Anatomical Relations
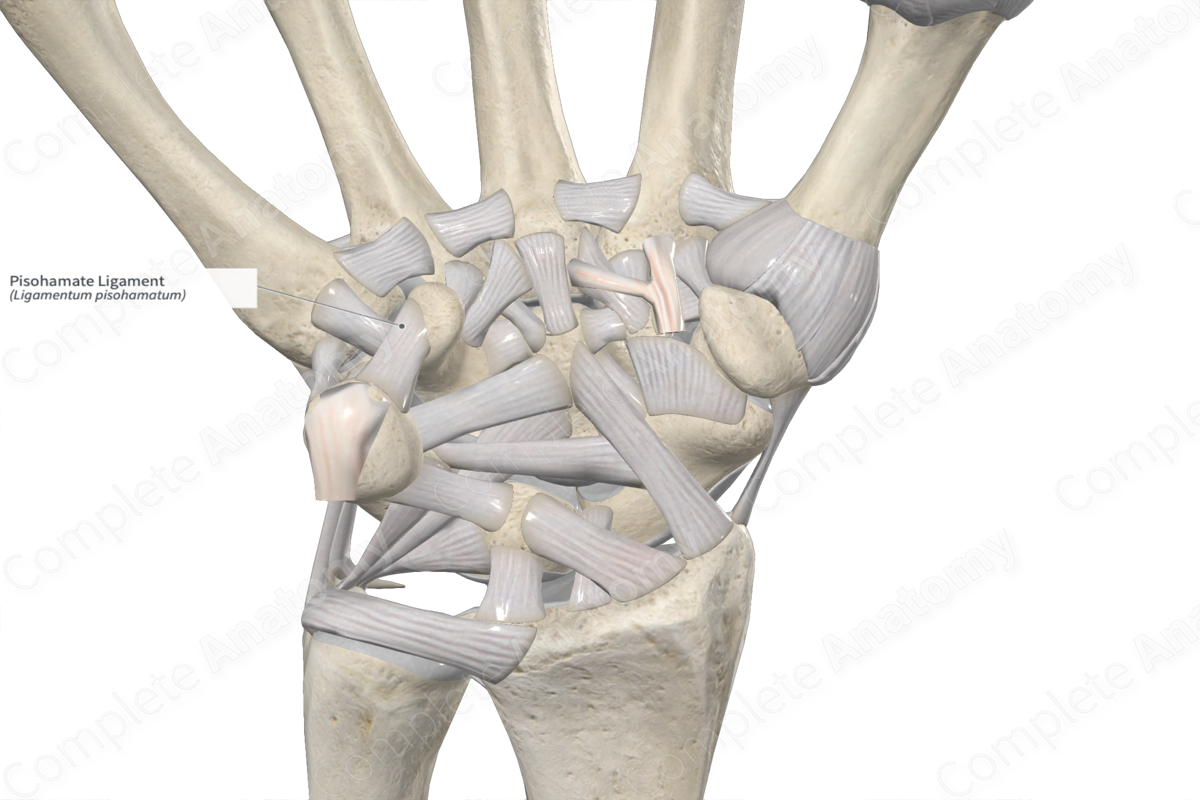
The pisohamate ligament forms part of the ligamentous complex of the pisiform (or pisotriquetral) joint. It attaches from the palmar aspect of the pisiform to the hamate. The pisohamate ligament, along with the flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament), pisometacarpal ligament, and flexor digiti minimi, forms the floor of Guyon’s canal. The ulnar nerve and artery pass through this canal.
Related parts of the anatomy
Function
The pisotriquetral, pisohamate, and pisometacarpal ligaments form a ligamentous complex around the pisiform joint and act as primary stabilizers, resisting to proximal, ulnar, and radial forces (Rayan et al., 2005).
List of Clinical Correlates
—Pisiform ligament complex syndrome
References
Rayan, G. M., Jameson, B. H. and Chung, K. W. (2005) 'The pisotriquetral joint: anatomic, biomechanical, and radiographic analysis', J Hand Surg Am, 30(3), pp. 596-602.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




