Quick Facts
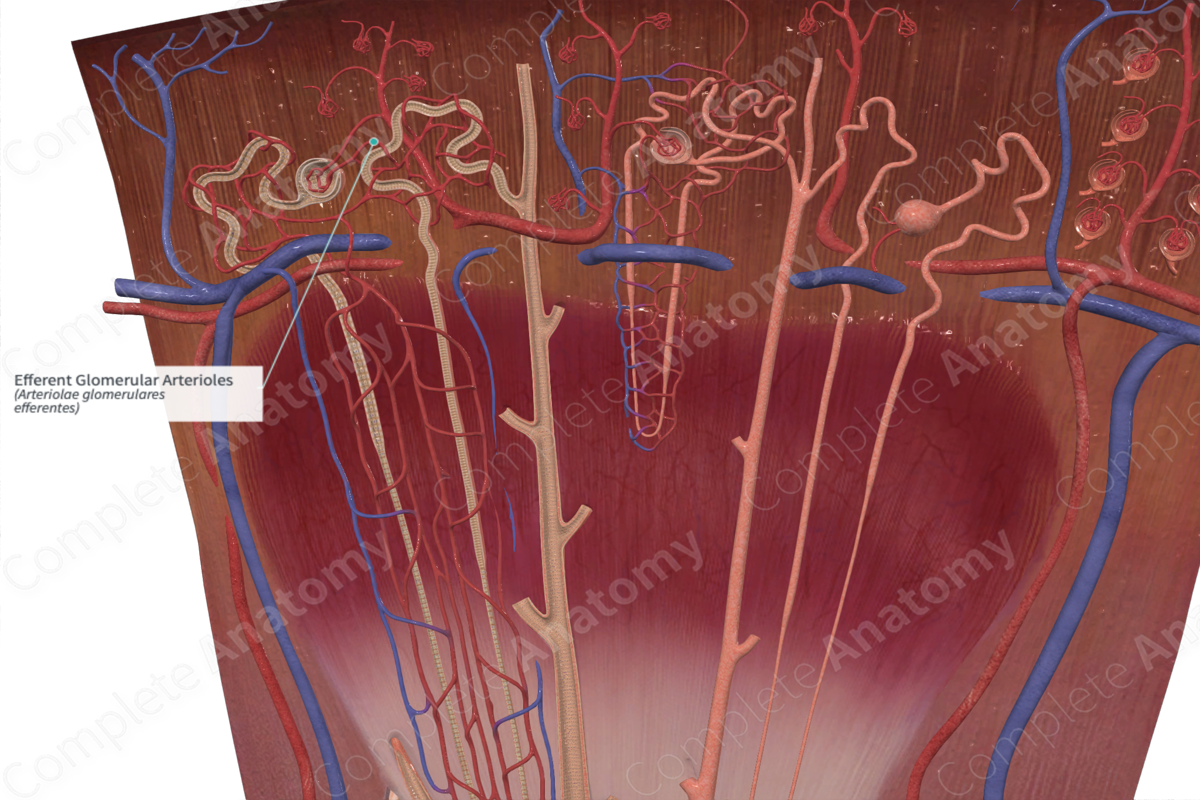
The efferent glomerular arteriole is an arteriole that arises from a renal glomerulus and breaks up into capillaries to supply renal tubules (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Features
Efferent glomerular arterioles carry blood away from the glomerulus. The walls of efferent glomerular arterioles are thicker than their afferent counterparts, and therefore the lumen of efferent arterioles tends to be narrower. This narrow lumen creates resistance which increases the pressure of blood traveling through the glomerulus.
Anatomical Relations
Upon leaving the glomerulus, efferent arterioles divide into:
—peritubular capillaries surround the cortical portions of the renal tubule;
—straight arterioles surround tubules that lie in the outer and inner zones of the medulla.
Function
Efferent arterioles are responsible for transporting blood away from the glomerulus.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
