Trabecular Sinus Quick Facts
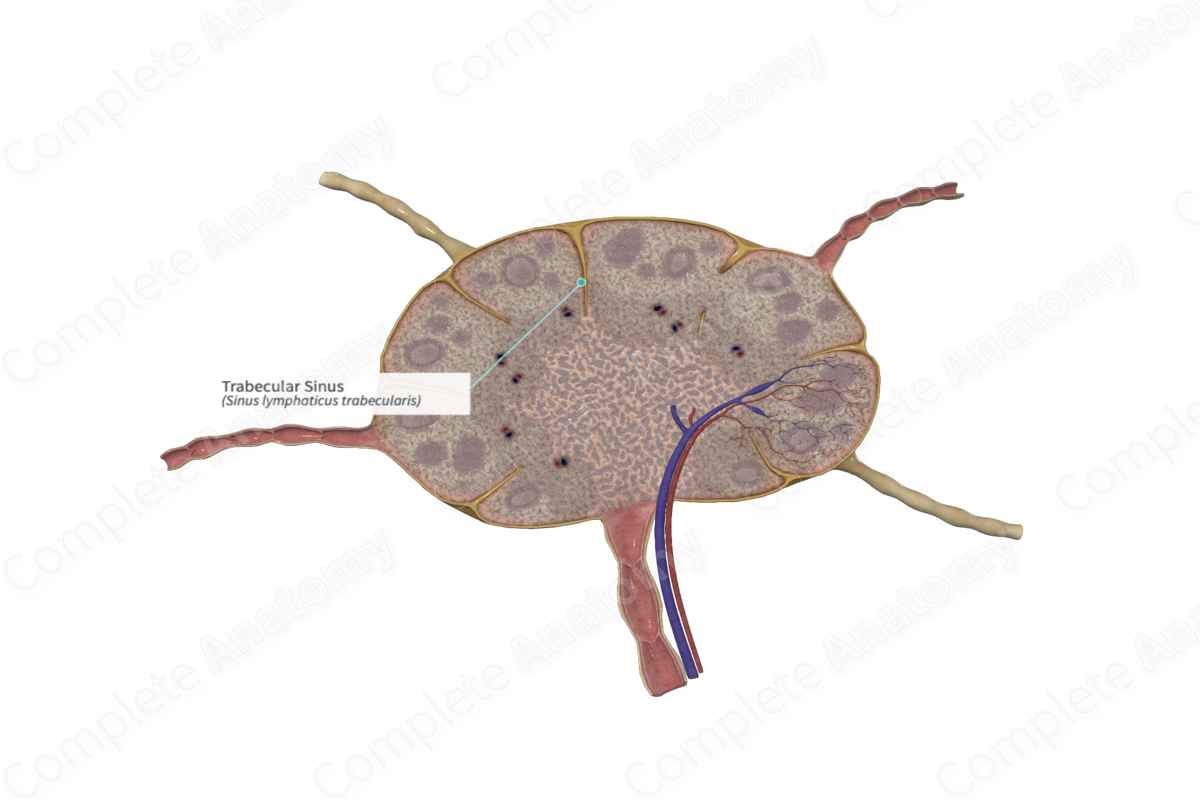
The trabecular sinuses are those surrounding the trabeculae of the lymph node.
Trabecular Sinus Structure/Morphology
The trabecular sinus originates from the subcapsular sinus. It is one of three sinuses in the lymph nodes, the others include the subcapsular and medullary sinuses. Unlike vascular sinuses, lymphatic sinuses are not open spaces. They are occupied by reticular fibers surrounded by reticular cell processes and macrophages (Willard-Mack, 2006). This forms a meshwork within the sinus, thus slowing down the flow of lymph through the sinus which enhances filtration.
Trabecular Sinus Anatomical Relations
The trabecular sinus follows the same trajectory as the trabeculae, extending through the cortex. The trabecular sinuses drain into the medullary sinuses.
Trabecular Sinus Function
The trabecular sinus receives lymph from the subcapsular sinus. The lymph is further filtered by the reticular meshwork in the trabecular sinus, where the antigenic material becomes trapped and phagocytosed by the macrophages.
Trabecular Sinus References
Willard-Mack, C. L. (2006) 'Normal structure, function, and histology of lymph nodes', Toxicologic Pathology, 5(34), pp. 409-424.
