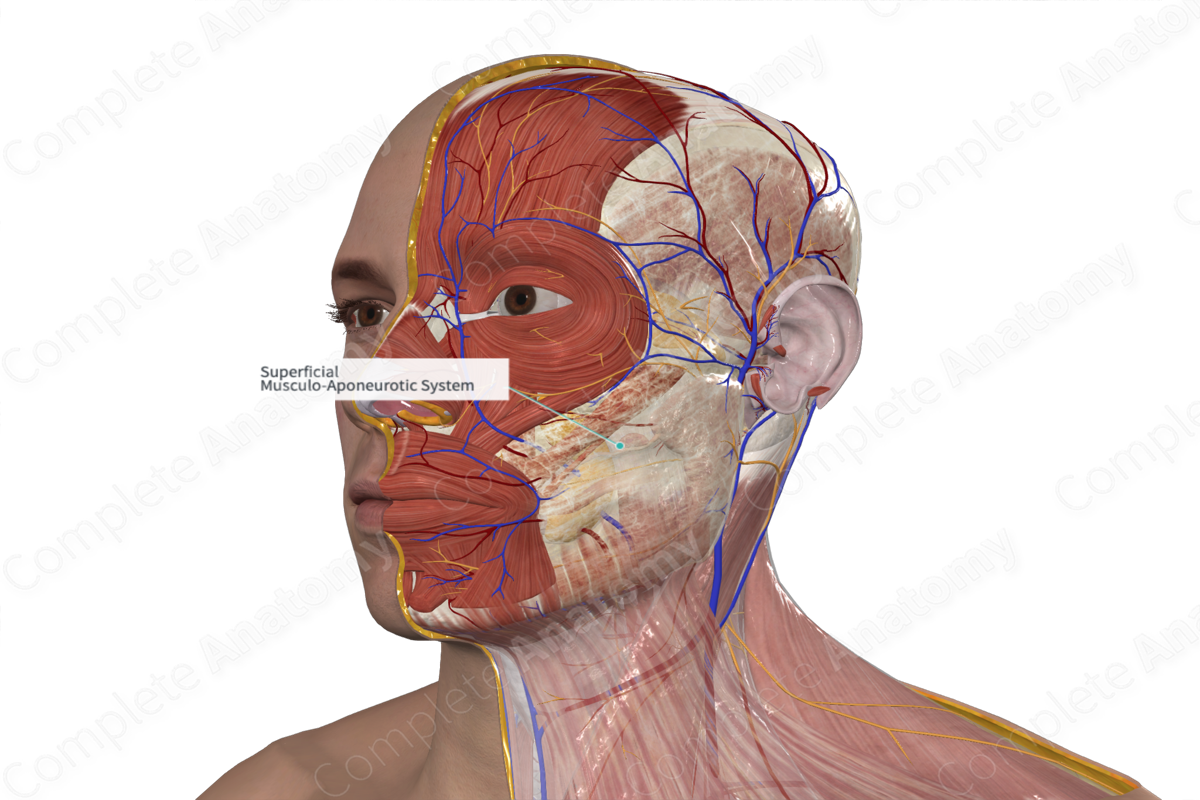
Superficial Musculo-Aponeurotic System
Structure
The superficial musculo-aponeurotic system (SMAS) is the collective name for the superficial fascial structures of the face into which the muscles of facial expression insert. Histologically, this fascia is composed of fibroelastic tissue with the elastic content decreasing with age, leading to sagging of the facial skin over time. Traction of the SMAS has become standard technique in aesthetic facial surgery (Stecco & Hammer, 2014).
Related parts of the anatomy
Anatomical Relations
The SMAS is continuous superiorly with the galea capitis and caudally with the platysma muscle. It fills in the spaces around other facial structures; thus its relations are ill-defined. Rather it is found in different thicknesses across the face.
Function
The SMAS connects facial muscles to the skin allowing for facial expression.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Cosmetic surgery
References
Stecco, C. & Hammer, W. I. (2014) Functional Atlas of the Human Fascial System E-BookElsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products



