Quick Facts
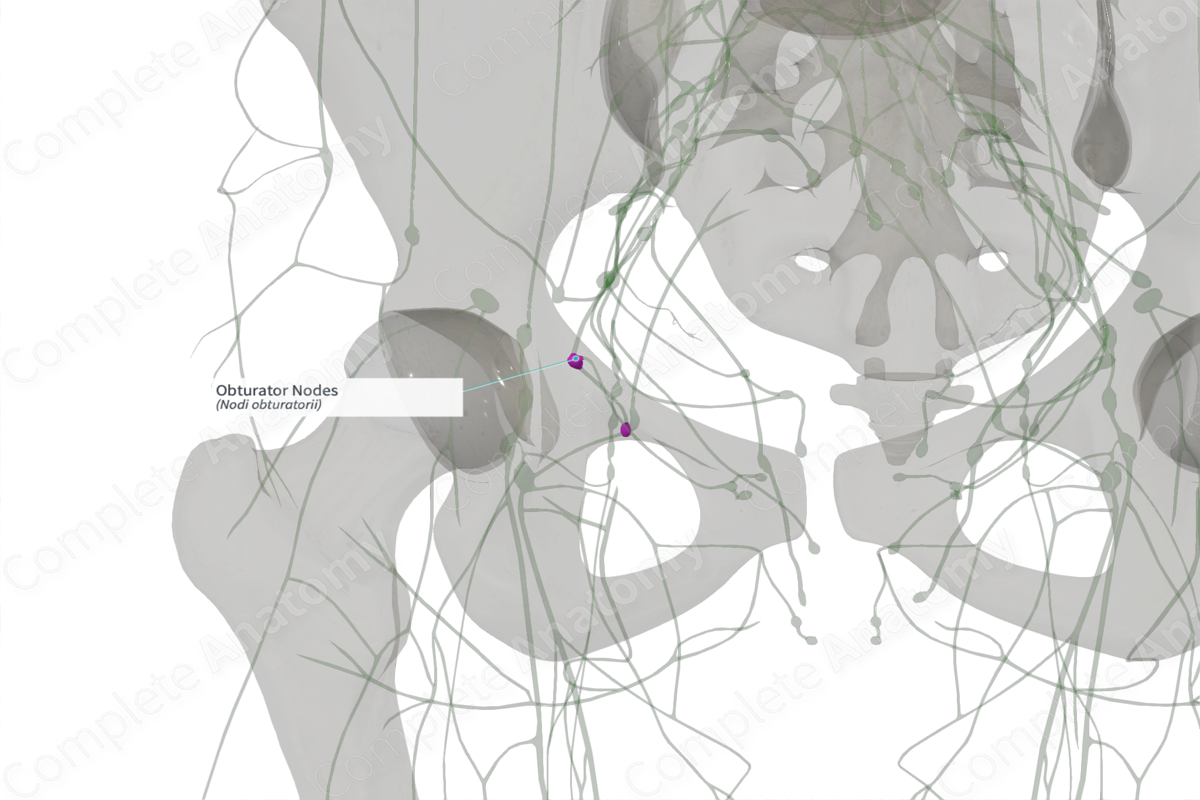
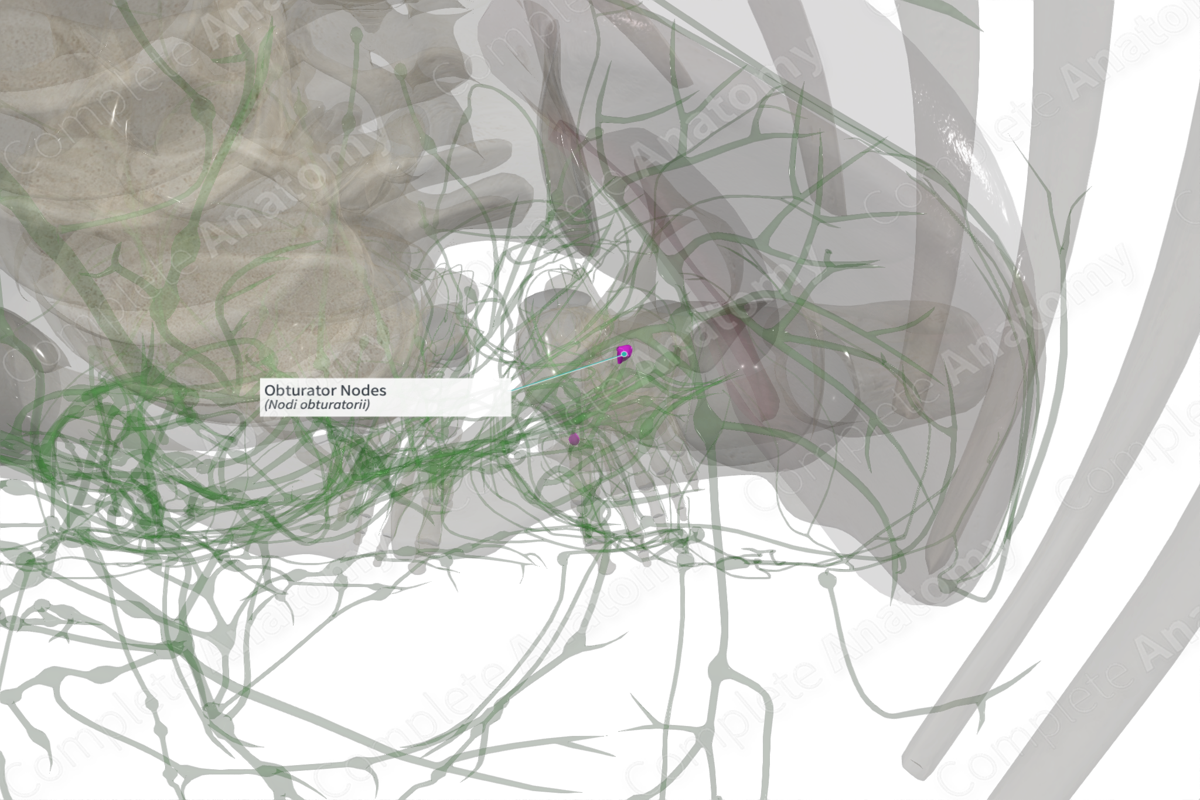
Location: Obturator canal.
Drainage: Prostate, uterus, and cervix.
Direction of Flow: External iliac lymph nodes > Common iliac lymph nodes > Lateral aortic lymph nodes (left) and lateral caval lymph nodes (right) > left and right lumbar lymph trunk > cisterna chyli > thoracic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The obturator lymph nodes belong to the external iliac lymph node group. These nodes are located in the obturator canal and are associated with the obturator artery. However, these nodes are variable, and are often absent (present in 0–3.5%) (Földi et al., 2012).
The obturator lymph nodes drain the prostate in males, and the body of the uterus and cervix in females. They send efferent vessels to the medial external and common iliac lymph nodes. Lymph is then returned to the lateral aortic and caval lymph nodes of the left and right side, respectively.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Cancer metastasis of the prostate and cervix (Sakuragi et al., 1999)
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Sakuragi, N., Satoh, C., Takeda, N., Hareyama, H., Takeda, M., Yamamoto, R., Fujimoto, T., Oikawa, M., Fujino, T. and Fujimoto, S. (1999) 'Incidence and distribution pattern of pelvic and paraaortic lymph node metastasis in patients with Stages IB, IIA, and IIB cervical carcinoma treated with radical hysterectomy', Cancer, 85(7), pp. 1547-54.
Description:
Description: (Location & Drainage)
The obturator lymph nodes belong to the external iliac lymph node group. These nodes are located in the obturator canal and are associated with the obturator artery. However, these nodes are variable, and are often absent (present in 0–3.5%) (Földi et al., 2012).
The obturator lymph nodes drain the prostate in males, and the body of the uterus and cervix in females. They send efferent vessels to the medial external and common iliac lymph nodes. Lymph is then returned to the lateral aortic and caval lymph nodes of the left and right side, respectively.