Quick Facts
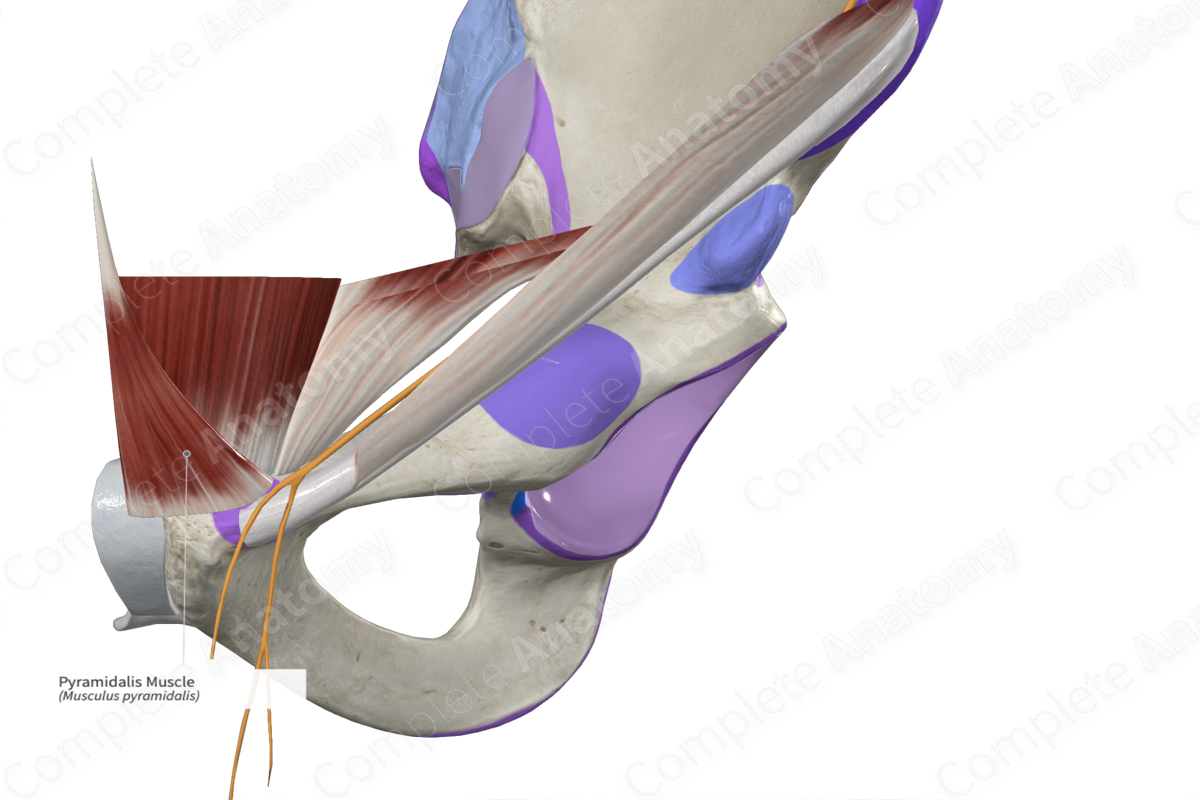
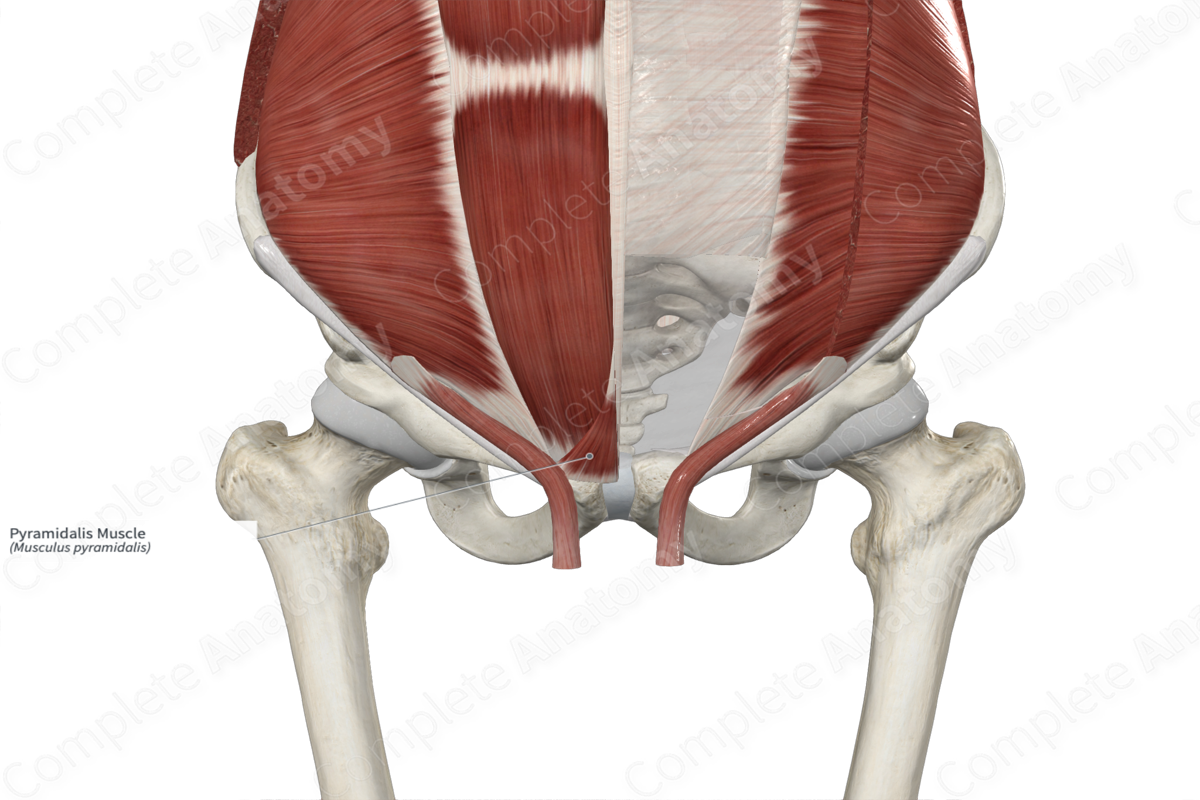
Origin: Body of pubis and anterior pubic ligament.
Insertion: Linea alba.
Action: Tenses linea alba.
