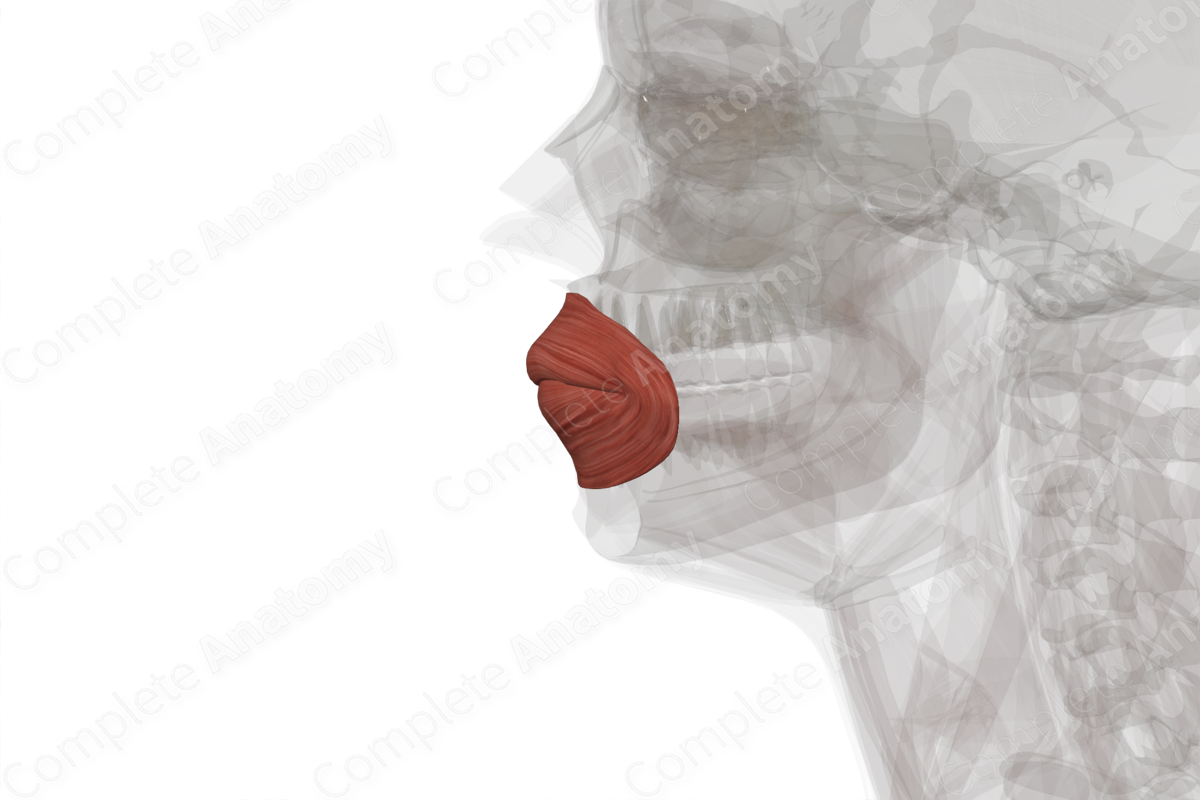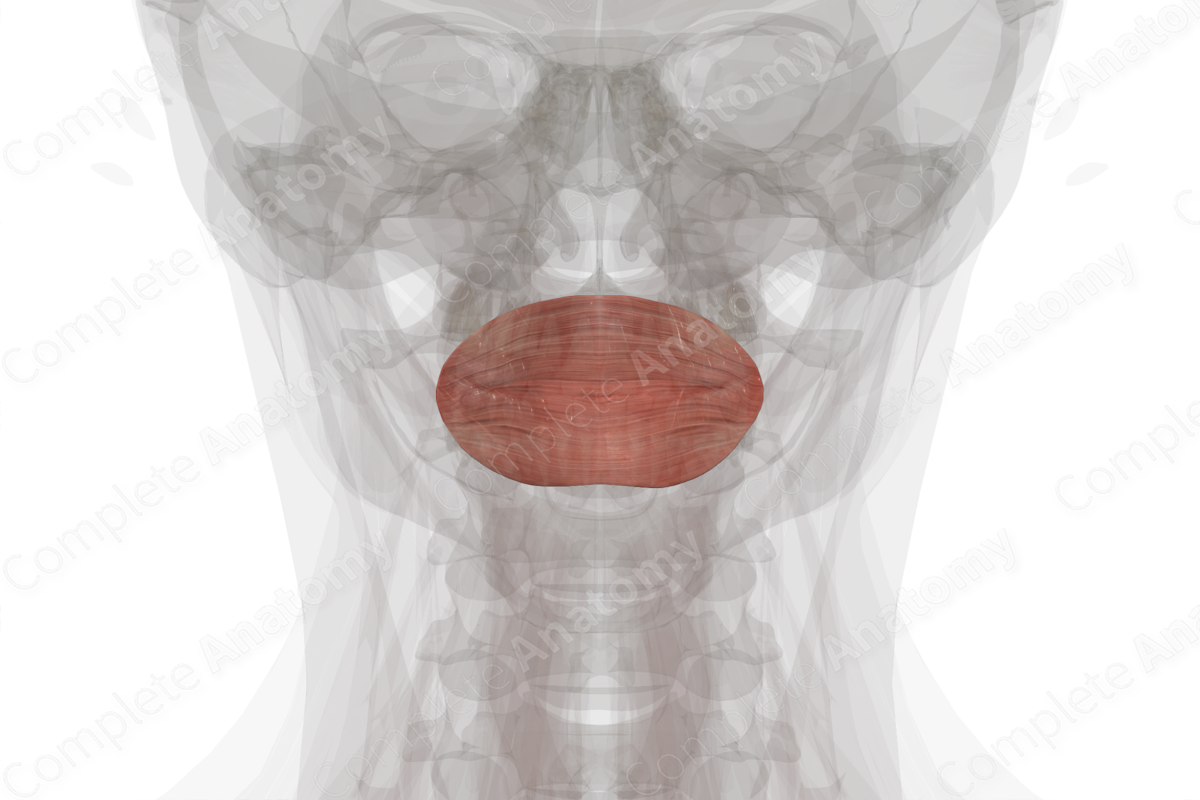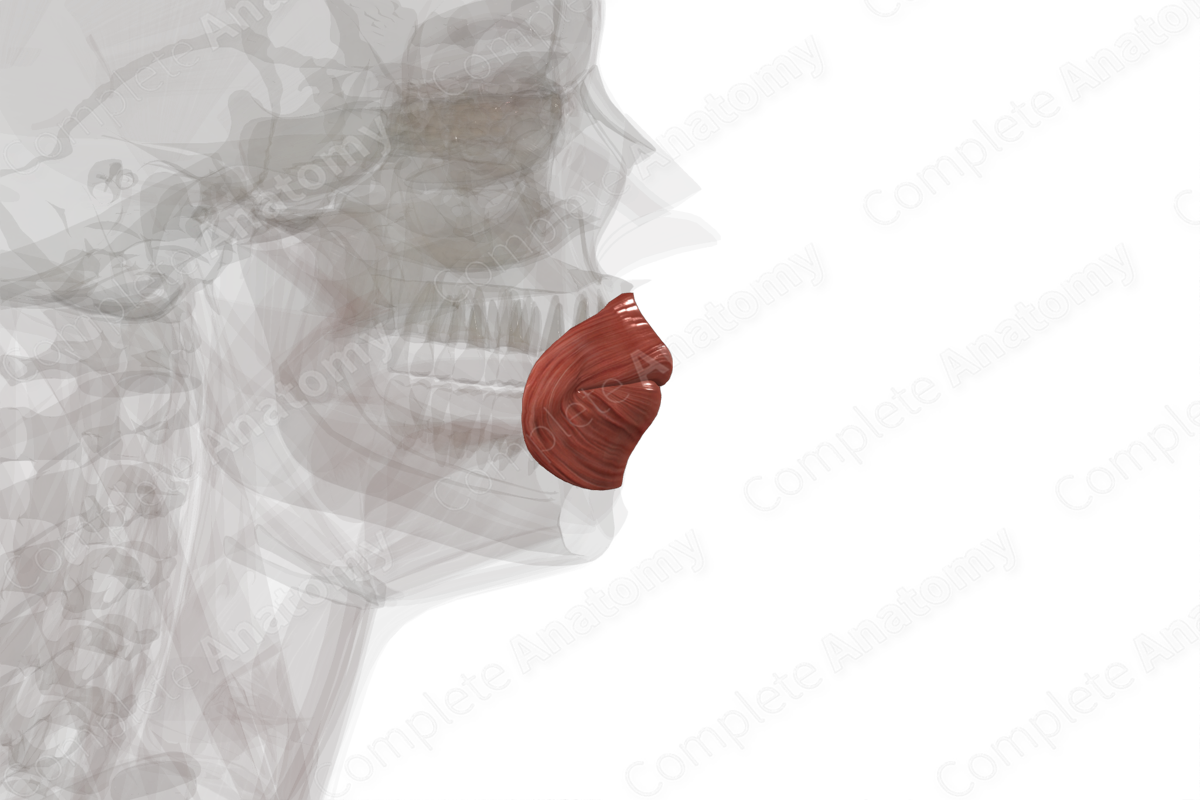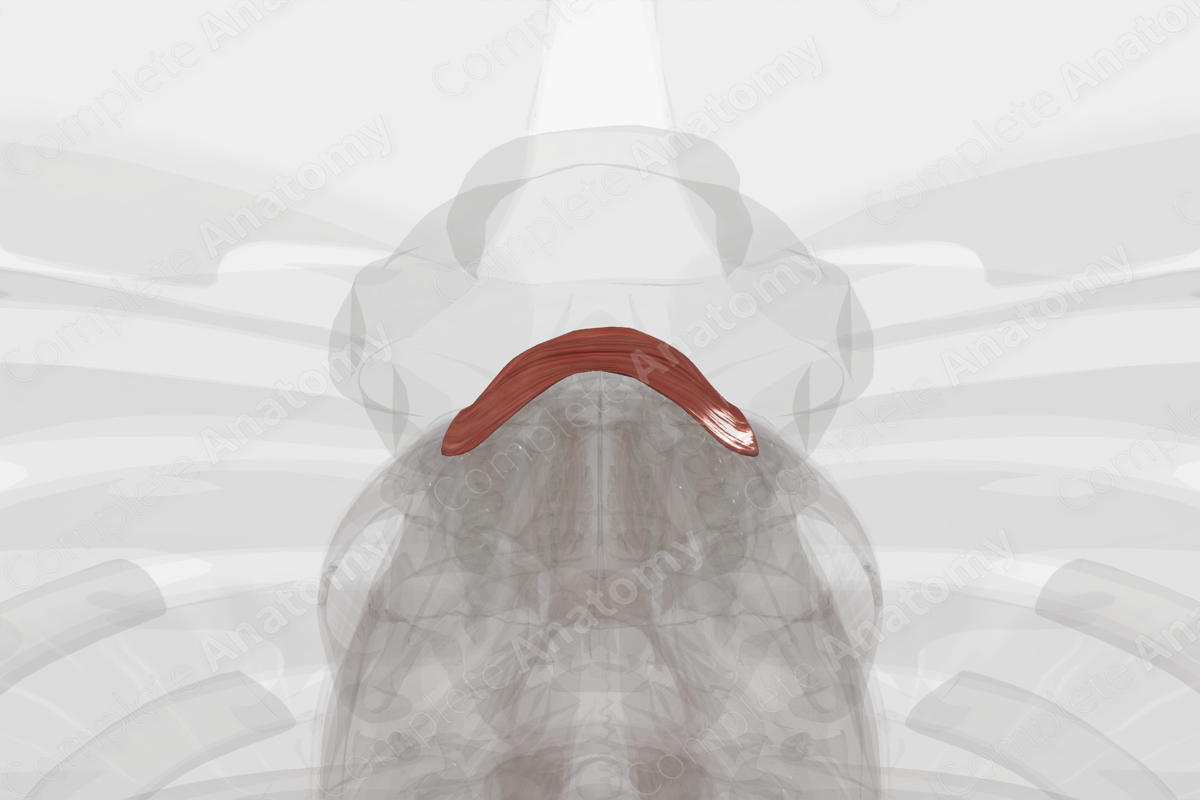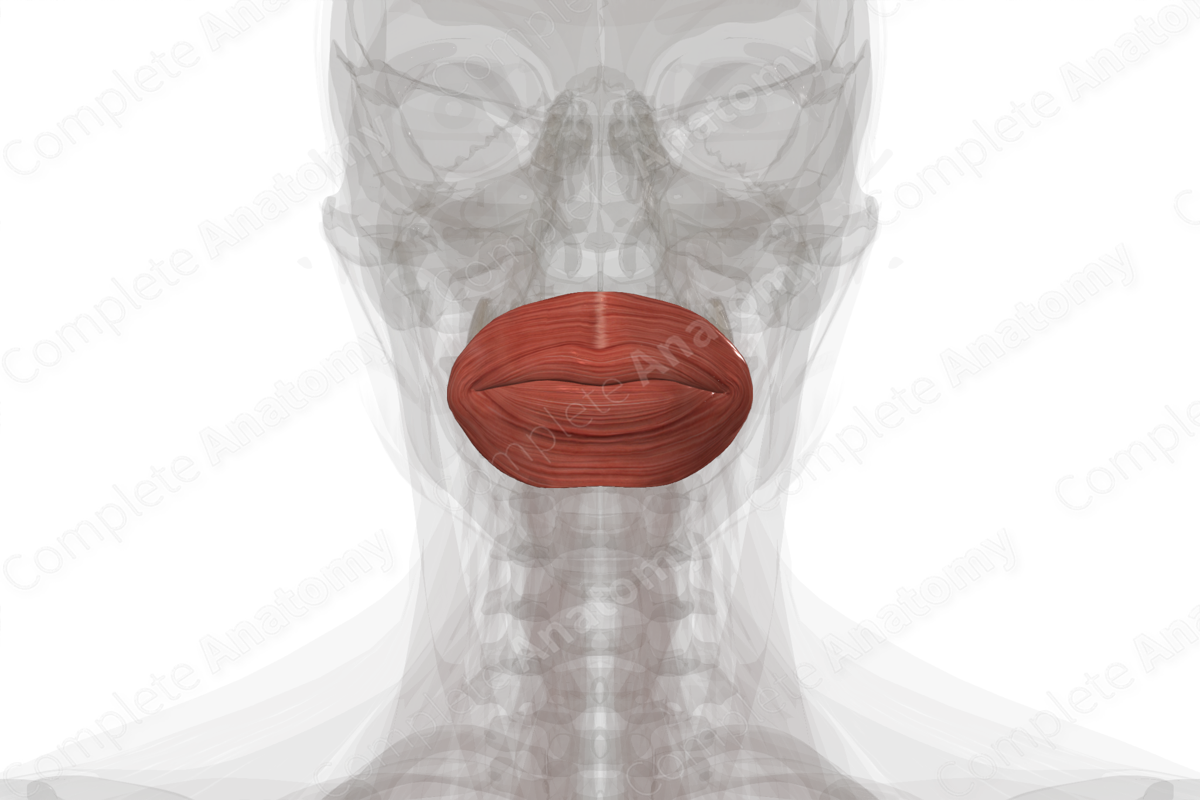
Quick Facts
Origin: Modiolus of angulus oris and vermillion line.
Insertion: Skin and fascia of lips.
Action: Compresses and protrudes lips.
Innervation: Buccal and marginal mandibular branches of facial nerve (CN VII).
Arterial Supply: Superior and inferior labial, infraorbital, and transverse facial arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The orbicularis oris muscle is an annular muscle consisting of an outer marginal part and an inner labial part. The marginal part of the orbicularis oris muscle arises from the labial sides of the modiolus of angulus oris. The inner labial part of the muscle arises from the vermillion line.
Insertion
The fibers from the marginal part of the orbicularis oris muscle course round into their respective upper and lower labial area, attaching to the surfaces of the maxilla and mandible, as well as to the labial part at the vermillion line. The fibers from the labial part extend into the submucosa of the lips and extend laterally to the base of the modiolus of angulus oris.
Actions
Overall, the orbicularis oris muscle compresses and protrudes the lips (Netter, 2011). This action is used when pursing the lips and whistling.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Bell’s palsy
References
Netter, F. H. (2011) Atlas of Human Anatomy. Netter Basic Science Series: Saunders/Elsevier.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Orbicularis Oris Muscle

The orbicularis oris muscle derived from the second branchial arch is composed of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the lip.