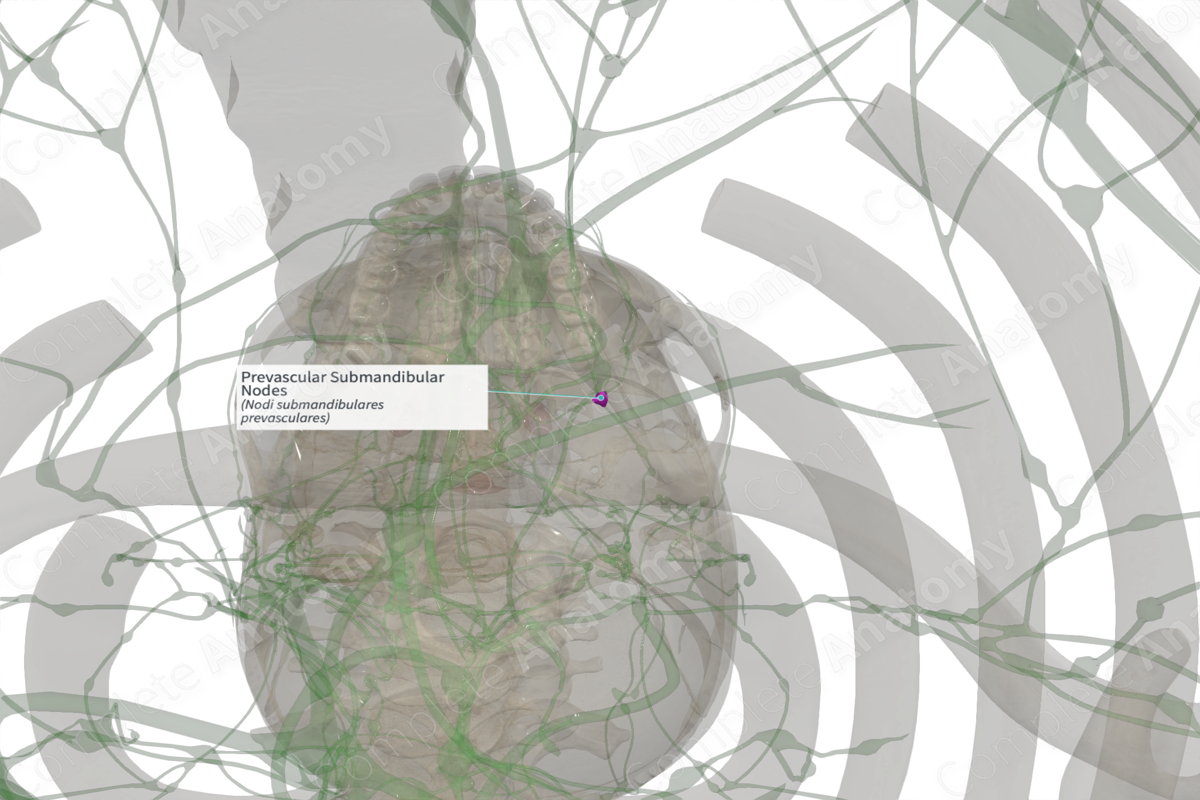
Quick Facts
Location: On the facial artery, superficial to the submandibular gland.
Drainage: Submandibular and sublingual glands, inferior oral cavity, tongue, gingiva, teeth, and skin covering the nose, lips, and chin.
Direction of Flow: Retrovascular submandibular node > jugulodigastric nodes > internal jugular nodes > supraclavicular nodes > jugular trunk > thoracic duct (left) or right lymphatic duct.
Description
The prevascular nodes consist of one or two small nodes in close anatomical relation to the submandibular gland and posterior to the facial artery.
These nodes receive afferents from the submandibular and sublingual glands, as well as the oral cavity and skin covering the lips, nose and chin.
Drainage from these nodes is initially via the retrovascular submandibular nodes to the jugulodigastric nodes and on to the deep lateral cervical nodes (Földi et al., 2012).
List of Clinical Correlates
—Oral, tooth or cutaneous infections or malignancies
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.




