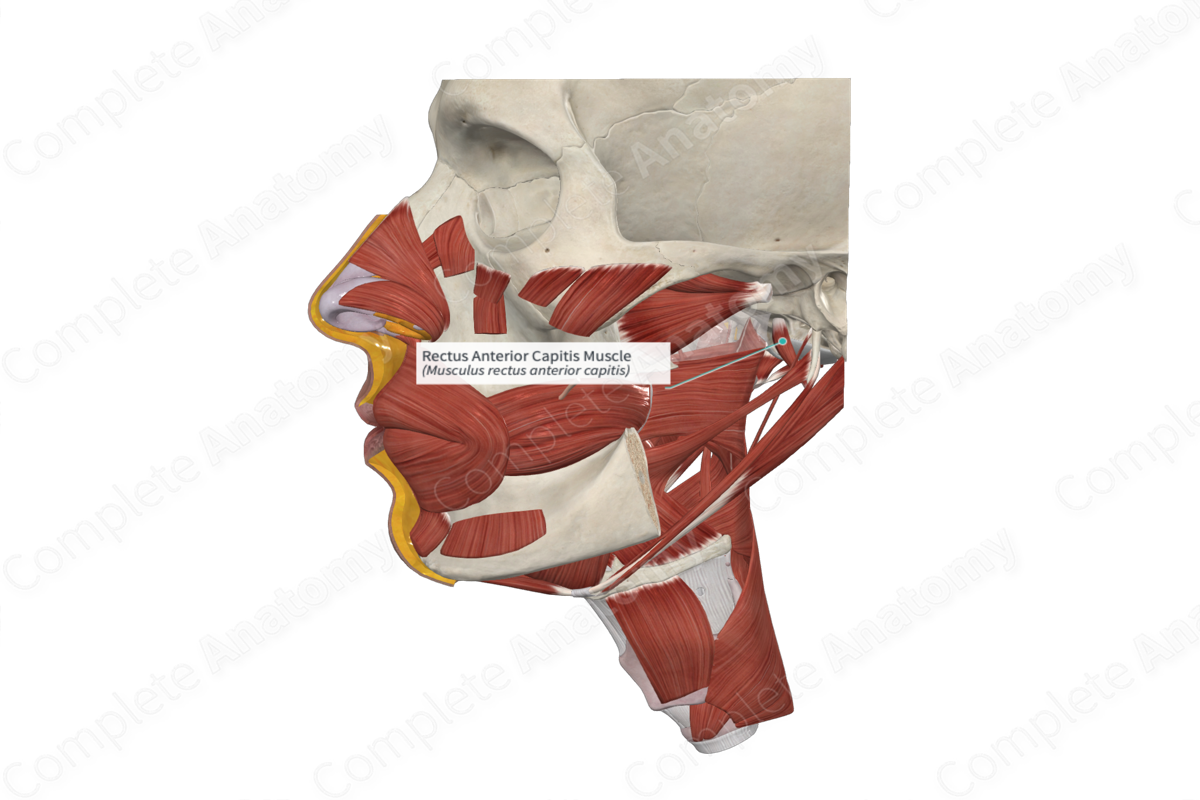
Quick Facts
Origin: Lateral mass and transverse process of atlas (C1).
Insertion: Basilar part of occipital bone.
Action: Flexes head.
Innervation: Anterior rami of first and second cervical nerves (C1-C2).
Arterial Supply: Vertebral and ascending pharyngeal arteries.
Origin
The fibers of the rectus capitis anterior muscle attach to the anterior aspect of the lateral mass of the atlas (first cervical vertebra) and its transverse process.
Insertion
The rectus capitis anterior muscle courses superiorly to the basilar part of the occipital bone. This portion of the occipital bone lies adjacent to the anterior aspect of the occipital condyle.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The rectus capitis anterior muscle lies deep to the longus capitis muscle.
Actions
The rectus capitis anterior muscle flexes the head at the atlantooccipital joints (Standring, 2016).
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.