Medial Femoral Intermuscular Septum
Septum intermusculare mediale femoris
Read moreStructure
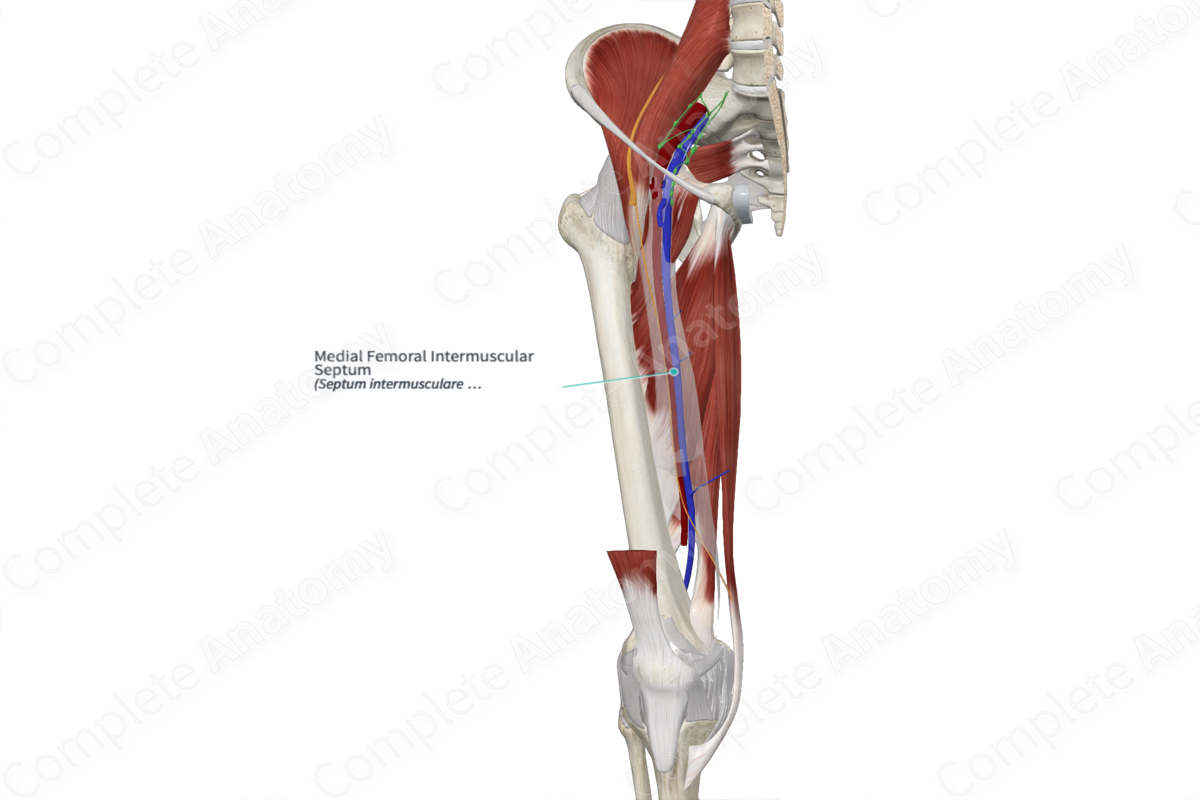
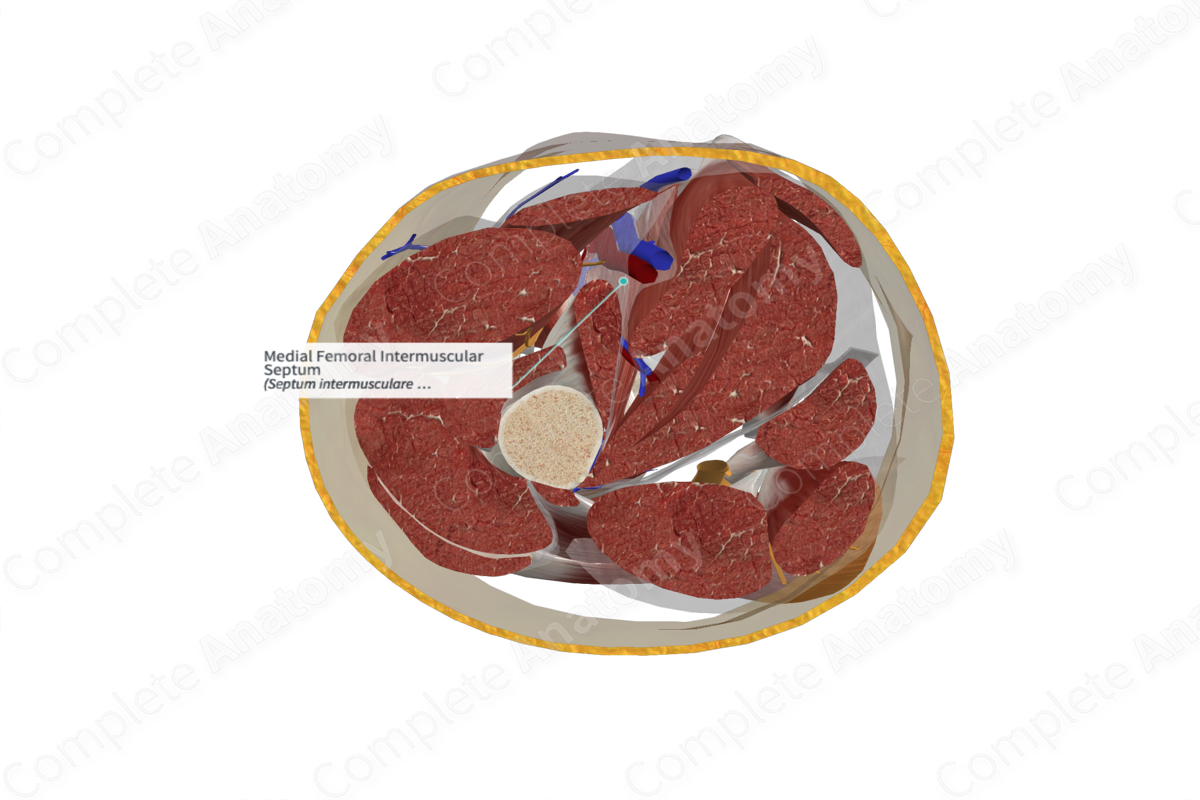
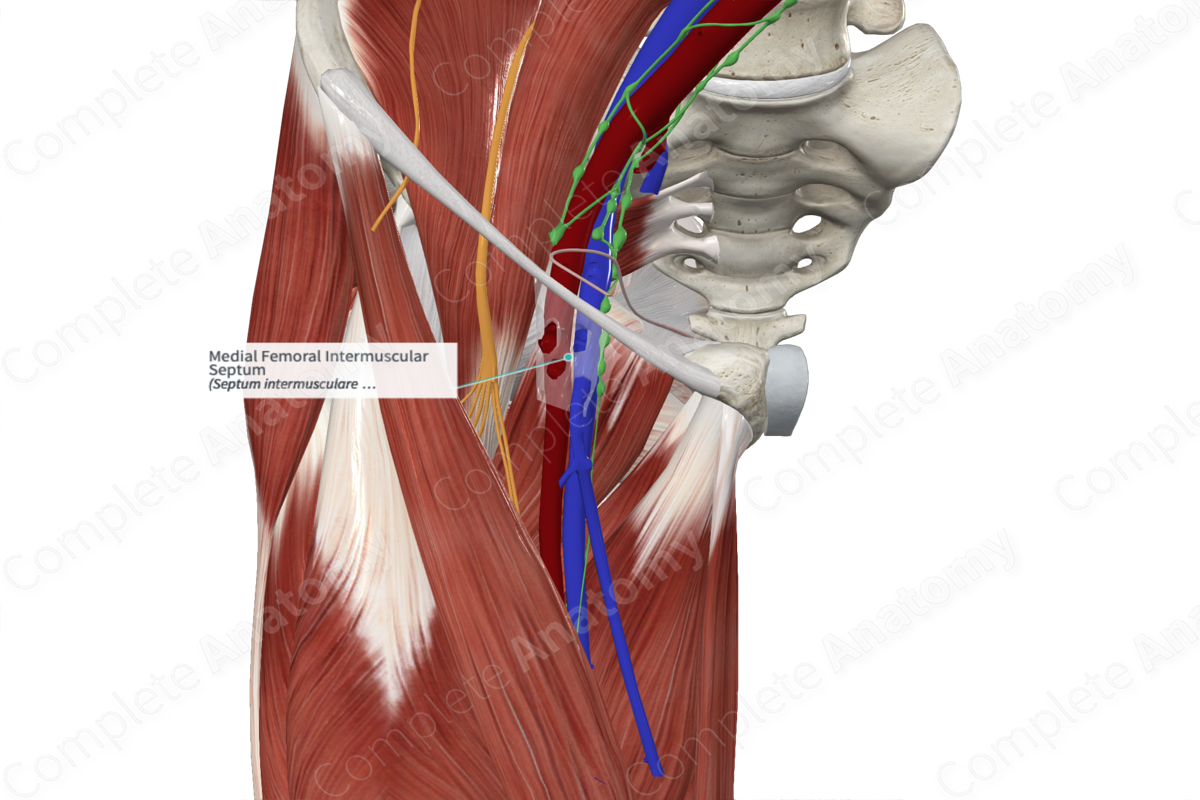
The medial femoral intermuscular septum (or medial intermuscular septum of the thigh) is a dense fold of deep fascia, which invaginates between the muscles of the thigh; separating the anterior and medial (adductor) compartments of the thigh from each other. The septum extends from the fascia lata to the linea aspera on the shaft of the femur.
The other major septa include the lateral and posterior femoral intermuscular septa. The lateral intermuscular septum is strong and least compliant, whereas the medial and posterior intermuscular septa are much thinner. Besides the major septa, there are numerous smaller septa, which separate the individual muscles from each other and enclose them in their distinct fascial sheaths.
Related parts of the anatomy
Anatomical Relations
The medial femoral intermuscular septum is related anteriorly to the vastus medialis, a quadriceps muscle. The pectineus and adductor muscles serve as the posterior relations of the septum.
Function
Septal compartmentalization of the thigh helps to provide support to the soft tissue structures, with septa giving partial origin to various muscles.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Compartment syndrome