Quick Facts
Origin: Angles of seventh to twelfth ribs.
Insertion: Angles of first to sixth ribs.
Action: Extends and laterally flexes trunk.
Innervation: Lateral branches of posterior rami of thoracic nerves.
Arterial Supply: Dorsal branches of posterior intercostal and subcostal arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
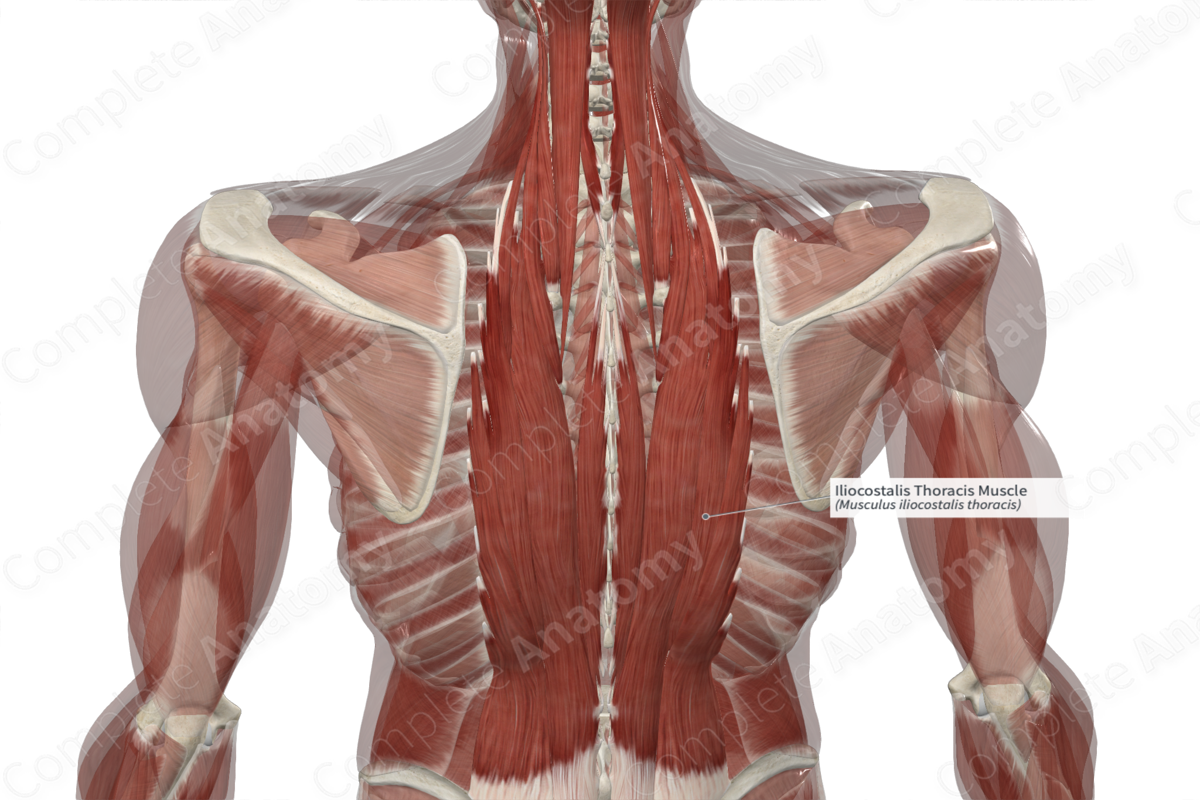
Origin
The iliocostalis thoracis muscle originates from the angles of the seventh to twelfth ribs.
There can be variations between individuals regarding the origin sites for the iliocostalis thoracis muscle (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
Insertion
The fibers of the iliocostalis thoracis muscle travel superiorly along the upper back region and insert onto the angles of the first to sixth ribs.
There can be variations between individuals regarding the insertion sites for the iliocostalis thoracis muscle (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
Overall, the iliocostalis muscles are one of the three muscles of the erector spinae. They are intrinsic muscles of the back and are found along the entire length of the back and posterior neck regions. They are long, flat skeletal muscles that are composed of three parts:
- iliocostalis colli, which is the superior portion;
- iliocostalis thoracis, which is the middle portion;
- iliocostalis lumborum, which is the inferior portion.
The iliocostalis muscles are located:
- superficial to the ribs, and the external intercostal and quadratus lumborum muscles;
- deep to the serratus posterior superior, rhomboid major, trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior muscles, and the thoracolumbar fascia;
- lateral to the longissimus muscle.
Actions
The iliocostalis thoracis muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- During unilateral contraction, it laterally flexes the trunk to the same side;
- During bilateral contraction, it extends the trunk (Standring, 2016).
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.




