Quick Facts
The tarsus is the firm framework of connective tissue that gives shape to the lower eyelid (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
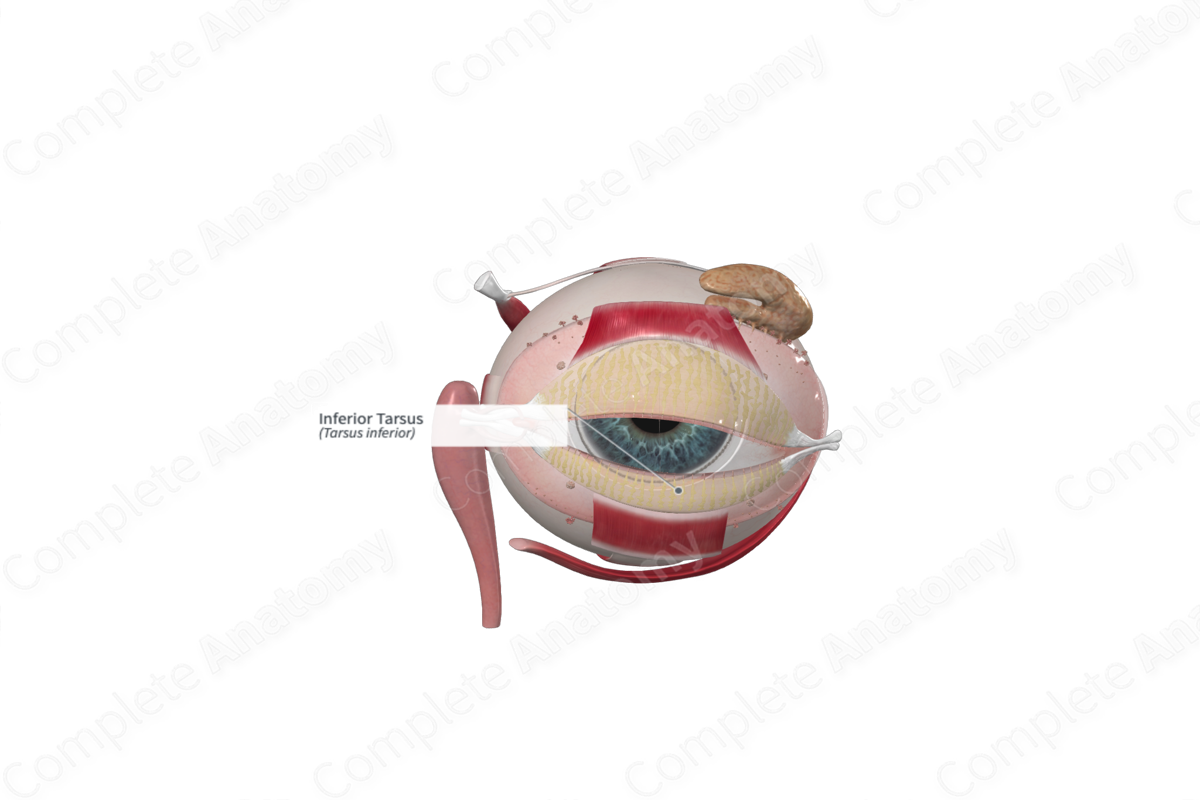
The superior and inferior eyelids contain a thin, elongated plate composed of tough collagenous tissue called the tarsal plate. Each plate is convex, conforming to the shape of the anterior surface of the eyeball. The inferior tarsus has a free straight ciliary border, adjacent to the hair follicles of the eyelashes, and a curved orbital border. The latter is attached to the orbital septum. The inferior tarsus is the smaller of the two tarsal plates, measuring approximately 2.5 cm long and 4 mm in height (Standring, 2016).
Anatomical Relations
The free ciliary margin of the tarsal plate is approximately 2 mm from the margin of the eyelid and runs parallel to it. The orbital margin is bound to the orbital septum and to the lateral and medial palpebral ligaments at each side. The medial palpebral (canthic) ligament extends from the medial edges of both tarsal plates and inserts into the anterior lacrimal crest and the frontal process of the maxilla (bone forming part of the orbital cavity). As it inserts into the tarsal plates, the ligament splits to surround the lacrimal canaliculi. The lateral palpebral ligament, on the other hand, is poorly developed. It passes from the lateral edges of the tarsal plates to the zygomatic bone that forms part of the orbital margin. Each tarsal plate has associated smooth muscle forming the superior and inferior tarsal muscles that aid in elevating or depressing the upper and lower eyelids, respectively.
Function
The superior and inferior tarsal plates provide support to the eyelids and determine the shape of each lid.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.



