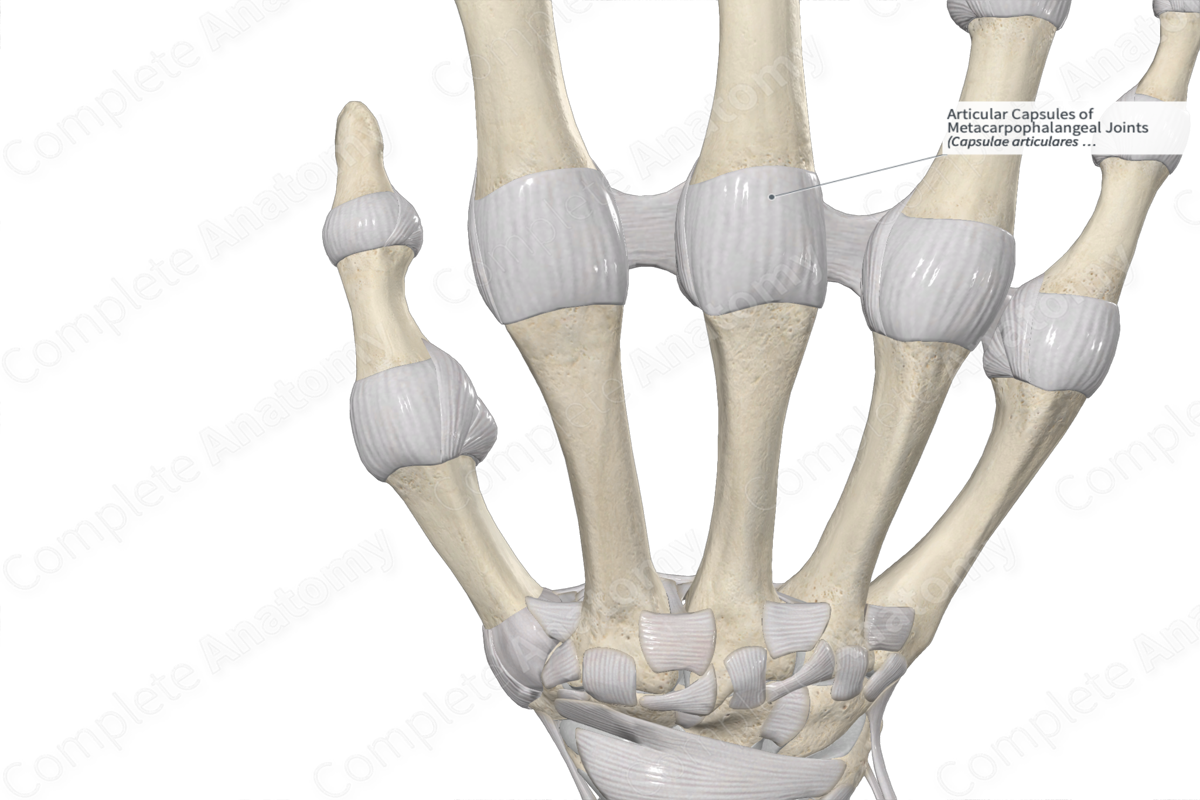
Articular Capsules of Metacarpophalangeal Joints
Capsulae articulares articulationum metacarpophalangearum
Read moreAnatomical Relations
The articular capsules of the metacarpophalangeal joints are the membranous sacs enclosing the articular surface of the distal metacarpal bones and the bases of the proximal phalanges. It is composed of an outer fibrous membrane and an inner synovial membrane. The ligament of the metacarpophalangeal joints, i.e., the palmar, collateral, and accessory collateral ligaments reinforce the articular capsule.
Function
The articular capsule of the metacarpophalangeal joint ensures that the joint is sealed, thus, keeping the lubricating synovial fluid within the joint. It provides passive stability to the joint by limiting the joint movement. Additionally, it provides active stability by containing numerous proprioceptive nerve endings which relay mechanical information back to the central nervous system (Ralphs and Benjamin, 1994).
References
Ralphs, J. R. and Benjamin, M. (1994) 'The joint capsule: structure, composition, ageing and disease', Journal of Anatomy, 184(Pt 3), pp. 503-509.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Metacarpophalangeal Joint

The synovial pad of the metacarpophalangeal (and metatarsophalangeal) joint is a fold (plica) of fibrous connective tissue located in the proximal recess of the dorsal compartment at the joint capsule attachment to McIII.



