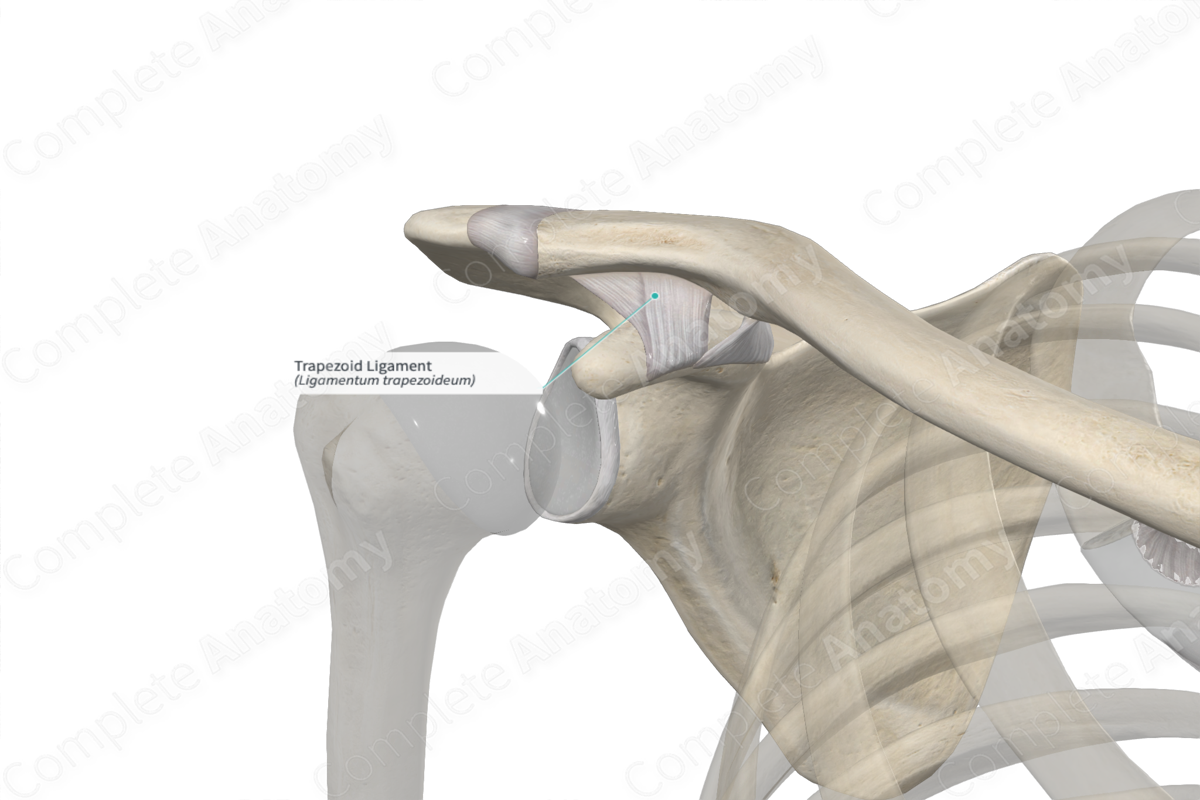
Anatomical Relations
The trapezoid ligament is one of two parts (along with the conoid ligament) that forms the coracoclavicular ligament.
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure
As its name suggests, the trapezoid ligament is quadrilateral and forms the lateral part of the coracoclavicular ligament. It is broad and thin, ascending from the upper surface of the coracoid process of the scapula to the trapezoid line on the inferior clavicular surface. It has a free anterior border, while its posterior border is joined with the coronoid ligament.
Function
As a rule, quadrilateral ligaments twist when its associated bones rotate. As the ligament twists, the distance between the opposed surfaces of the adjacent bones shortens. This ensures that excessive rotation of the adjoining bones is limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




