Description
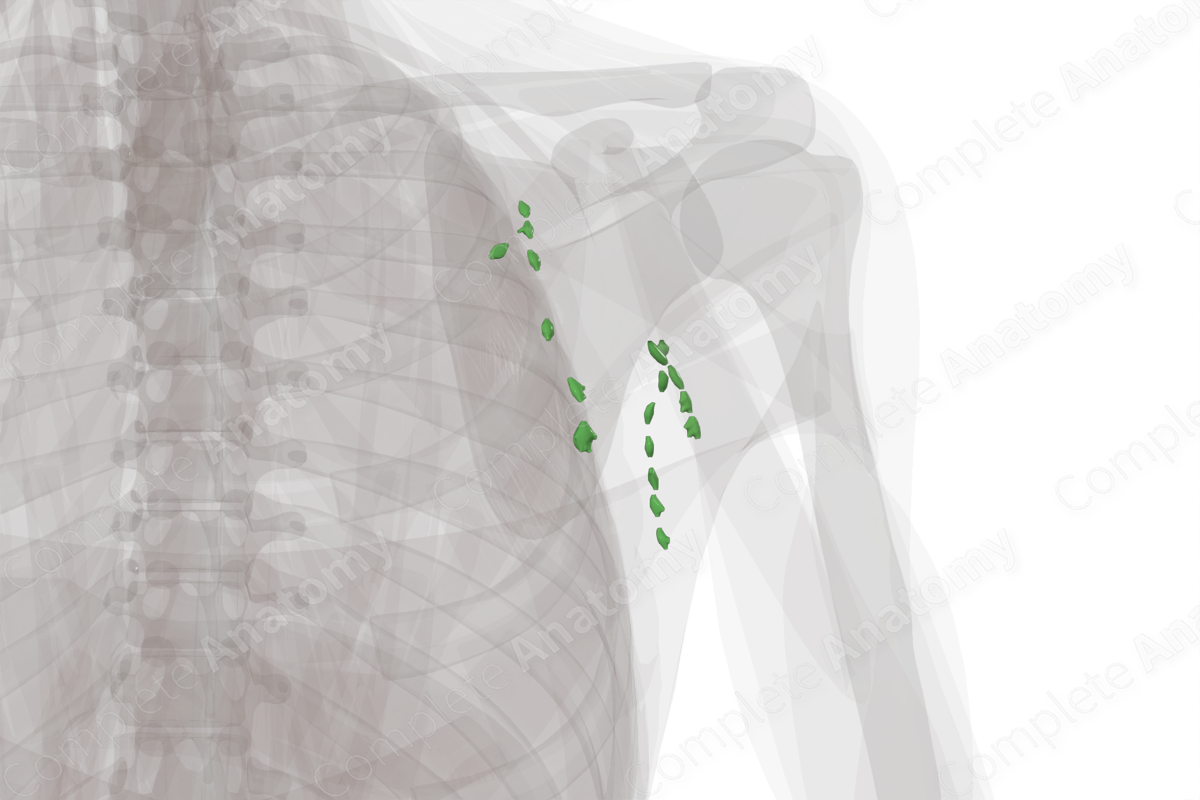
The axillary lymph nodes receive lymph from the upper limb, shoulder, and thoracic and abdominal walls. The nodes are divided into superficial and deep subgroups. The superficial axillary lymph nodes include the lateral, posterior, anterior, and interpectoral nodes. The deep group includes the central and infraclavicular nodes. The largest lymph nodes are usually located at the base of the axilla, whilst the smaller lymph nodes are located at the apex.
In the axillary region lymph travels from the parietal lymph nodes (anterior, posterior, and lateral) towards the central axillary lymph node. From the central nodes, lymph travels in an apical direction to the infraclavicular nodes.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





