Quick Facts
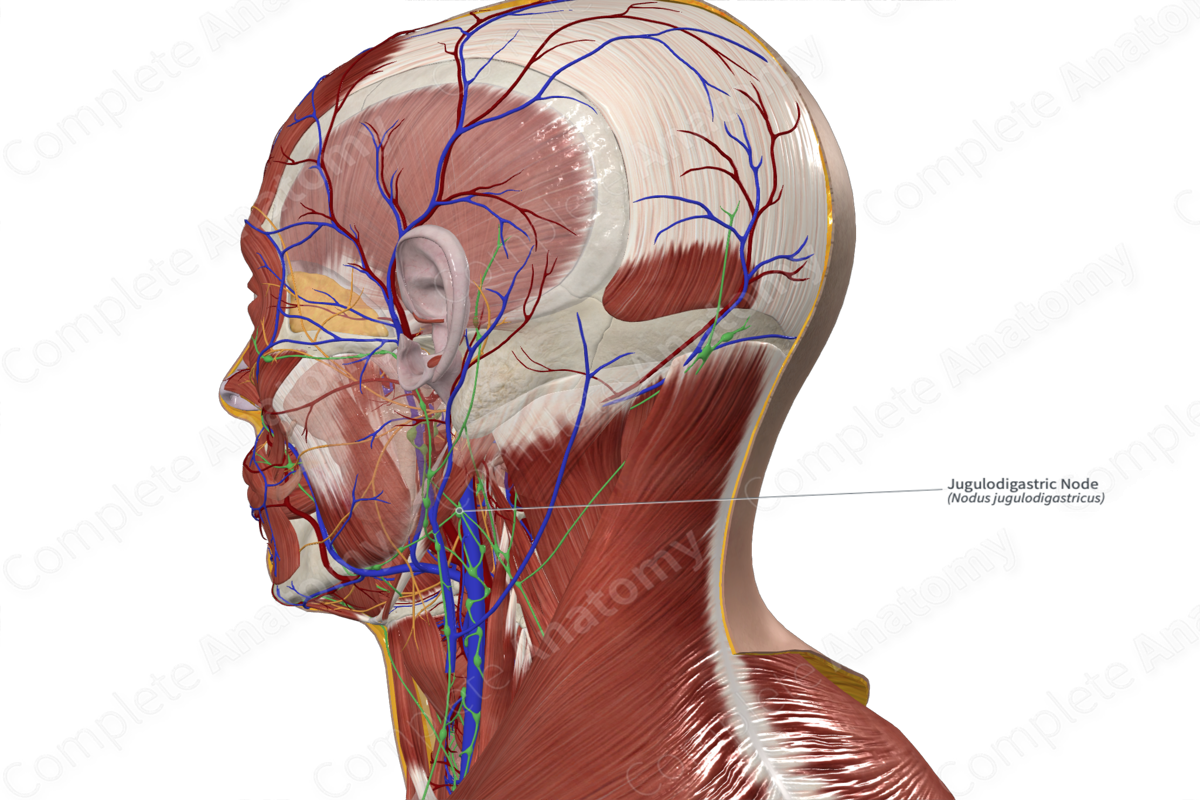
Location: In a triangle bordered posteriorly by the internal jugular vein, inferiorly by the common facial vein, and superiorly by the posterior belly of digastric.
Drainage: The tongue, pharynx, and palatine tonsils.
Direction of Flow: Lateral internal jugular nodes > jugular trunk > thoracic duct (left) or right lymphatic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
Often the largest lymph node in the neck, the jugulodigastric node is located just below the inferior margin of the mandible, close to the insertion of masseter muscle. This node receives lymph from the tongue, pharynx, and palatine tonsils. For this reason, the jugulodigastric lymph node typically becomes swollen during tonsil infections (Földi et al., 2012).
List of Clinical Correlates
—Tonsillitis
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





