Quick Facts
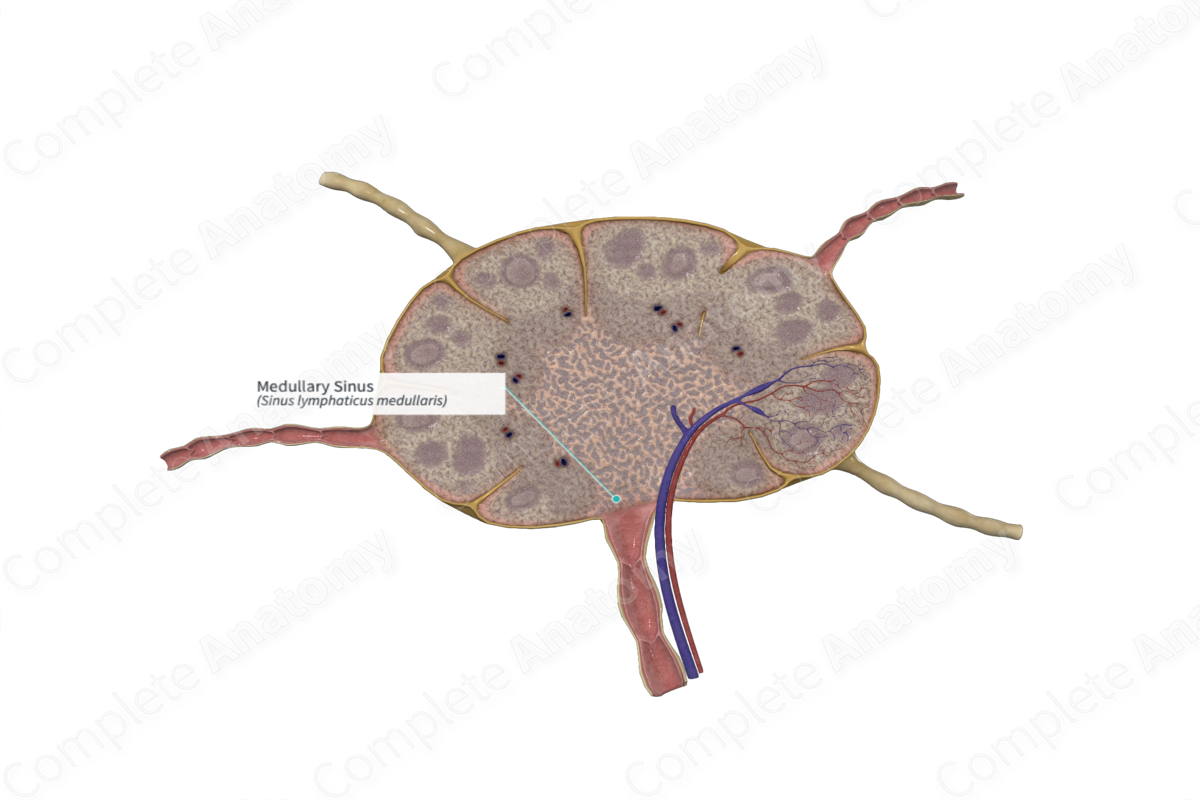
The medullary sinuses are lymph sinuses in the medulla of a lymph node, which divide the lymphoid tissue into a number of medullary cords (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure/Morphology
The medullary sinus is one of three sinuses in the lymph node, the others include the trabecular and subcapsular sinuses. The medullary sinuses are irregular spaces found between the medullary cords in the medulla of the lymph node. It receives lymph from the trabecular sinuses. Unlike vascular sinuses, lymphatic sinuses are not open spaces. They are occupied by reticular fibers surrounded by reticular cell processes and macrophages. This forms a meshwork within the sinus, thus slowing down the flow of lymph through the sinus which enhances filtration. Medullary sinuses also contain lymphocytes and erythrocytes (Willard-Mack, 2006).
Anatomical Relations
Lymph passes from the subcapsular sinus to the trabecular sinus and then the medullary sinus, where it collects at an efferent lymph vessel on the hilar side of the lymph node.
Function
The medullary sinus receives lymph from the trabecular sinus. As the medullary sinuses converge towards the hilum of the lymph node, they empty their contents into the efferent lymphatic vessel. The lymph is filtered by the reticular meshwork in the sinus, where the antigenic material becomes trapped and phagocytosed by the macrophages.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Willard-Mack, C. L. (2006) 'Normal structure, function, and histology of lymph nodes', Toxicologic Pathology, 5(34), pp. 409-424.
