Quick Facts
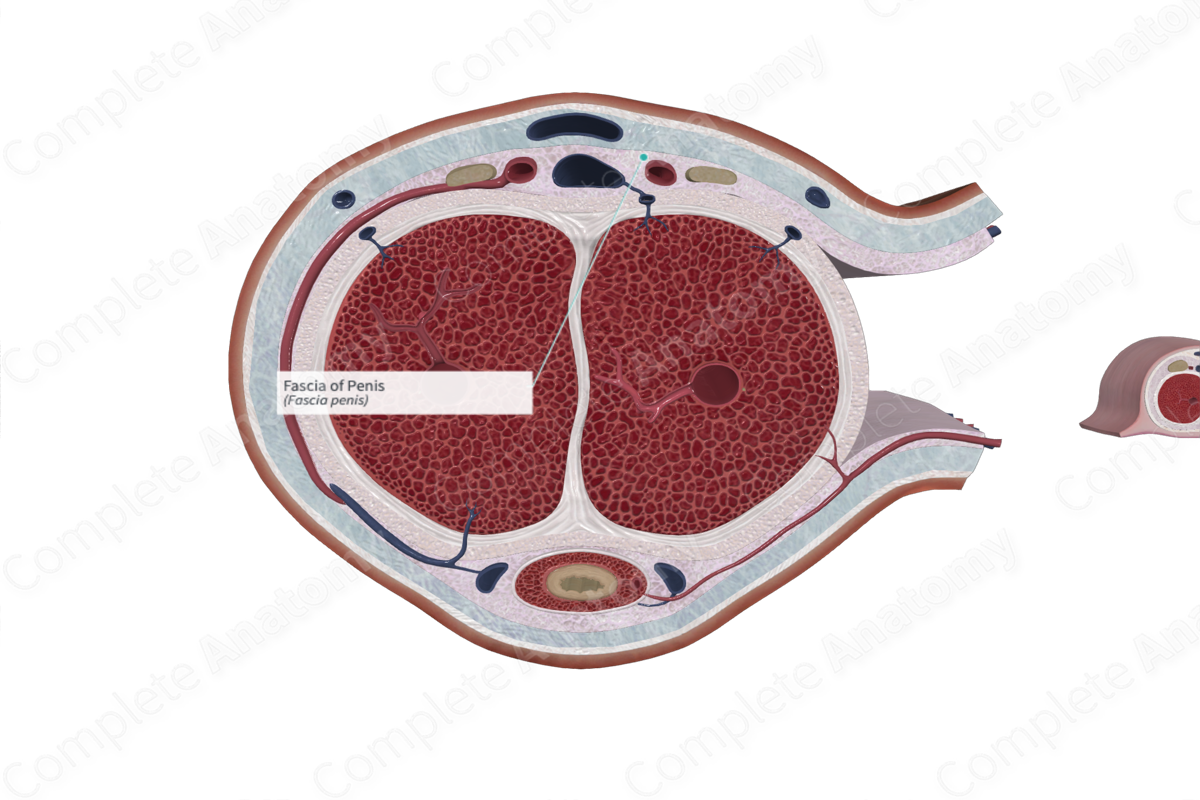
The fascia of penis is the firm inner fascial layer that surrounds the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum of the shaft of the penis collectively. It’s continuous with the fascia of the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
The fascia of the penis consists of a deep layer of fibrous tissue, which surrounds the corpora cavernosa, and splits to surround the corpus spongiosum. Distally, it blends with the tunica albuginea of all corporal bodies. Proximally, the fascia of the penis is continuous with the perineal fascia that invests the muscles of the superficial perineal space (i.e., bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, and superficial transverse perineal muscles). It is also anchored to the suspensory ligament of the penis.
Anatomical Relations
The fascia of the penis surrounds the three corpora erectile bodies, as well as the deep dorsal vein, the dorsal arteries of the penis, and the dorsal nerves of the penis.
Function
The fascia of the penis is responsible for the structural integrity of the three erectile bodies of the penis.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
