Quick Facts
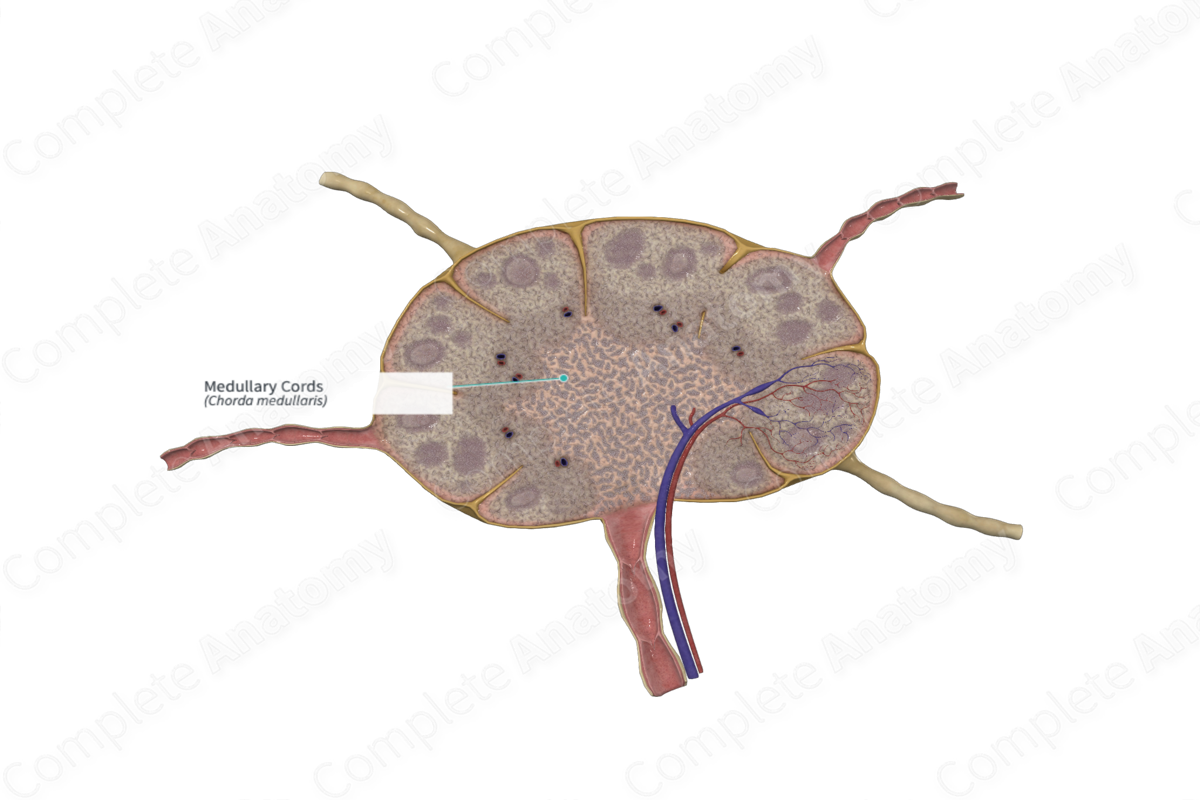
The medullary cords are strands of dense lymphoid tissue surrounded by the sinuses of the medulla of a lymph node (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure/Morphology
The medullary cords and sinuses constitute the medulla of the lymph node. Medullary cords are usually clearly delineated because of their dense cellularity compared to the surrounding medullary sinuses. The cords are composed of dense, irregular reticular fibers, which are denser than the fibers in the cortex and paracortex. Arterioles and venules supplying and draining blood from the lymph node are conveyed through the medullary cords.
The medullary cords contain a large number of mature plasma cells, lymphocytes and macrophages. The plasma cells are capable of secreting antibodies into the medullary sinuses or migrate into the sinus so that they enter the lymph that is transported into the efferent lymphatic vessel, and eventually enters the circulatory system.
Function
The medullary cords anchor and house macrophages, dendritic cells, plasma cells, and B lymphocytes. In addition, blood vessels traverse through the medullary cords (Willard-Mack, 2006).
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Willard-Mack, C. L. (2006) 'Normal structure, function, and histology of lymph nodes', Toxicologic Pathology, 5(34), pp. 409-424.
