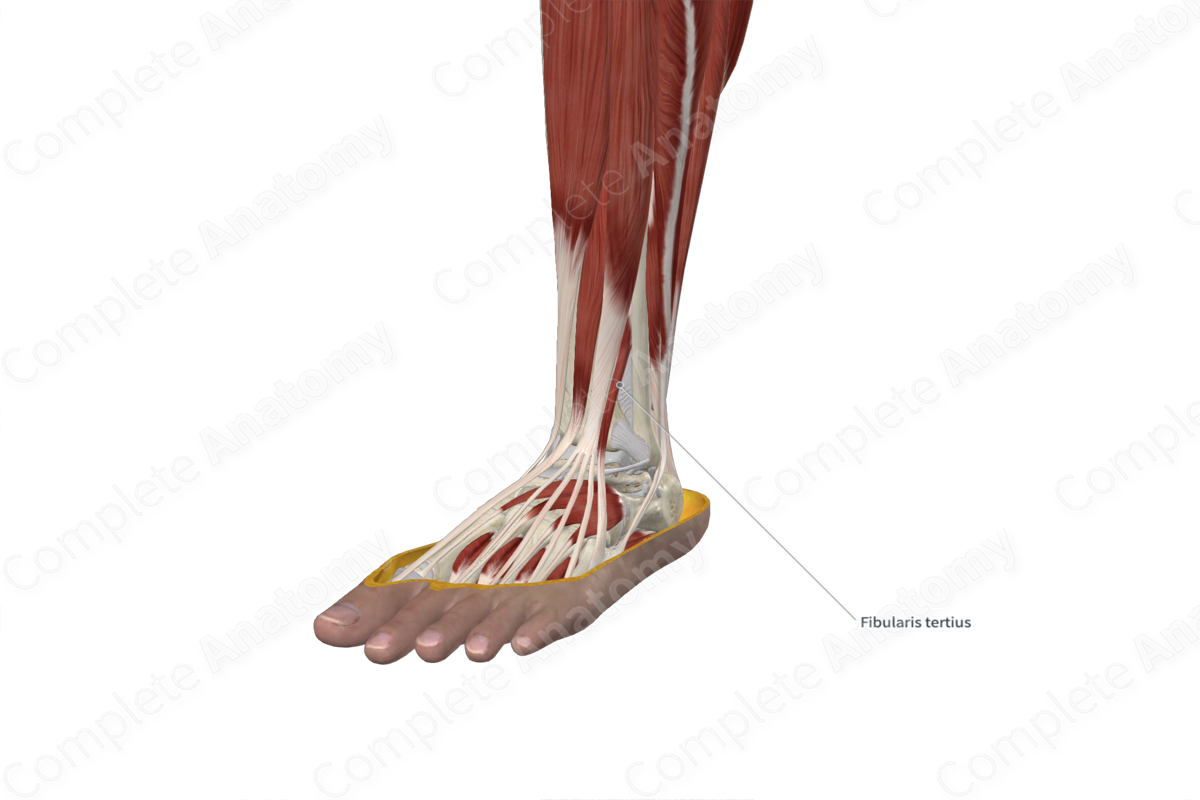
Quick Facts
Origin: Medial surface of fibula and adjacent interosseous membrane of leg.
Insertion: Dorsal aspect of base and body of fifth metatarsal bone.
Action: Dorsiflexes foot at ankle joint; assists in eversion of foot at subtalar and transverse tarsal joints.
Innervation: Deep fibular nerve (L5-S1).
Arterial Supply: Anterior tibial artery and perforating branch of fibular artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The fibularis tertius muscle originates from the:
- distal one third of the medial surface of fibula;
- anterior aspect of the adjacent interosseous membrane of leg;
- adjacent intermuscular septum.
Insertion
The fibers of the fibularis tertius muscle travel inferolaterally to the foot and insert, via a long tendon, onto the dorsal aspect of the base and body of the fifth metatarsal bone.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The fibularis tertius (peroneus tertius) muscle is found in the anterior compartment of the leg. It is a thin, unipennate type of skeletal muscle. Superior to the ankle, the muscle belly travels deep to the superior retinaculum of the foot, where it passes through the tendinous sheath of fibularis tertius. Along the ankle, the muscle belly gives rise to a tendon which travels deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot, as it continues to pass through the tendinous sheath of fibularis tertius. Along the dorsum of the foot, the tendon then travels anterolaterally to its insertion site.
The fibularis tertius muscle is located:
- anterior to the fibula;
- superficial to the extensor digitorum brevis muscle;
- lateral to the tibia and the extensor digitorum longus muscle.
Actions & Testing
The fibularis tertius muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- dorsiflexes the foot at the ankle joint;
- assists in eversion of the foot at the subtalar and transverse tarsal joints.
The fibularis tertius muscle cannot be tested in isolation, therefore all four muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg are tested simultaneously by dorsiflexing the foot at the ankle joint against resistance, during which the tendon of the fibularis tertius can be palpated (Standring, 2016).
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





