Quick Facts
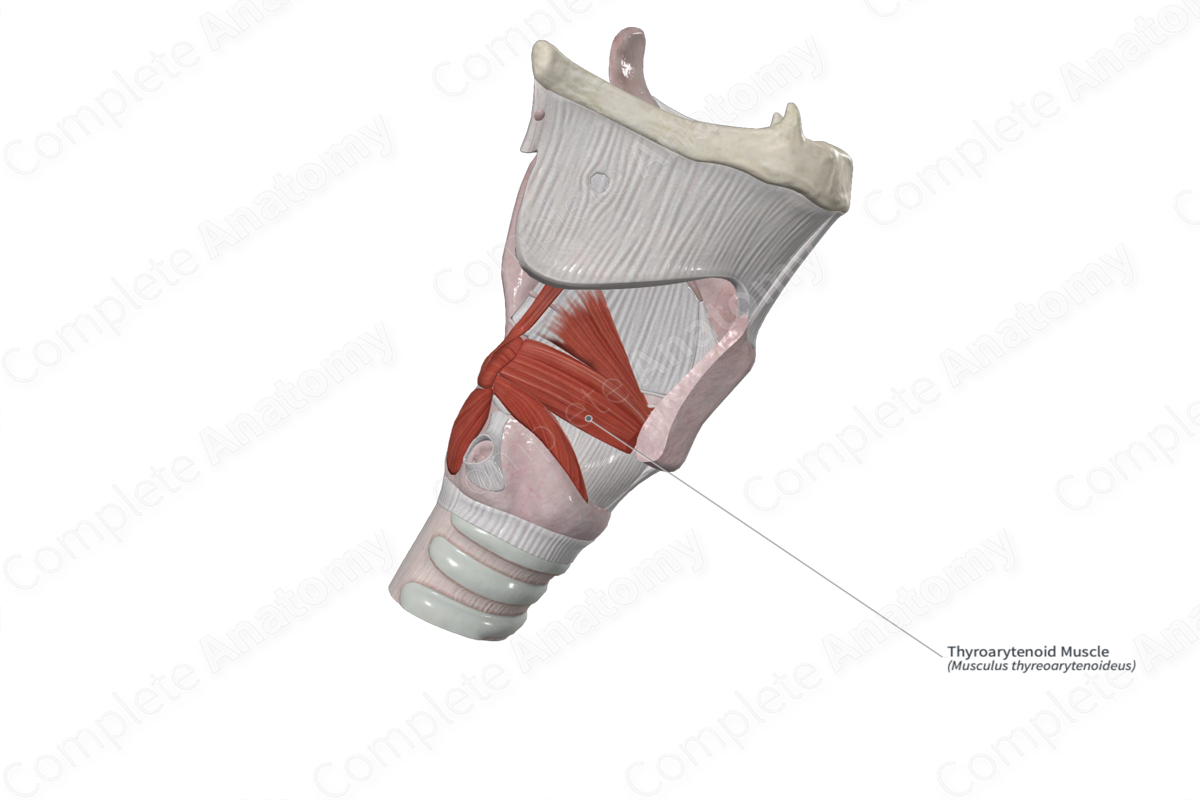
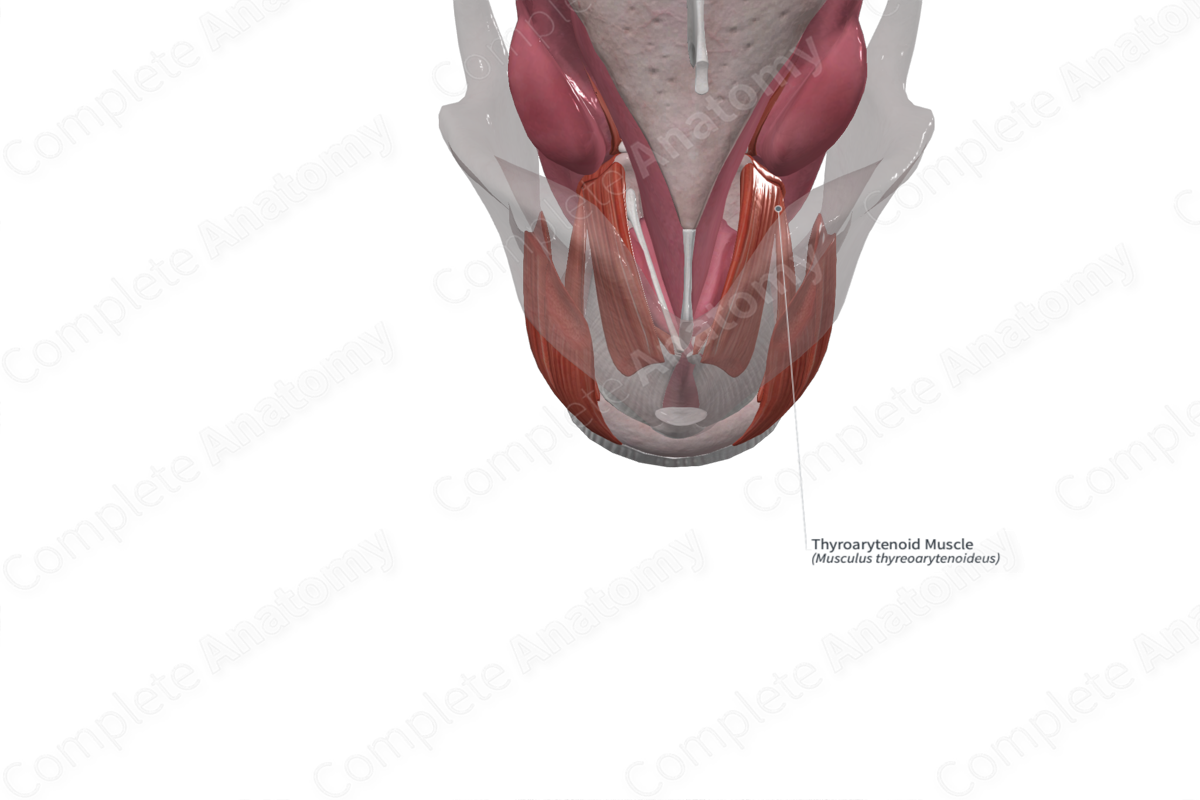
Origin: Inner surface of thyroid cartilage.
Insertion: Arytenoid cartilage.
Action: Shortens and adducts vocal ligament; widens laryngeal inlet.
Innervation: Recurrent laryngeal nerve (CN X).
Arterial Supply: Superior and inferior thyroid arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The thyroarytenoid muscle sits within the larynx on the lateral aspect to the vocal fold. It is attached to the internal surface of the thyroid lamina and the cricothyroid ligament.
Insertion
The thyroarytenoid fibers insert into the anterolateral aspect of the arytenoid cartilages.
The muscular fibers that lie parallel to and adjacent to the vocal ligament form the vocalis muscle, although it is often described as a separate muscle.
Additionally, a number of muscular fibers extend past the arytenoid cartilages. These fibers insert into the aryepiglottic fold or onto the lateral aspect of the epiglottis. These are the thyroepiglottic muscle fibers.
Actions
The thyroarytenoid muscle shortens and adducts the vocal ligament and the thyroepiglottic fibers widen the laryngeal inlet.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products