Description
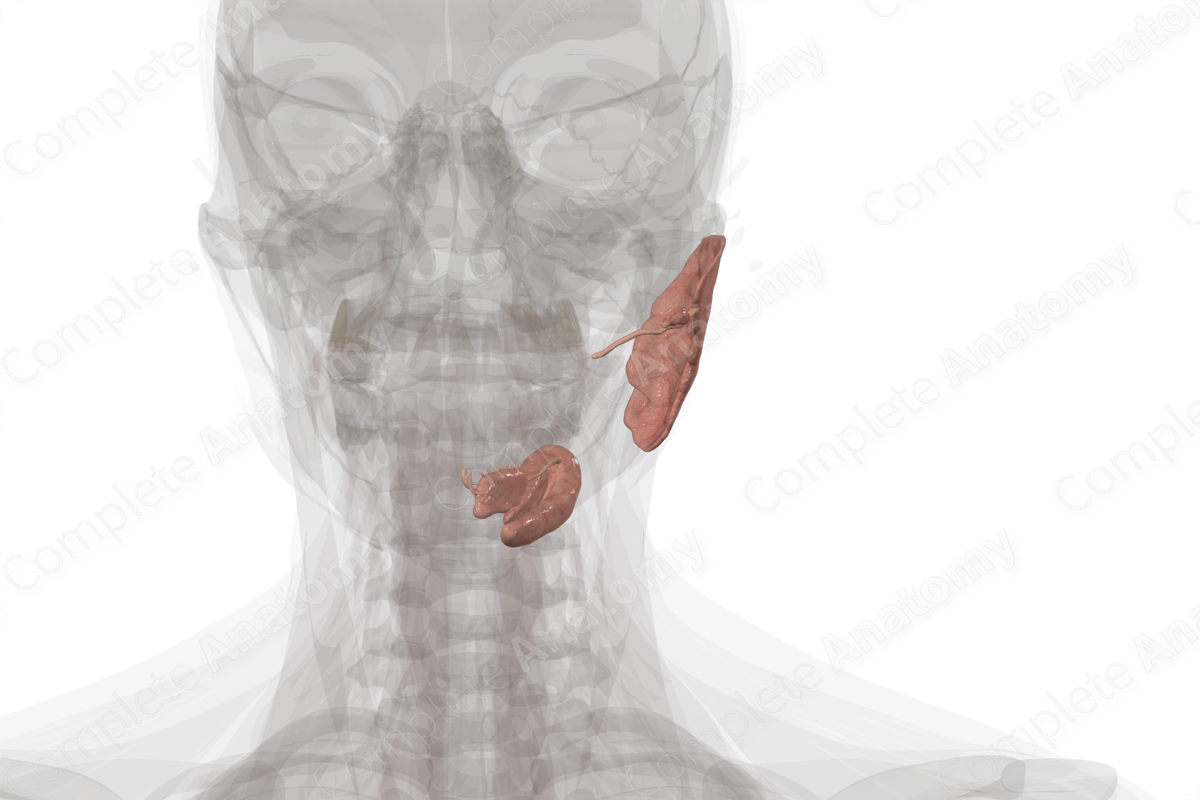
The major salivary glands include the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands. These are compound tuboacinar exocrine glands. Each gland produces saliva which aids in mastication, digestion, deglutition, and phonation.
Around 500 ml of salvia is produced daily primarily during waking hours (Standring, 2016). The submandibular gland contributes most to saliva production; however, the parotid gland may also contribute significantly to the volume produced.
The parotid gland produces mainly serous secretions; the submandibular gland secretes mucus and serous secretions; the sublingual gland produces mainly mucus secretions.
Additionally, there are several minor salivary glands present in the oral cavity which also produce saliva. These include lingual, buccal, palatal, and labial glands.
Related parts of the anatomy
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.




