Quick Facts
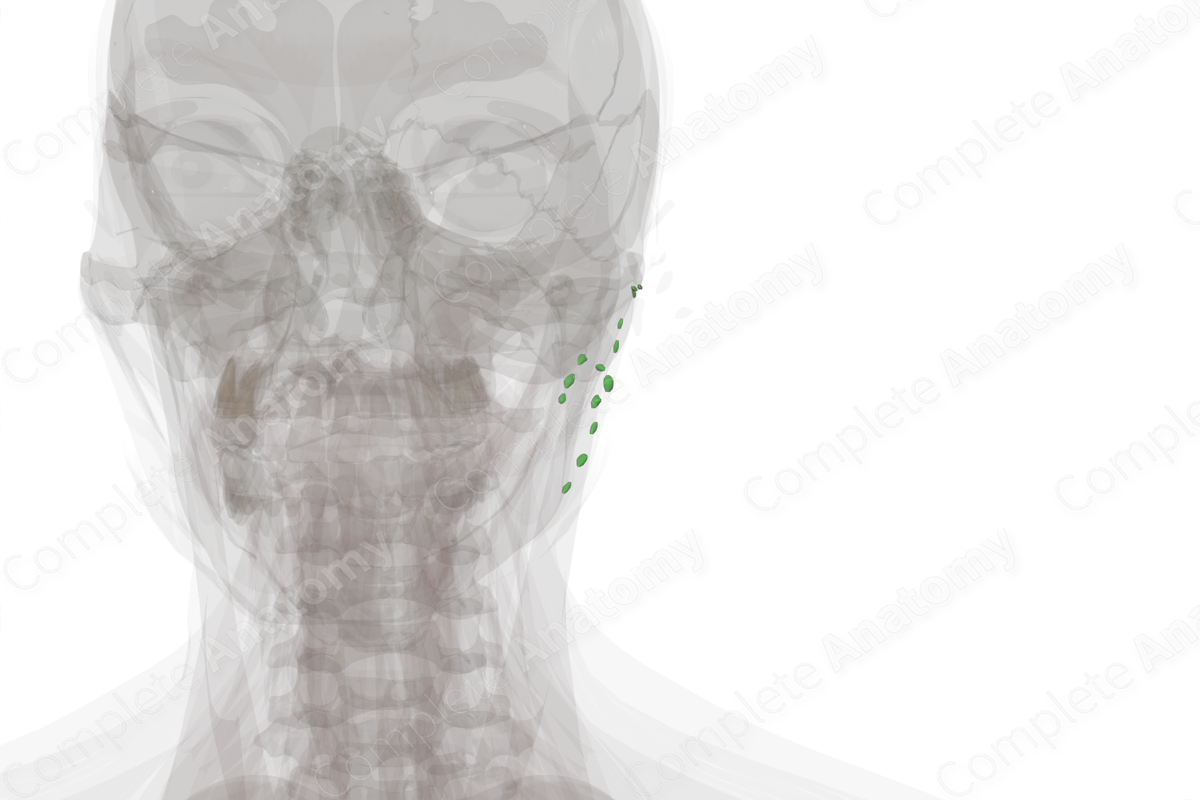
Location: Embedded in and surrounding the parotid gland
Drainage: Parotid gland, frontal, parietal, and temporal scalp, nares, gingiva, and the upper lip, the eyelids, the outer and middle ear, the oral cavity.
Direction of Flow: Internal jugular nodes > supraclavicular nodes > jugular trunk > thoracic duct (left) or right lymphatic duct.
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
The parotid lymph nodes are located within the parotid gland and embedded in the fascia surrounding the gland. These nodes filter lymph that has drained from the parotid gland itself as well as a large area of the face and scalp and parts of the facial cavities, including the oral and nasal cavities.
Short efferent vessels connect the nodes within the gland. Drainage of these nodes occurs through the deep lateral cervical nodes, primarily the internal jugular nodes either directly or via the infraauricular nodes. In 58% of cases, there is collateral drainage along lymph vessels that follow the course of the external jugular vein (Földi et al., 2012).
These nodes are often implicated following metastasis of malignancies in the skin of the face, particularly squamous cell carcinomas. They are palpable when enlarged and may cause facial nerve weakness, due to the course of the facial nerve through the parotid gland.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Parotid gland tumor
—Parotitis
—Cutaneous malignancy of the ear, cheek, temple, forehead and anterior scalp
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.




