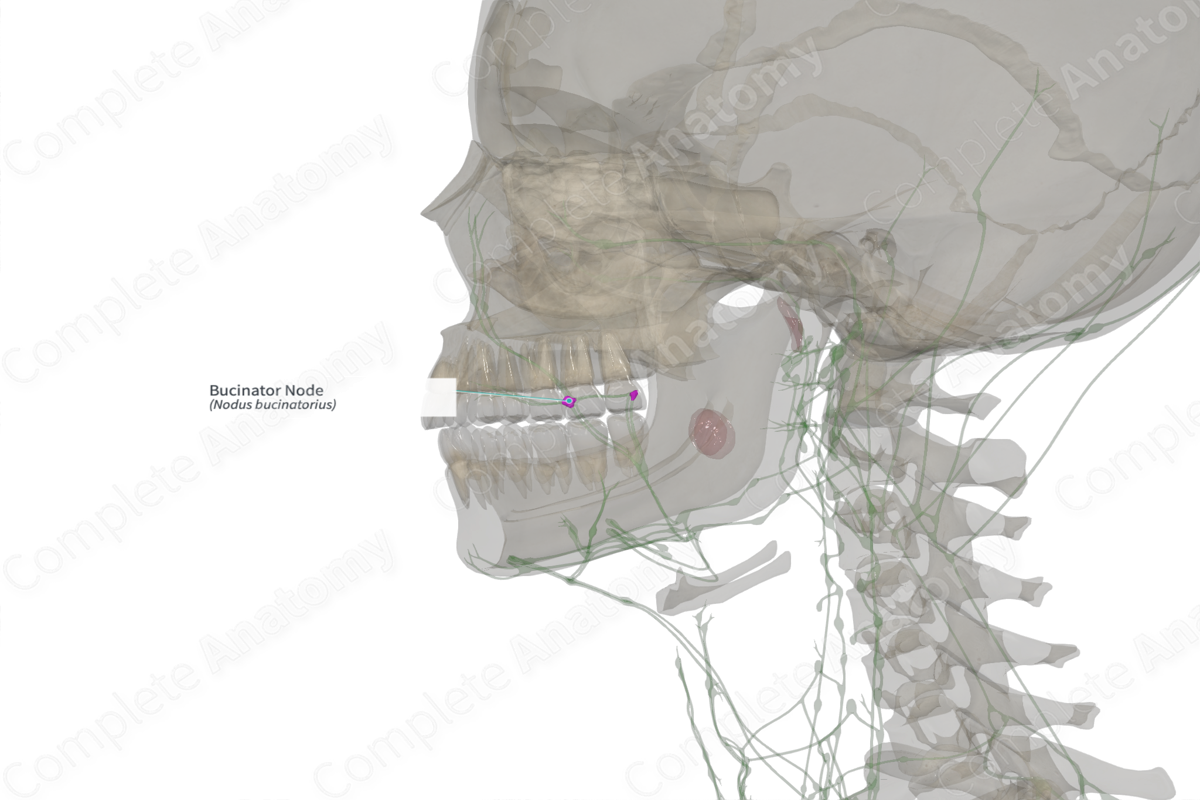
Quick Facts
Location: Overlying the buccinator muscle and its fascia or within the buccal fat pad.
Drainage: The skin and subcutaneous tissues of the lower eyelid, nose, and cheek.
Direction of Flow: Submandibular nodes > jugulodigastric nodes > internal jugular nodes > supraclavicular nodes > jugular trunk > thoracic duct (left) or right lymphatic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
The bucinator nodes are present only in 20–30% of the population. There are usually one or two nodes found overlying the bucinator muscle and fascia or within the buccal fat pad (Földi et al., 2012).
The drainage territory of these nodes includes an undefined region over the eye, nose, and cheek, and rarely the temporal region.
Efferent vessels connect these nodes with the submandibular nodes for drainage through the deep lateral cervical nodes.
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.



