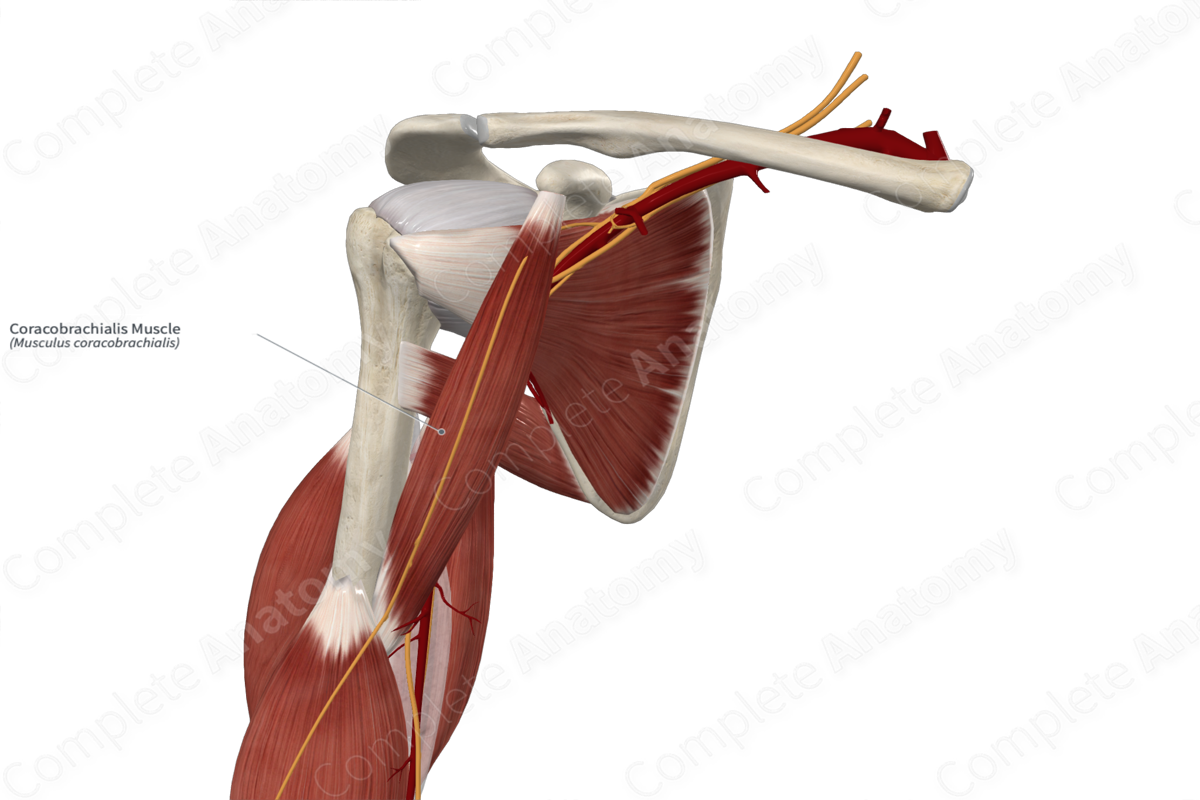
Quick Facts
Origin: Coracoid process of scapula.
Insertion: Middle third of medial aspect of humerus.
Action: Adducts and flexes arm at glenohumeral (shoulder) joint.
Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7).
Arterial Supply: Brachial and anterior circumflex humeral arteries.
Origin
The coracobrachialis muscle originates from the apex of the coracoid process of scapula. This origin site is located posteroinferior to the origin site of the short head of biceps brachii muscle.
Insertion
The fibers of the coracobrachialis muscle travel inferolaterally and insert onto the middle third of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. This insertion site is located between the origin sites of the brachialis and medial head of triceps brachii muscles.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The coracobrachialis muscle is found in the anterior compartment of the arm. It is a strap-like type of skeletal muscle. It is located:
- anterior (superficial) to the subscapularis, teres major, latissimus dorsi, and medial head of triceps brachii muscles, the axillary and brachial arteries, the axillary vein, and the median nerve;
- posterior (deep) to the pectoralis major muscle;
- medial to the brachialis and biceps brachii muscles.
The musculocutaneous nerve pierces the coracobrachialis muscle. The pulse of the brachial artery can be palpated in the depression that lies posterior to the muscle.
Actions & Testing
The coracobrachialis muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- adducts the arm at the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint;
- flexes the arm at the glenohumeral joint.
The coracobrachialis muscle acts as an antagonist to the deltoid muscle. This is due to the insertion sites of both muscles being found on almost opposite sides of the humerus. It can be tested by adducting the arm at the glenohumeral joint against resistance, during which it can be palpated (Standring, 2016).
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Coracobrachialis: What Is It, Location, and More

The coracobrachialis is a muscle located in the anterior (i.e., front) compartment of the upper arm. It is responsible for flexion (i.e., Learn with Osmosis




