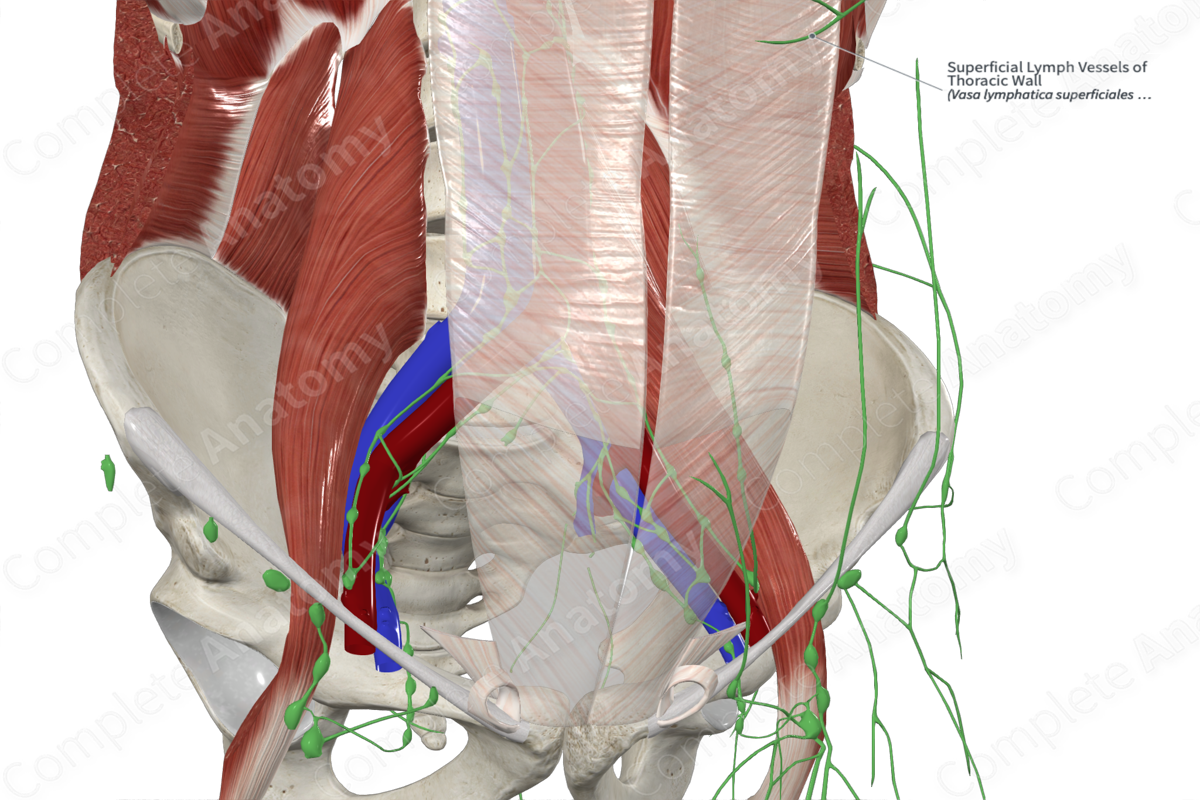
Superficial Lymph Vessels of Thoracic Wall
Vasa lymphatica superficiales parietis thoracis
Read moreQuick Facts
Location: Loose epifascial connective tissue of thoracic wall.
Drainage: Skin and subcutaneous layer of anterior and posterior thoracic
Direction of Flow: Pectoral nodes > central axillary nodes > infraclavicular nodes > subclavian trunk > right lymphatic duct (right) or thoracic duct (left).
Related parts of the anatomy
Description
The superficial lymph vessels of the thoracic wall are located on the anterior and posterior aspect of the thoracic wall, within the loose connective and epifascial connective tissue. The vessels drain lymph from this region into the axillary lymph nodes. The vessels of the anterior wall drain into the pectoral lymph nodes, while vessels that are located close to the clavicle drain into the supraclavicular nodes. Vessels of the posterior aspect of the thoracic wall drain into the axillary lymph nodes. At the midline of both the anterior and posterior thoracic wall, small networks of lymphatic vessels anastomose with each other, connecting lymph from the left and right sides of the body (Földi et al., 2012).
References
Földi, M., Földi, E., Strößenreuther, R. and Kubik, S. (2012) Földi's Textbook of Lymphology: for Physicians and Lymphedema Therapists. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products



