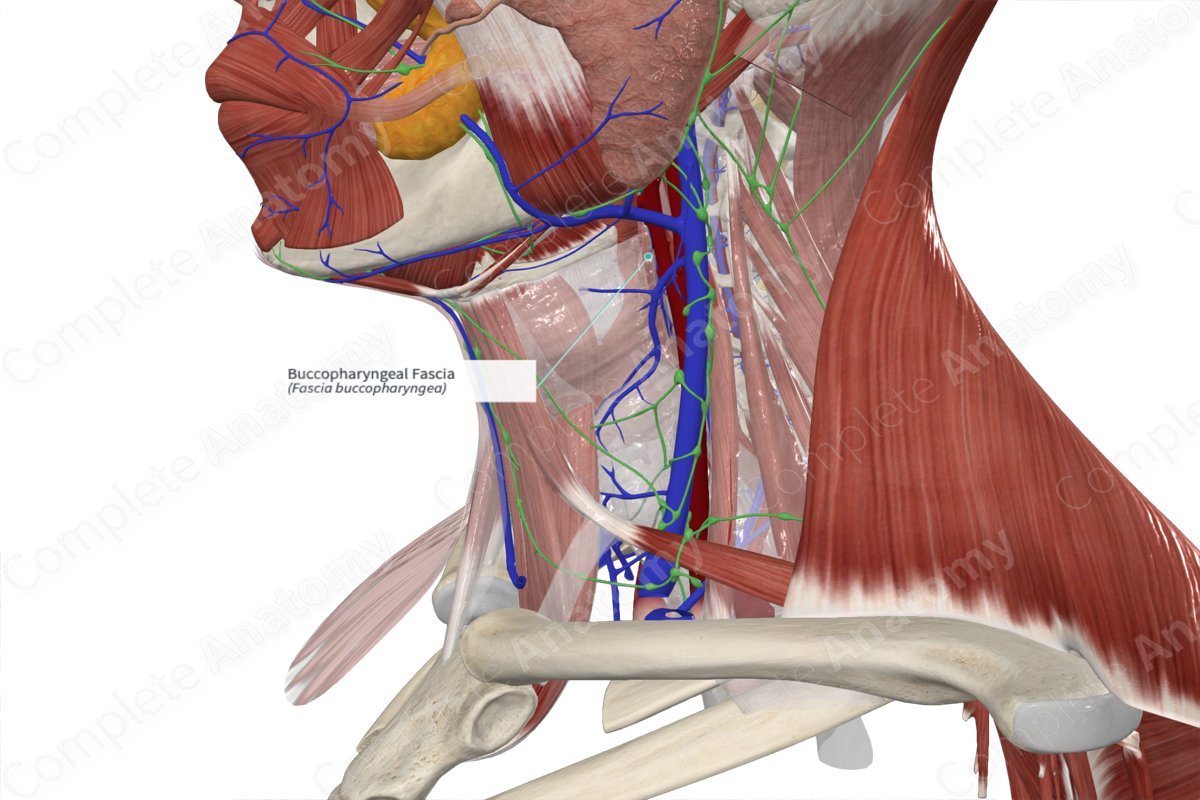
Buccopharyngeal Fascia Structure
The buccopharyngeal fascia is part of the visceral division of the deep cervical fascia. It commences laterally as it fuses with the periosteum on the posterior alveolar process of the maxilla and the periosteum of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. The fascia travels posteriorly to cover the buccinator muscle and the lateral parts of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle before curving posteromedially to cover the back of the superior pharyngeal constrictor (Stecco & Hammer, 2014). It descends in the midline to cover the posterior aspect of middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles.
Buccopharyngeal Fascia Function
The buccopharyngeal fascia anchors some of the fibers of buccinator muscle to enable coordination of the mouth and pharynx and playing a role in chewing and swallowing (Stecco & Hammer, 2014).
Buccopharyngeal Fascia References
Stecco, C. & Hammer, W. I. (2014) Functional Atlas of the Human Fascial System E-BookElsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Buccopharyngeal Fascia

The buccopharyngeal fascia is the middle layer of the deep cervical fascia, and it represents the fascial limit of the lateral and posterior portions of the nasopharynx.



