Structure/Morphology
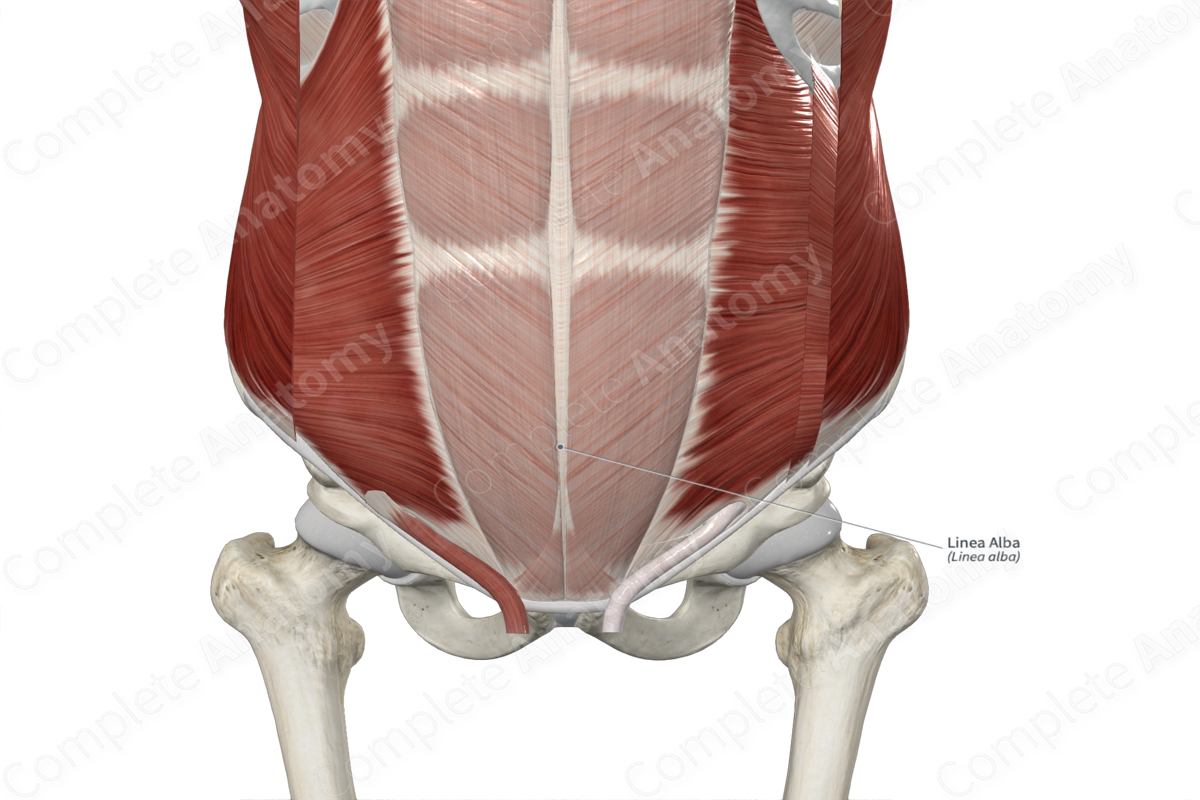
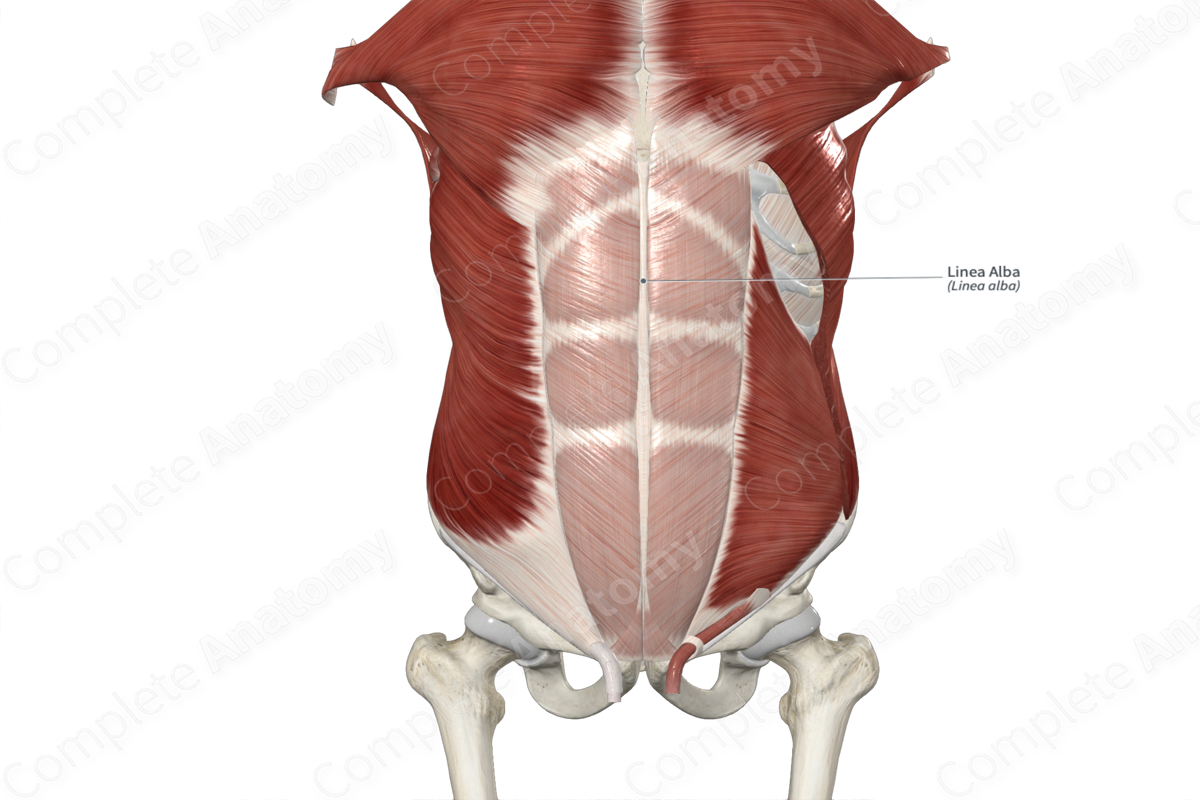
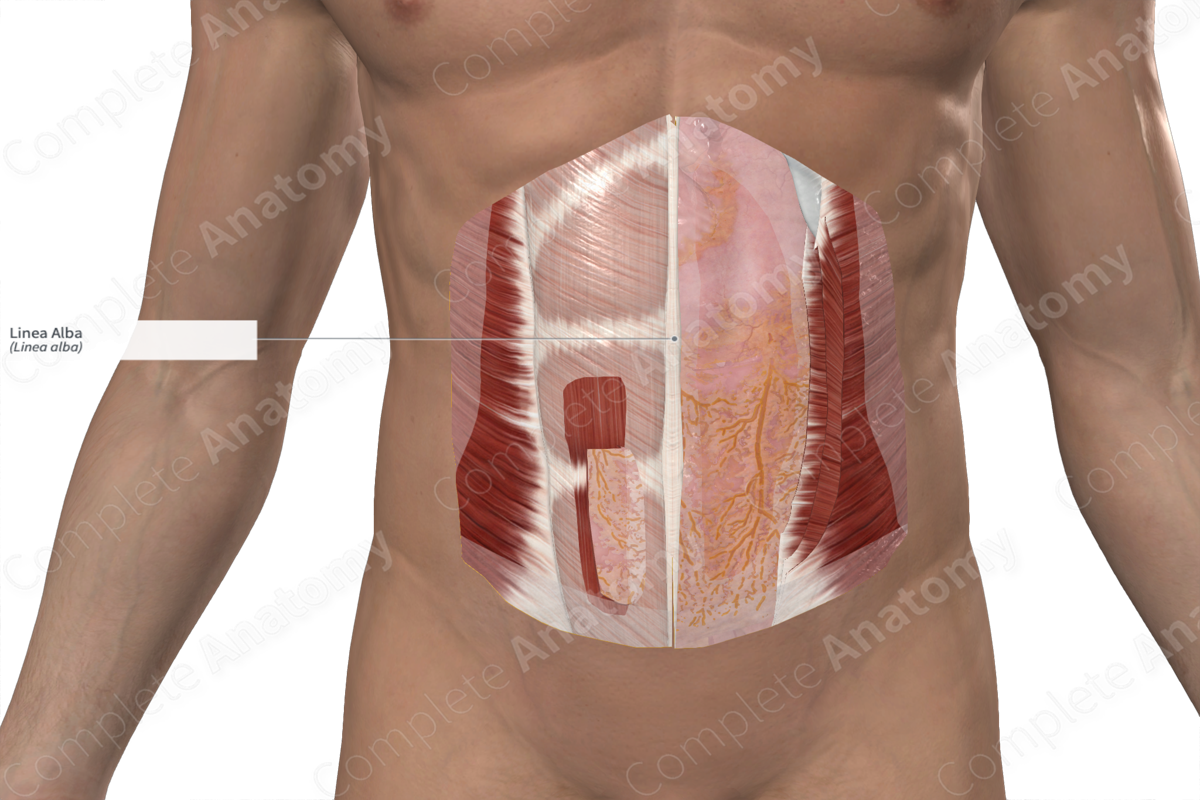
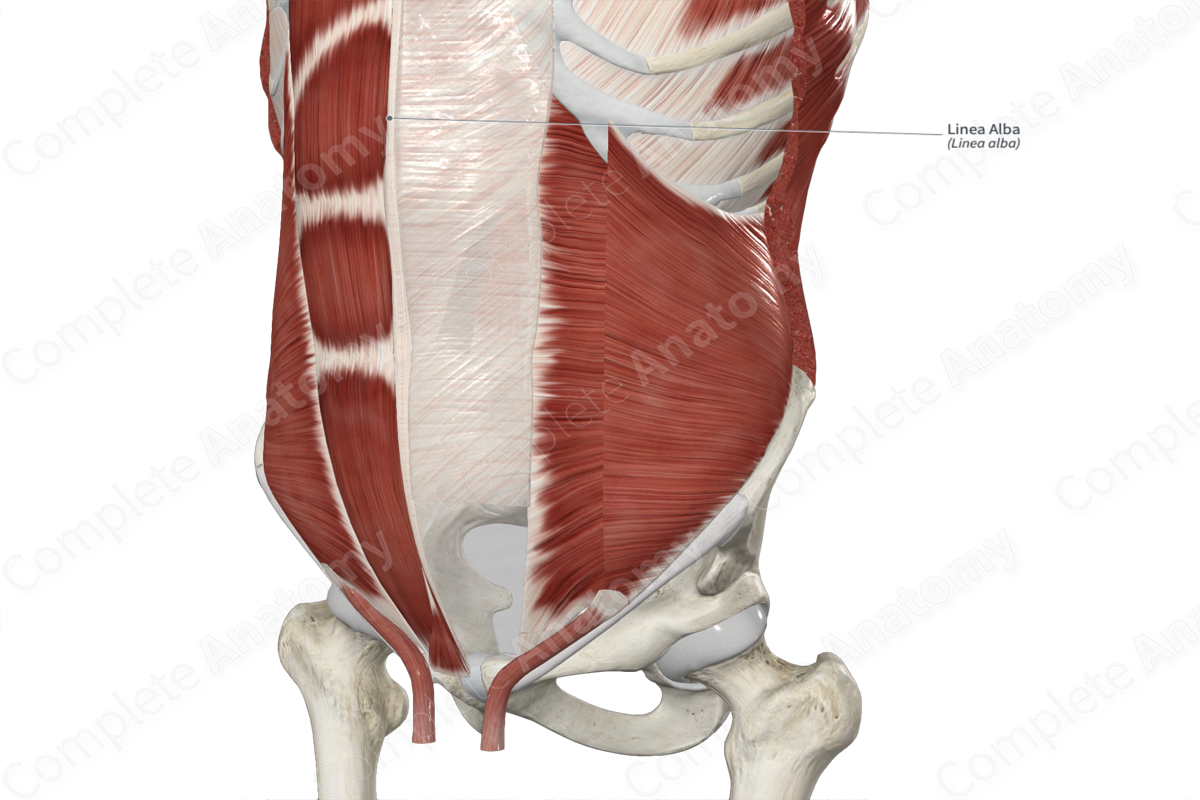
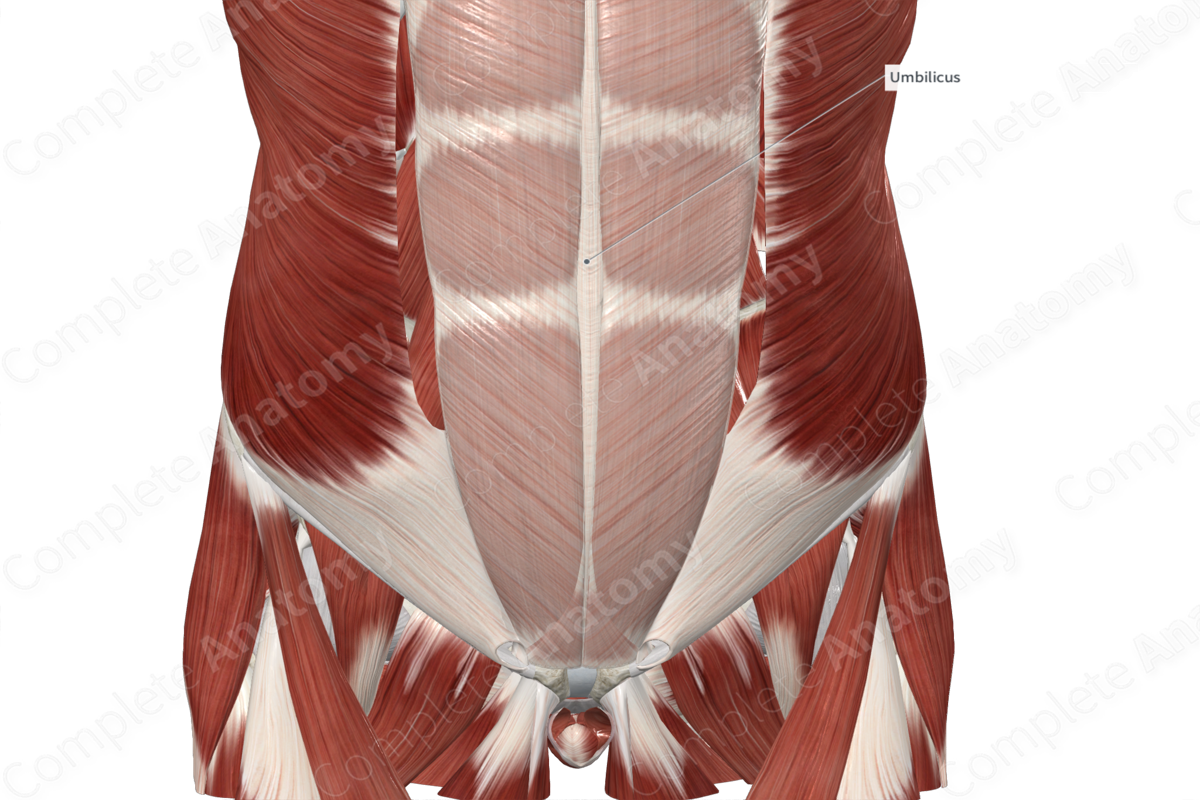
The linea alba (white line) is the thick, fibrous band that extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis. It is formed along the midline of the anterior abdominal wall, where the anterior and posterior layers of the rectus sheath blend with each other and with the fibers of the contralateral rectus sheath.
Related parts of the anatomy
Anatomical Relations
The linea alba is located between the left and right rectus abdominis and pyramidalis muscles. Deep to the umbilicus, the linea alba contains the umbilical ring, which is an opening through which the umbilical vessels passed through in the fetus.
Function
Both the rectus sheath and linea alba are the sites where the aponeuroses of the external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, and transversus abdominis muscles blend together. They act as attachment sites for these muscles, allowing them to work in unison.
The linea alba also provides attachment sites for the:
- left and right pyramidalis muscles;
- suspensory ligament of clitoris in females;
- suspensory ligament of penis in males.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Diastasis recti
- Median abdominal incision
- Midline laparotomy incision