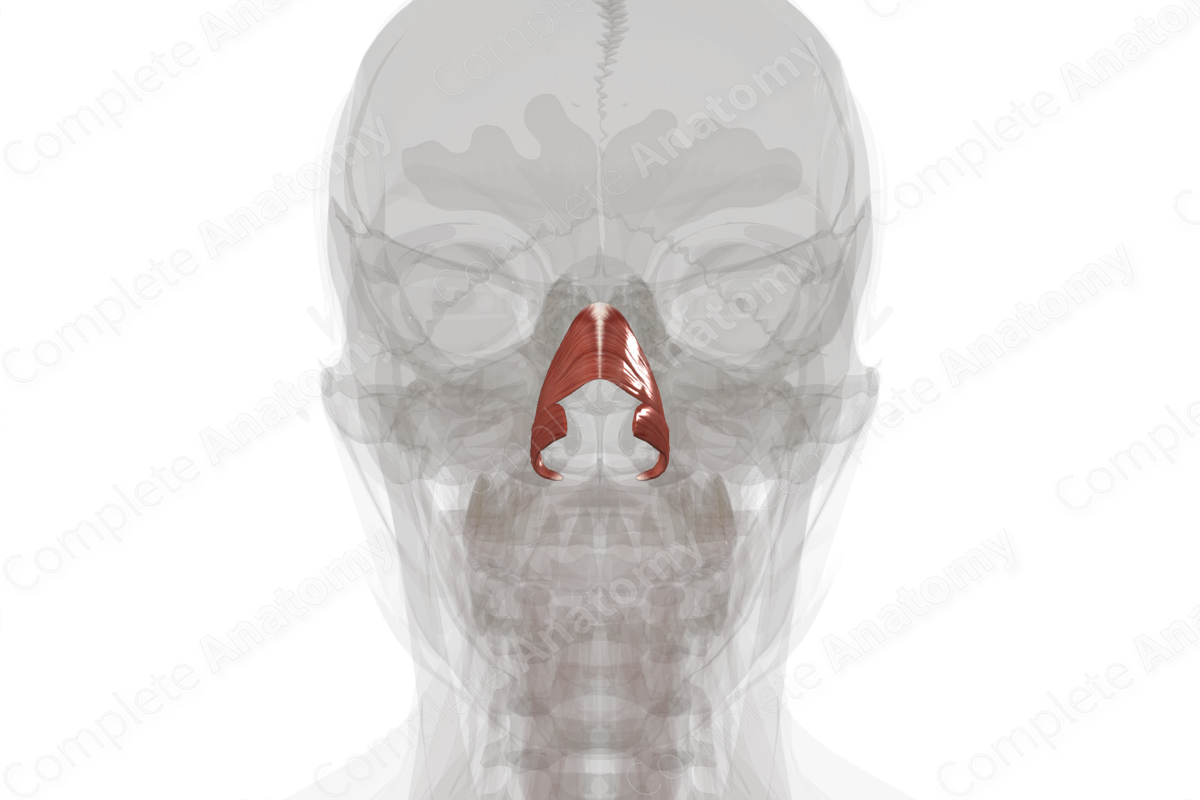
Quick Facts
Origin: Transverse part: area of maxilla superolateral to incisive fossa; Alar part: area of maxilla superior to lateral incisor and canine teeth.
Insertion: Transverse part: aponeurotic fascia crossing bridge of nose; Alar part: skin overlying lateral crus of major alar cartilage.
Action: Transverse part: compresses nostrils; Alar part: dilates nostrils.
Innervation: Buccal branches of facial nerve (CN VII).
Arterial Supply: Superior labial and infraorbital arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The nasalis muscle is divided into transverse and alar parts. The transverse part of the nasalis muscle arises from the maxilla, superolateral to the incisive fossa. The alar part of the nasalis muscle also arises from the maxilla, superior to the lateral incisor and canine teeth.
Insertion
The transverse part of the nasalis muscle blends with its contralateral counterpart via an aponeurotic fascia crossing the bridge of the nose. The alar part of the nasalis muscle attaches to the skin overlying the lateral crus of the major alar cartilage and the posterior part of the mobile septum.
Actions
The transverse part of the nasalis muscle compresses the nostrils, while the alar part of the nasalis muscle dilates the nostrils by drawing the nasal septum downwards (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Bell’s palsy
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.




