Anatomical Relations
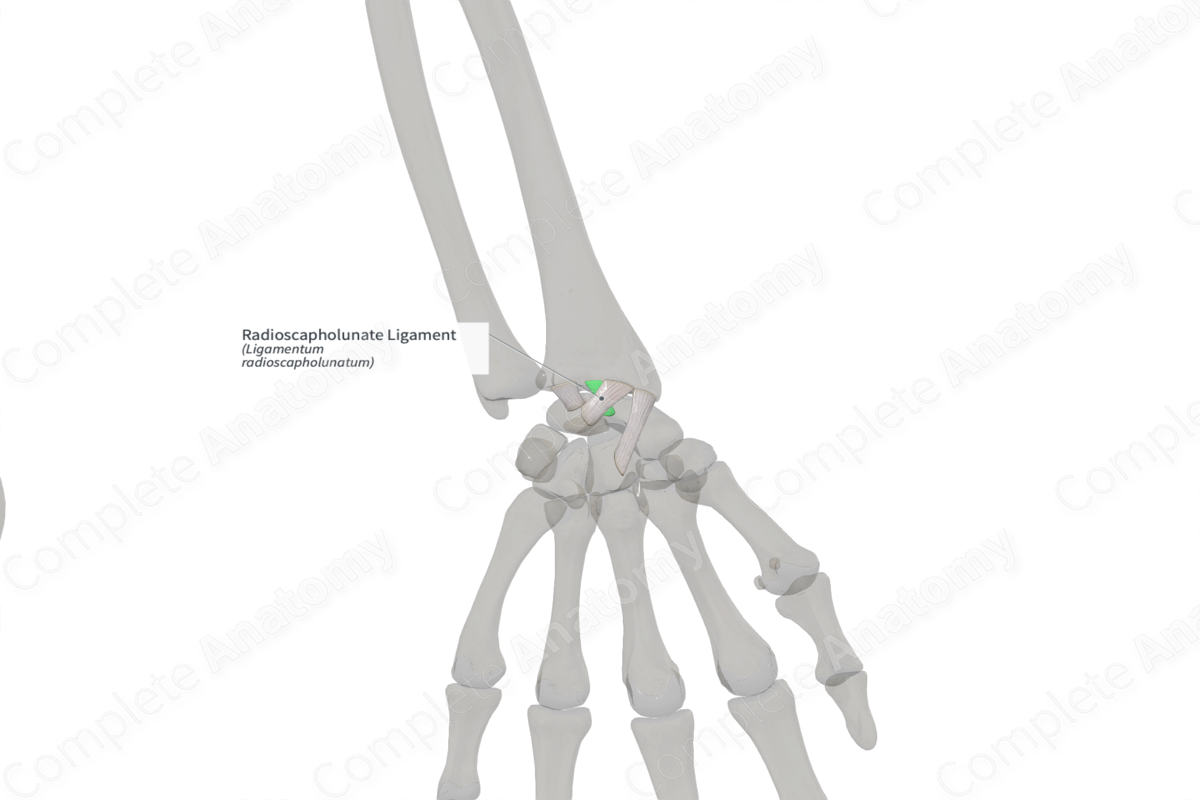
The radioscapholunate ligament forms part of the palmar radiocarpal ligament. It arises from the palmar lip of the distal radius, between the long and short radiolunate ligaments. It extends distally to the scaphoid and lunate bones and blends with the scapholunate interosseous ligament (Berger et al., 1991).
Related parts of the anatomy
Function
The palmar radiocarpal ligament strengthens the articular capsule of the radiocarpal joint. The oblique nature of the ligaments ensures that the hand follows the radius during supination of the forearm (Moore et al., 2013). Additionally, the radioscapholunate ligament may be clinically important for the vascular supply of the scapholunate interosseous ligament and nervous supply (sensory) from the scapholunate articulation (Berger et al., 1991).
References
Berger, R. A., Kauer, J. M. G. and Landsmeer, J. M. F. (1991) 'Radioscapholunate ligament: A gross anatomic and histologic study of fetal and adult wrists', Journal of Hand Surgery, 16(2), pp. 350-355.
Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F. and Agur, A. M. R. (2013) Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th edn.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products

