Quick Facts
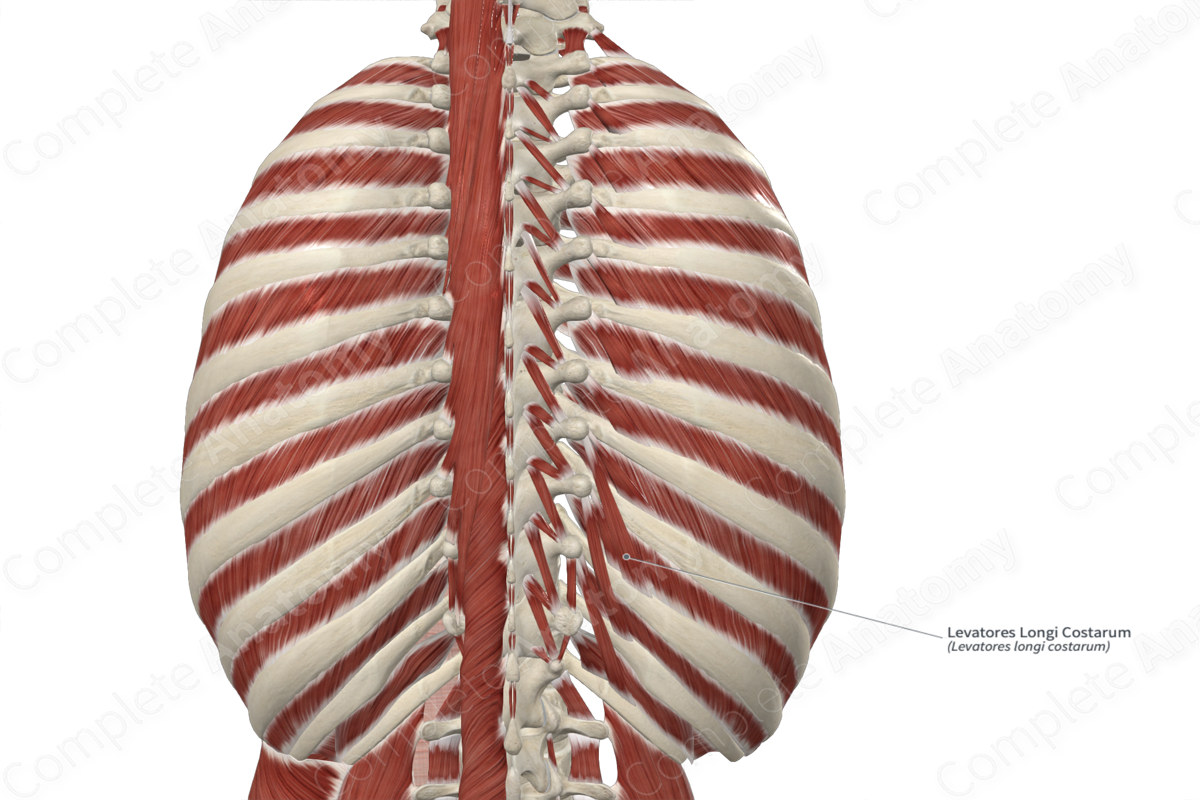
Origin: Transverse processes of T8-T10 vertebrae.
Insertion: Superior borders and external surfaces of tenth to twelfth ribs.
Action: Elevate ribs at their costovertebral joints.
Innervation: Adjacent lateral branches of posterior rami of thoracic nerves.
Arterial Supply: Adjacent dorsal branches of posterior intercostal arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The levatores costarum longi muscles originate from the tips of the transverse processes of the eighth to tenth thoracic vertebrae.
Insertion
The fibers of the levatores costarum longi muscles travel inferolaterally to insert onto the second rib that is inferior to their origin sites (i.e., the tenth to twelfth ribs). They insert onto the superior borders and external surfaces of these ribs, in the area located between their tubercles and angles. For example, its muscle fibers that originate from the eighth thoracic vertebra insert onto the superior borders and external surfaces of the tenth rib.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The levatores costarum muscles are a group of muscles of the thorax. They are composed of many individual muscles that are classified as belonging to either the:
- levatores costarum breves muscles, which are composed of muscles that insert onto the first rib that is inferior to their origin sites;
- levatores costarum longi muscles, which are composed of muscles that insert onto the second rib that is inferior to their origin sites.
The levatores costarum muscles are located:
- superficial to the external intercostal muscles;
- deep to the longissimus muscle;
- lateral to the transversospinal and thoracic intertransversarii muscles.
Actions
The levatores costarum muscles elevate the ribs at their costovertebral joints (Netter, 2011).
References
Netter, F. H. (2011) Atlas of Human Anatomy. Netter Basic Science Series: Saunders/Elsevier.
Actions
The levatores costarum muscles elevate the ribs at their costovertebral joints (Netter, 2011).