Innervation: Anterior ramus of twelfth thoracic nerve, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves.
Arterial Supply: Inferior epigastric artery.
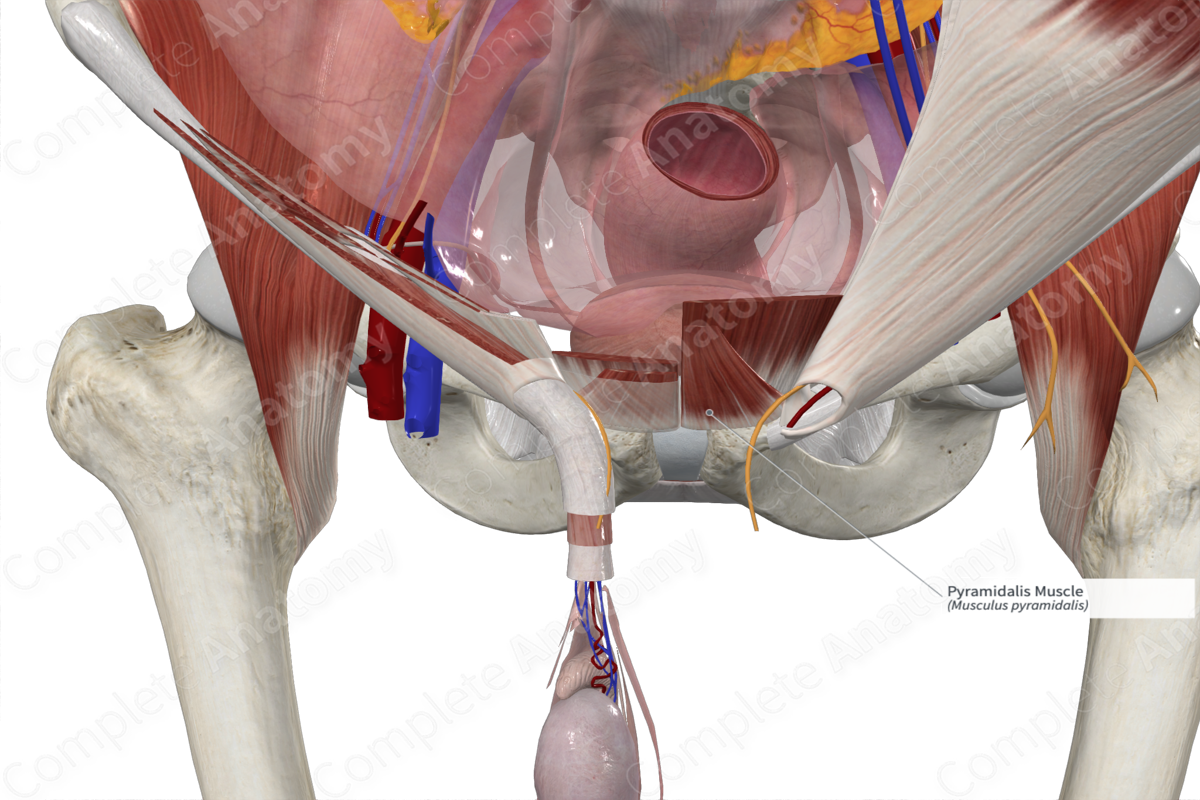
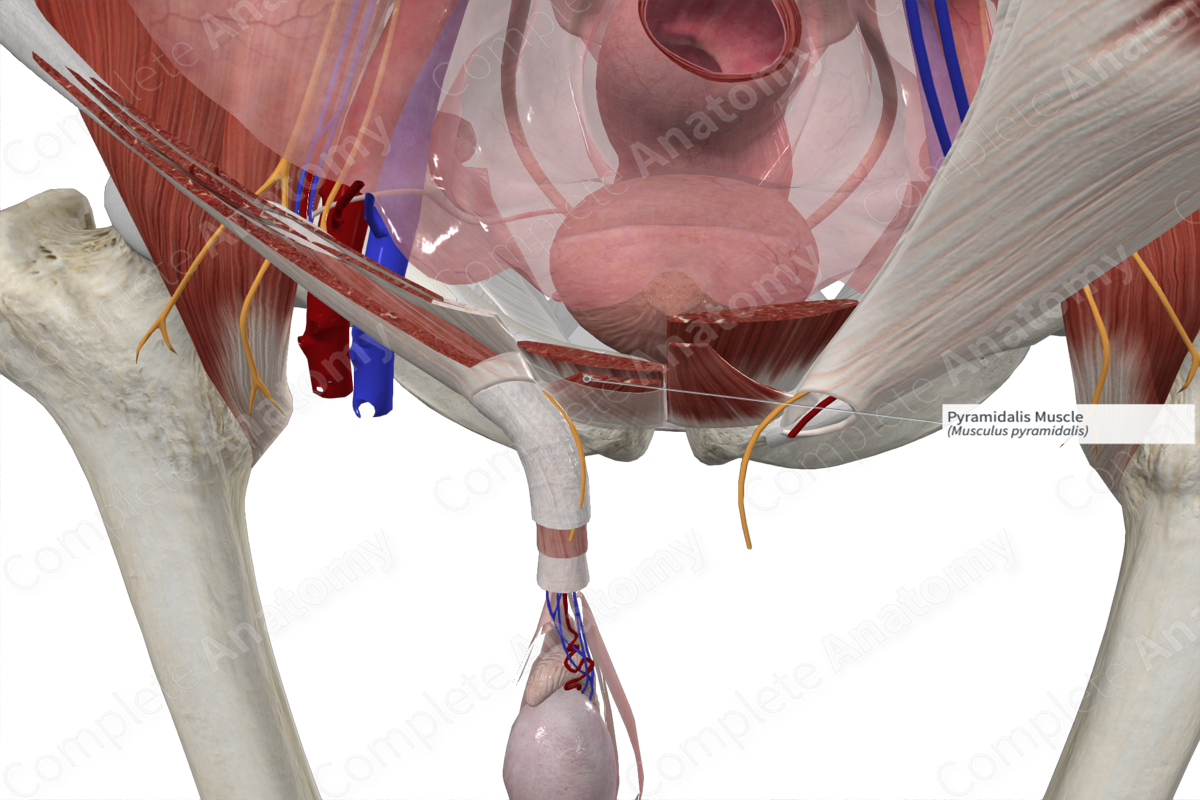
Origin
The pyramidalis muscle originates from the:
- superior aspect of the body of pubis;
- anterior pubic ligament.
