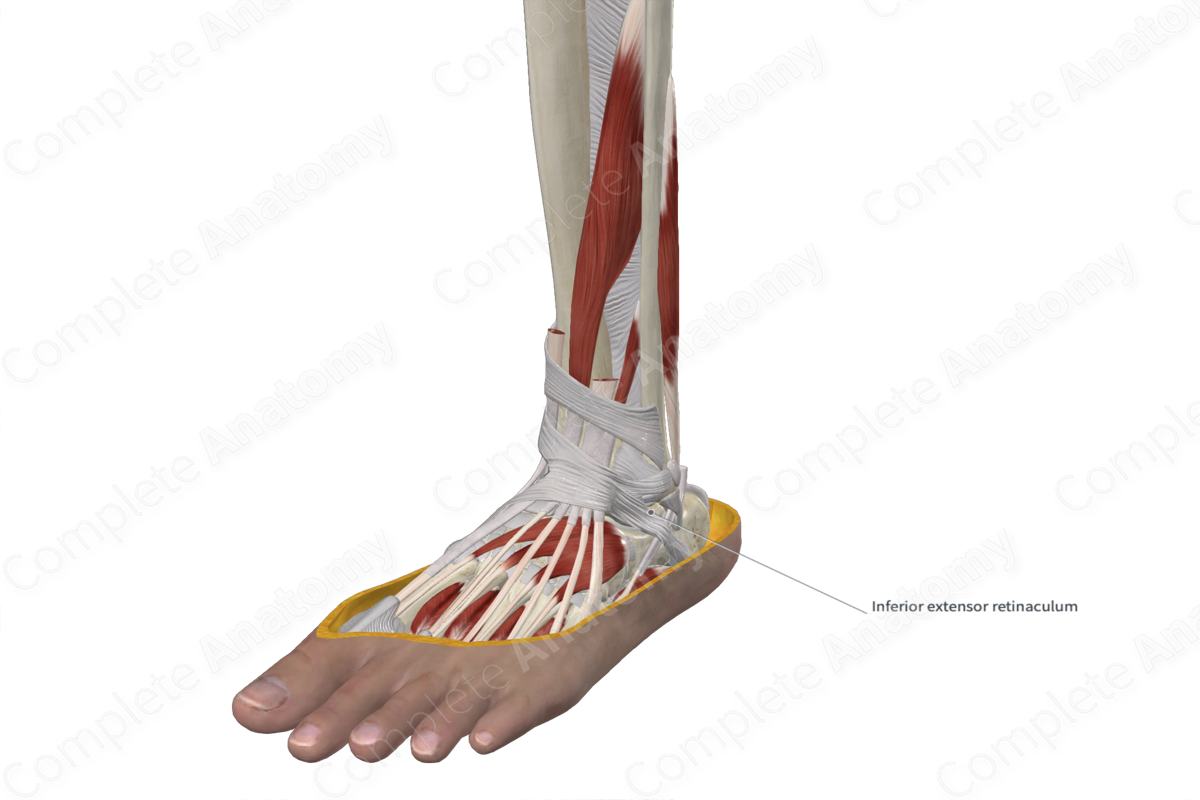
Inferior Extensor Retinaculum of Ankle
Retinaculum extensorium inferius tali
Read moreStructure
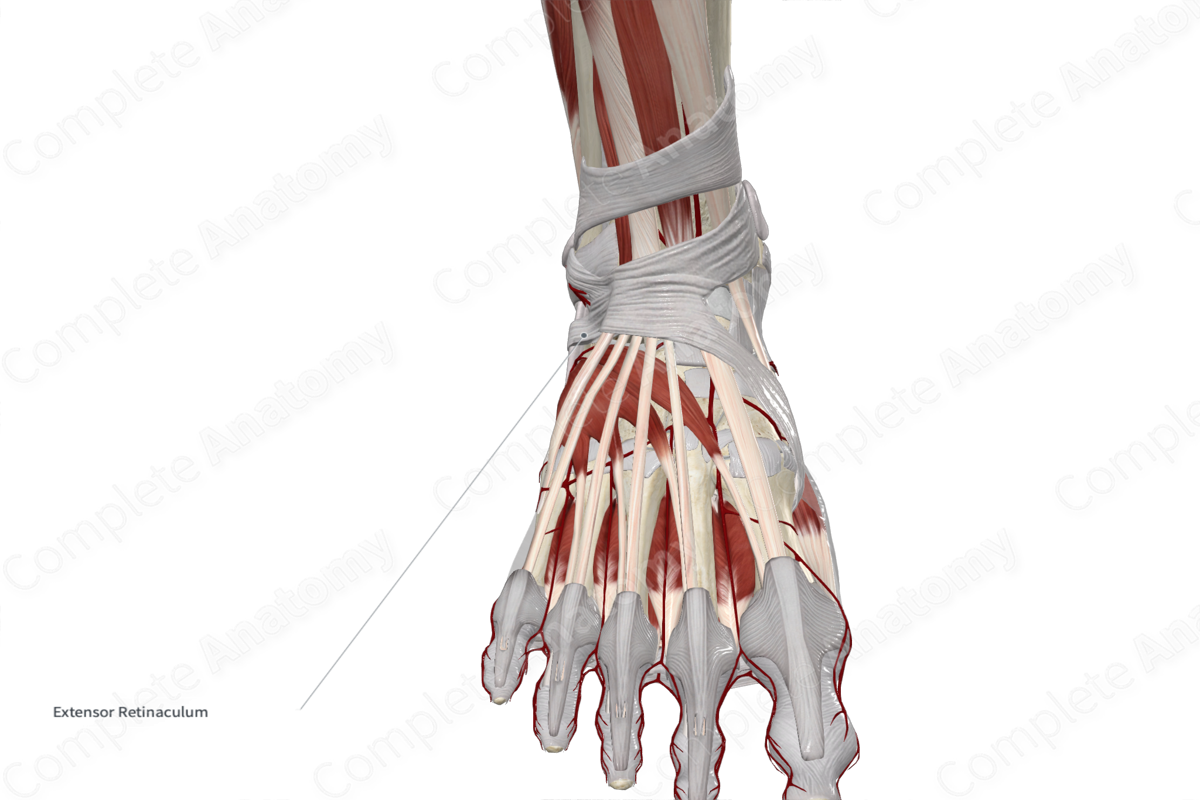
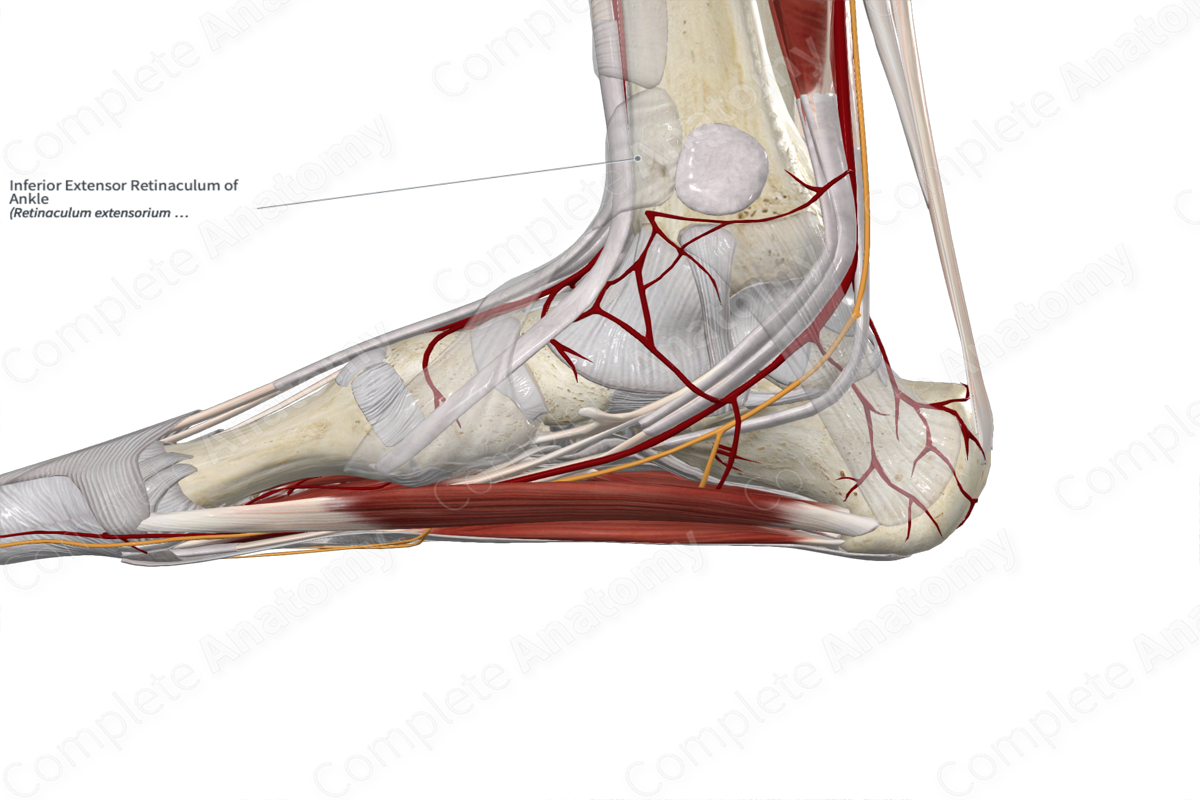
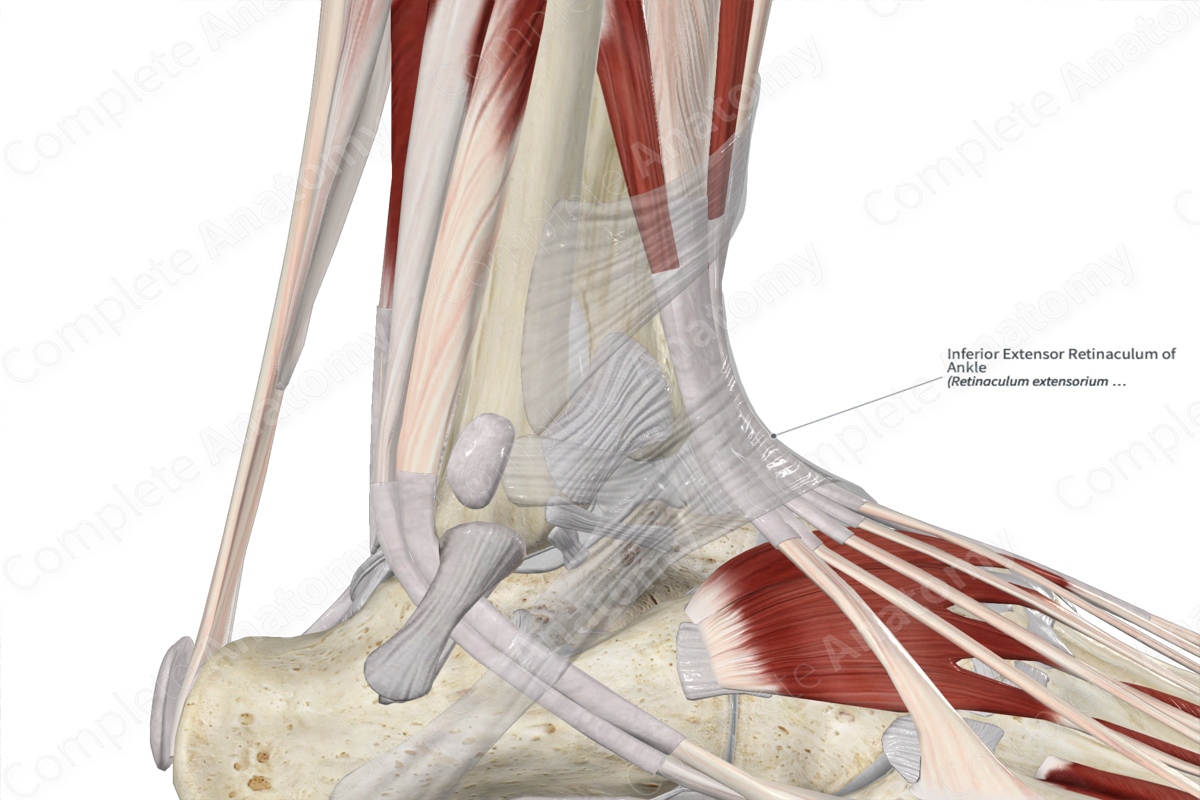
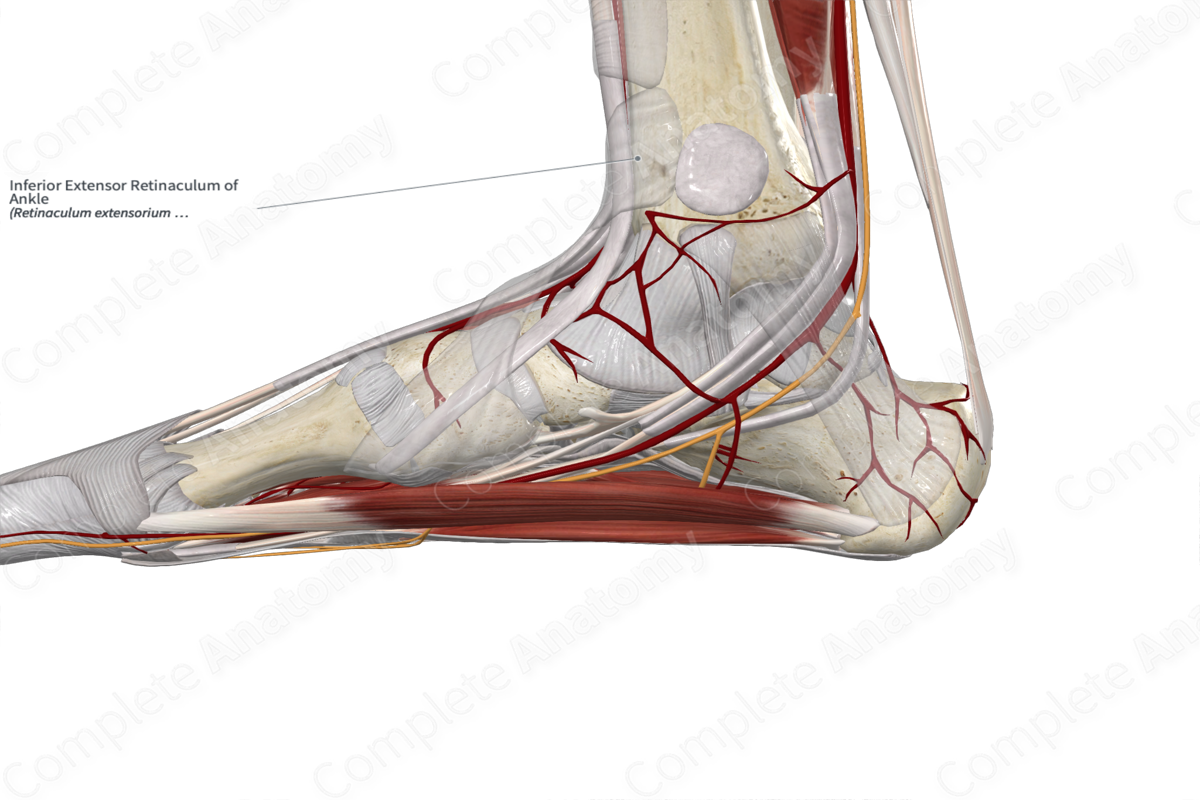
The inferior extensor retinaculum of the ankle is a thickened Y-shaped band of fascia located anterior to the ankle joint. The fibers originate from the upper surface of the lateral aspect of the calcaneus. It extends medially to attach to the medial malleolus and the medial side of the plantar aponeurosis.
Anatomical Relations
The tendons of the extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, and fibularis tertius muscles, as well as the anterior tibial vessels and deep fibular nerve pass deep to the extensor retinaculum. The superficial fibular nerve passes superficial to the inferior extensor retinaculum.
Function
The inferior extensor retinaculum of the ankle holds the extensor tendons in place before they pass over the ankle joint, thus preventing them from bowstringing anteriorly during dorsiflexion of the ankle joint (Moore, Dalley and Agur, 2013).
List of Clinical Correlates
—Deep fibular nerve entrapment
References
Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F. and Agur, A. M. R. (2013) Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th edn.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.