Quick Facts
An artery is a vessel through which the blood passes away from the heart to the various parts of the body. The wall of an artery consists typically of an outer coat (tunica externa), a middle coat (tunica media), and an inner coat (tunica intima) (Dorland, 2011).
Structure/Morphology
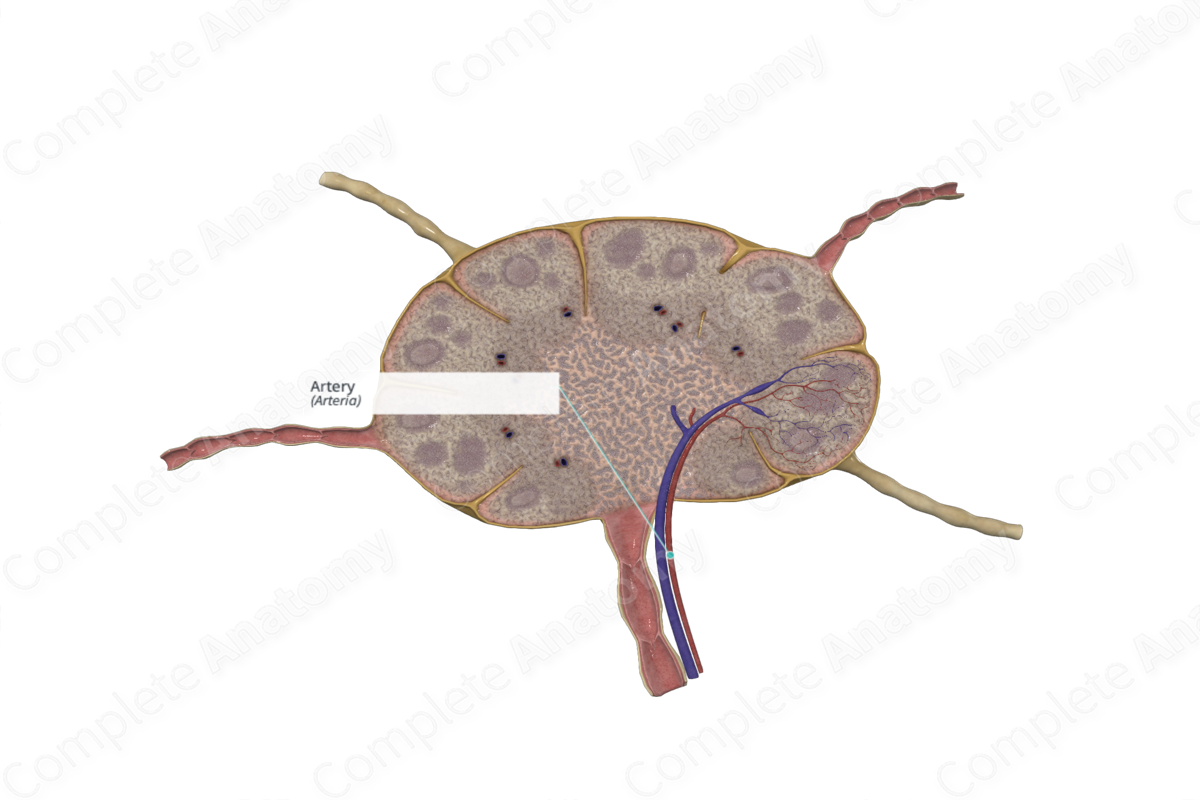
Arteries supplying blood to the lymph node enter at the hilum, accompanied by a vein and an efferent lymphatic vessel which are exiting the lymph node.
As the artery enters the medullary region of the node, it divides to supply medullary arterioles and are conveyed in the medullary cords. Each lobule of the lymph node receives an arteriole, however, for descriptive purposes this is not shown in the 3D model. The arterioles continue to branch in the paracortex, or deep cortex, giving rise to capillary beds in the cortex.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