Insertion
The fibers of the pyramidalis muscle travel superomedially and insert onto the area of the linea alba that is located between the pubic symphysis and umbilicus.
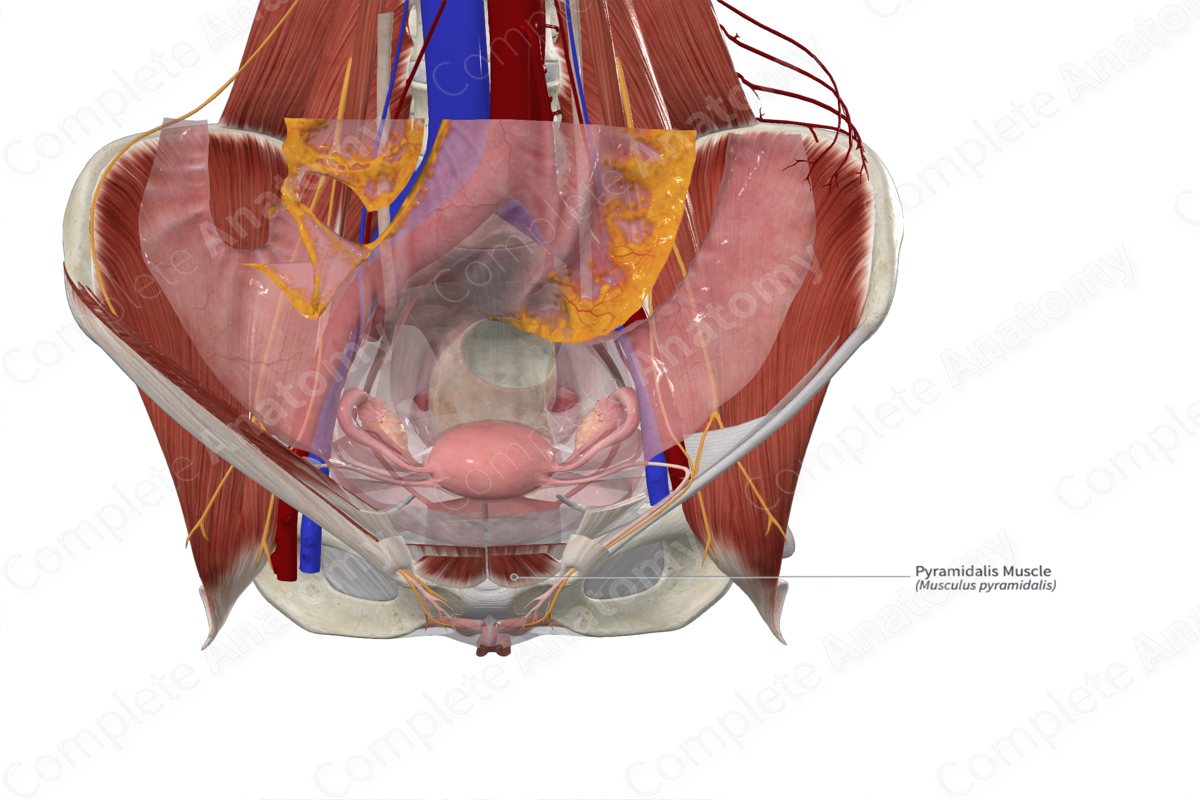
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The pyramidalis muscle is one of the muscles of the abdomen. It is a short, triangular, convergent type of skeletal muscle that is absent in some individuals (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
It is located:
- anterior to the rectus abdominis muscle;
- posterior to the anterior layer of the rectus sheath;
- lateral to the linea alba.
Actions
The pyramidalis muscle tenses the lower part of the linea alba (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Landmark for median abdominal incision
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Actions
The pyramidalis muscle tenses the lower part of the linea alba (Standring, 2016).