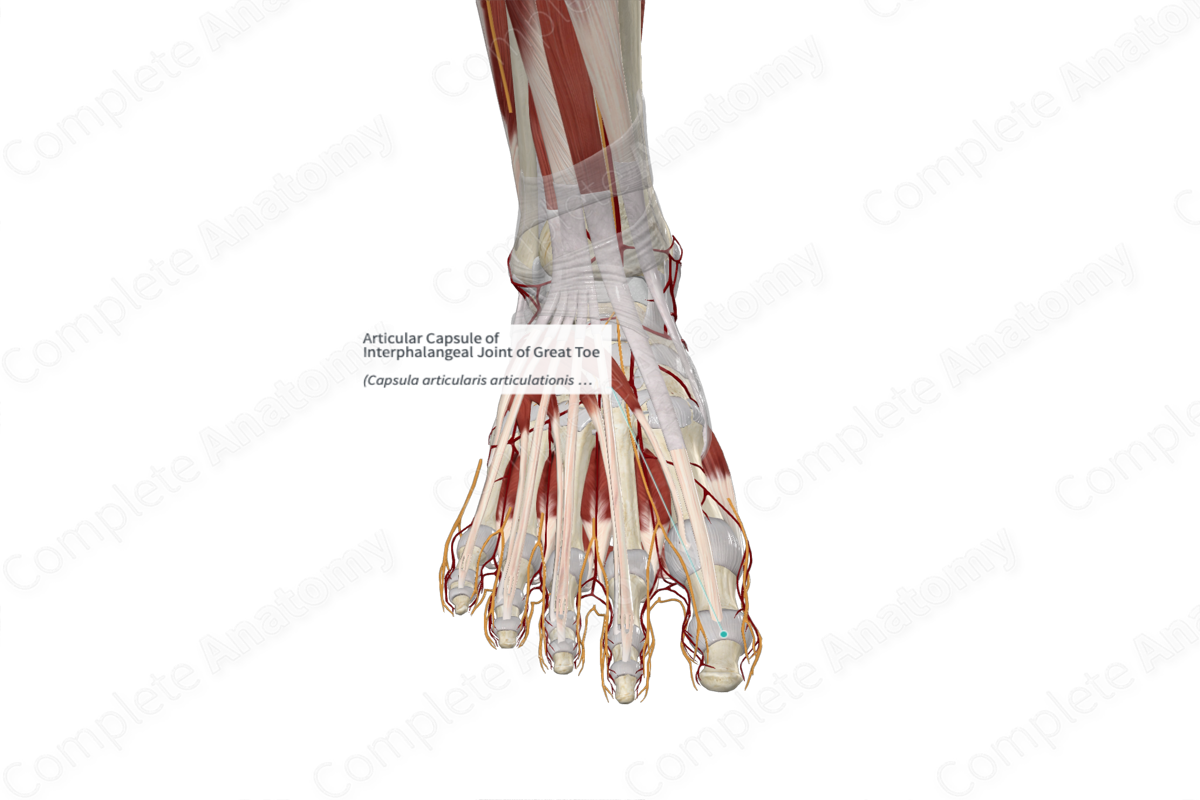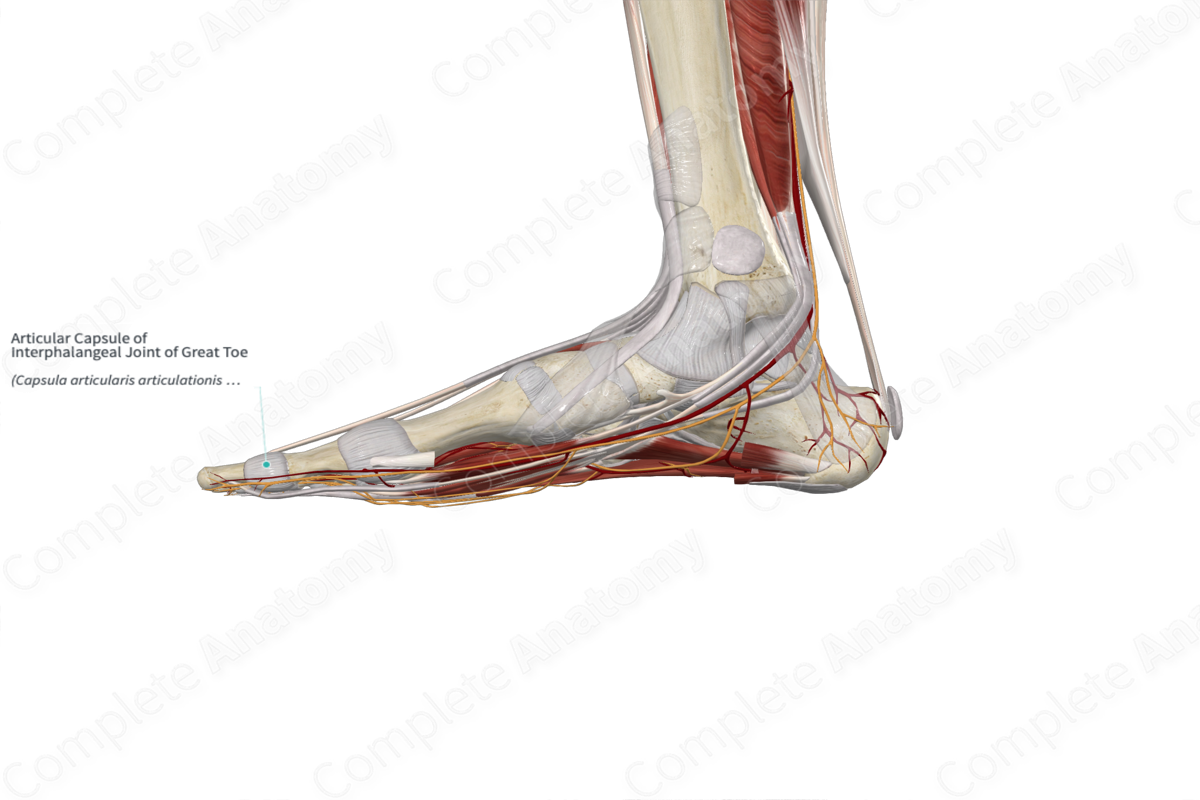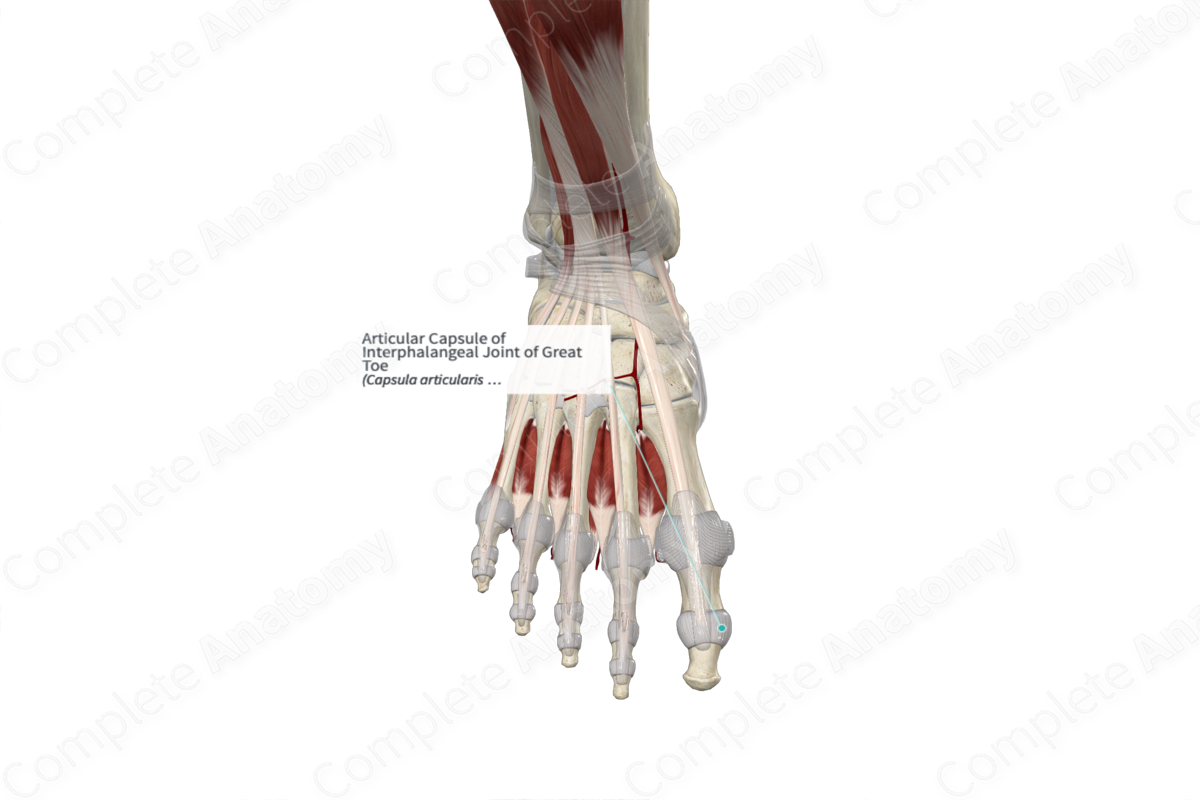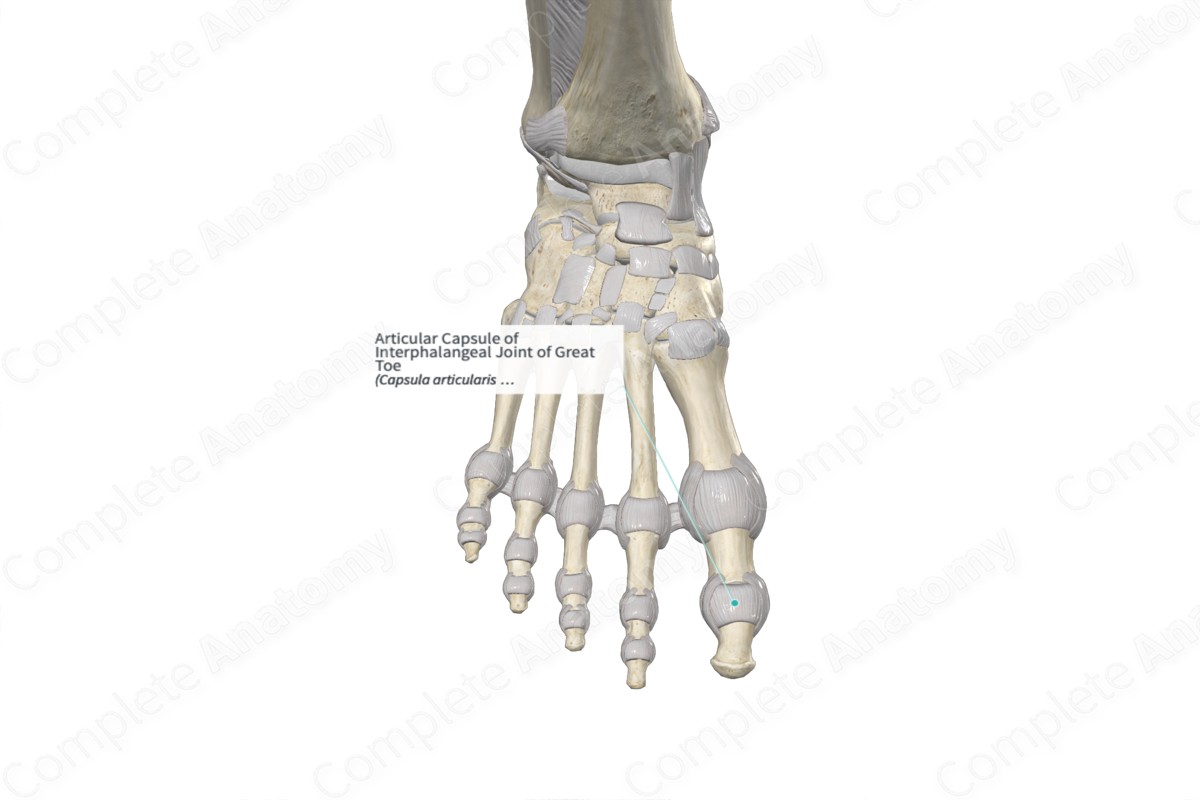
Articular Capsule of Interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe
Capsula articularis articulationis interphalangeae hallucis
Read moreStructure
The articular capsules of the interphalangeal joints are loosely attached to the articular margins of the bones. It is composed of two layers. The external layer, the fibrous membrane, is composed of dense fibrous tissue. The internal layer, the synovial membrane, lines the joint cavity and is composed of loose connective tissue.
Related parts of the anatomy
Anatomical Relations
The articular capsules of the interphalangeal joints are reinforced laterally and medially by the collateral ligaments, on its plantar aspect by the plantar ligaments, and dorsally by the extensor expansion.
Function
The articular capsule of the interphalangeal joints ensures that the joint is sealed, thus, keeping the lubricating synovial fluid within the joint. It provides passive stability to the joint by limiting the joint movement. Additionally, it provides active stability but containing numerous proprioceptive nerve endings which relay mechanical information back to the central nervous system (Ralphs and Benjamin, 1994).
References
Ralphs, J. R. and Benjamin, M. (1994) 'The joint capsule: structure, composition, ageing and disease', Journal of Anatomy, 184(Pt 3), pp. 503-509.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Interphalangeal Joint

The distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint is a hinge joint that is composed of the middle phalanx head and distal phalanx base.