Quick Facts
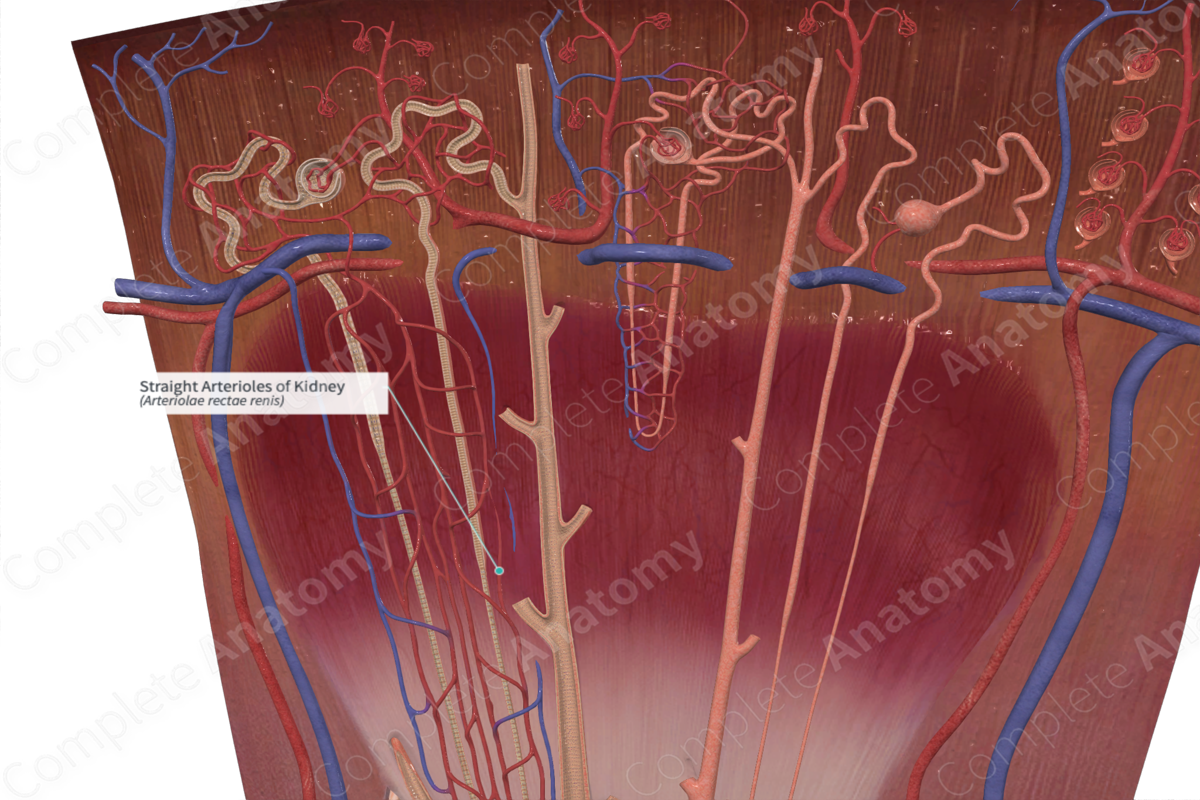
The straight arterioles are branches of the arcuate arteries arising from the efferent glomerular arterioles and passing down to the renal pyramids (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Features
The straight arterioles arise from the efferent arterioles. These capillaries are responsible for the vascular supply of the medulla. Specifically, efferent arterioles divide into peritubular capillaries that surrounds the renal tubules in the cortex and then further divide and into a series of straight arterioles, known as the vasa recta. The straight arterioles enter the medulla and surrounds the nephron loop (Liao & Madersbacher, 2019).
The straight arterioles are primarily located in the inner medulla and near the papilla. They lie in very close proximity with the nephron loops and the medullary and papillary collecting ducts. These tubules along with the straight arterioles can be arranged into bundles known as the medullary rays.
Function
Straight arterioles are responsible for the delivery of nutrients to the structures of renal medulla. Furthermore, they are responsible for the reabsorption of water and solutes that have been reabsorbed in the nephron loop and collecting ducts.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Liao, L. & Madersbacher, H. (2019) Neurourology: Theory and PracticeSpringer Netherlands.
