Description
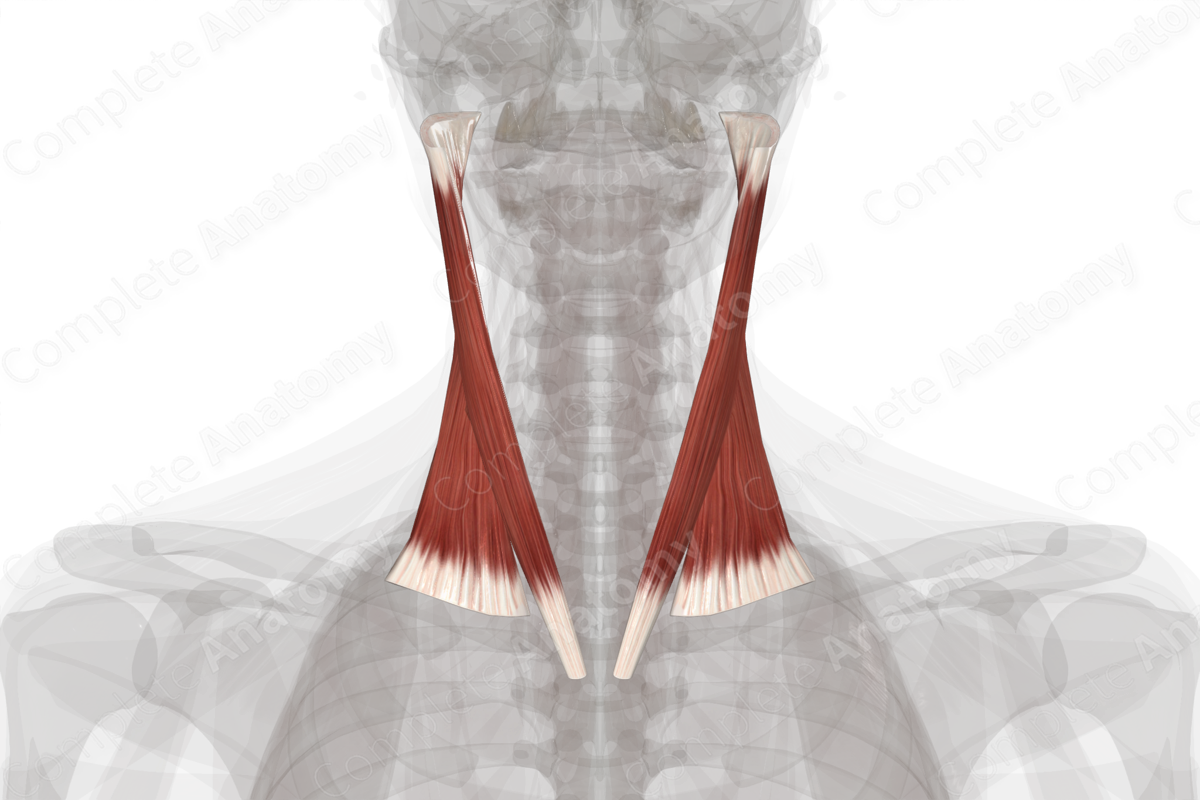
The superficial muscles of the neck include the platysma, sternocleidomastoid, and trapezius muscles. The sternocleidomastoid muscle is an important landmark, as it divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles.
The platysma is also considered to be a muscle of facial expression as it arises from the second pharyngeal arch during embryonic development and, thus, is innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII). The trapezius muscle is considered a superficially placed, extrinsic muscle of the back due to its location and involvement in scapular movement.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





