Quick Facts
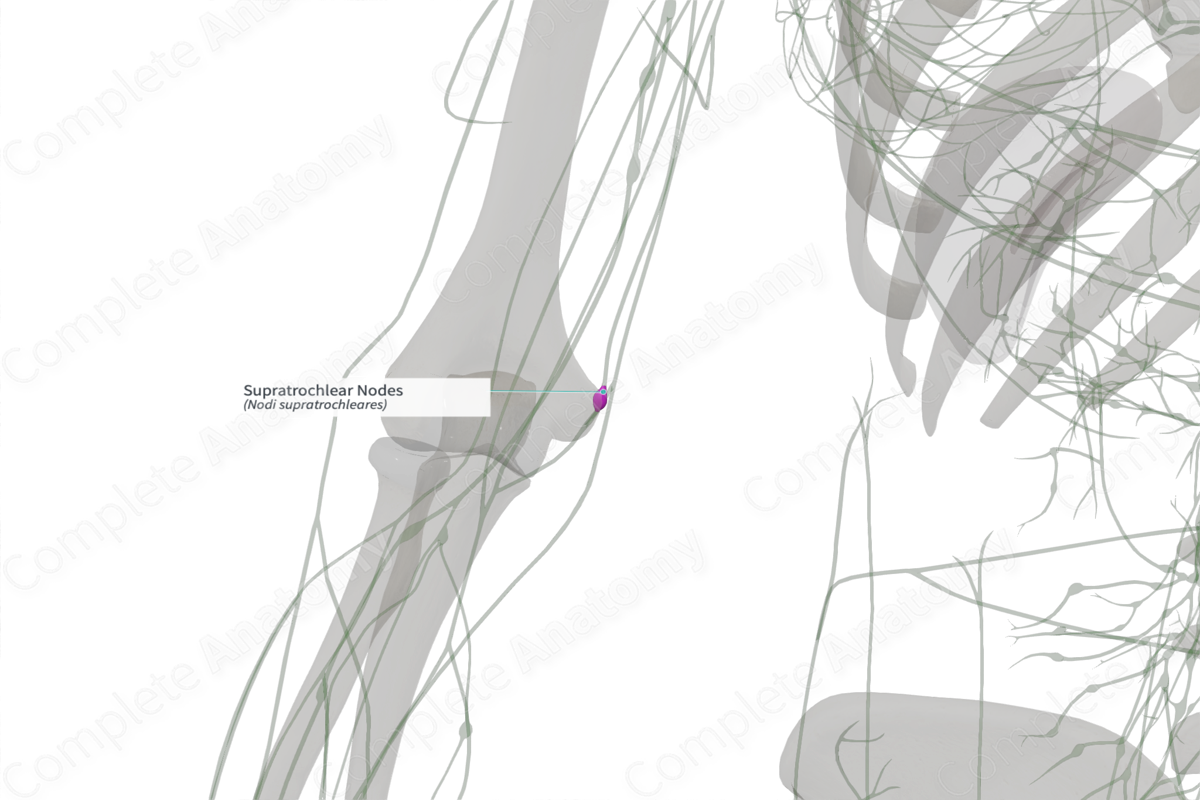
Location: Superior to medial epicondyle of the humerus.
Drainage: Third to fifth fingers and medial forearm.
Direction of Flow: Lateral axillary lymph nodes> central axillary lymph nodes > infraclavicular lymph nodes > subclavian trunk > right lymphatic duct (right) or thoracic duct (left).
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
The supratrochlear lymph nodes are comprised of one to two nodes located superior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and medial to the basilic vein. These nodes form part of the cubital lymph nodes, nodes which are scattered within the cubital fossa, near the bifurcation of the brachial artery.
The supratrochlear lymph nodes drain lymph from the third to fifth fingers, and the medial portions of the forearm. The efferent vessels of the nodes accompany the basilic vein in the arm.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Lymph Node

Lymph nodes are a part of the lymphatic system, which also includes lymphatic vessels that collect interstitial fluid or lymph (including invaded microbes in case of infections) from all vascularized tissues and discharge it into their draining lymph nodes.