Quick Facts
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus, via common extensor tendon, and posterior border of ulna.
Insertion: Medial aspect of base of fifth metacarpal bone.
Action: Extends and adducts hand at radiocarpal (wrist) joint.
Innervation: Posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve (C7-C8).
Arterial Supply: Radial recurrent and posterior interosseous arteries.
Origin
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle originates from the:
- lateral epicondyle of humerus, via the common extensor tendon;
- posterior border of ulna, via a common aponeurosis that it shares with the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle;
- adjacent antebrachial fascia.
The common extensor tendon is the combined tendon for four of the six superficial muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which are the:
- extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle;
- extensor digitorum muscle;
- extensor digiti minimi muscle;
- extensor carpi ulnaris muscle.
Insertion
The fibers of the extensor carpi ulnaris muscle travel inferiorly to the hand and insert, via a flat tendon, onto the medial aspect of the base of fifth metacarpal bone.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
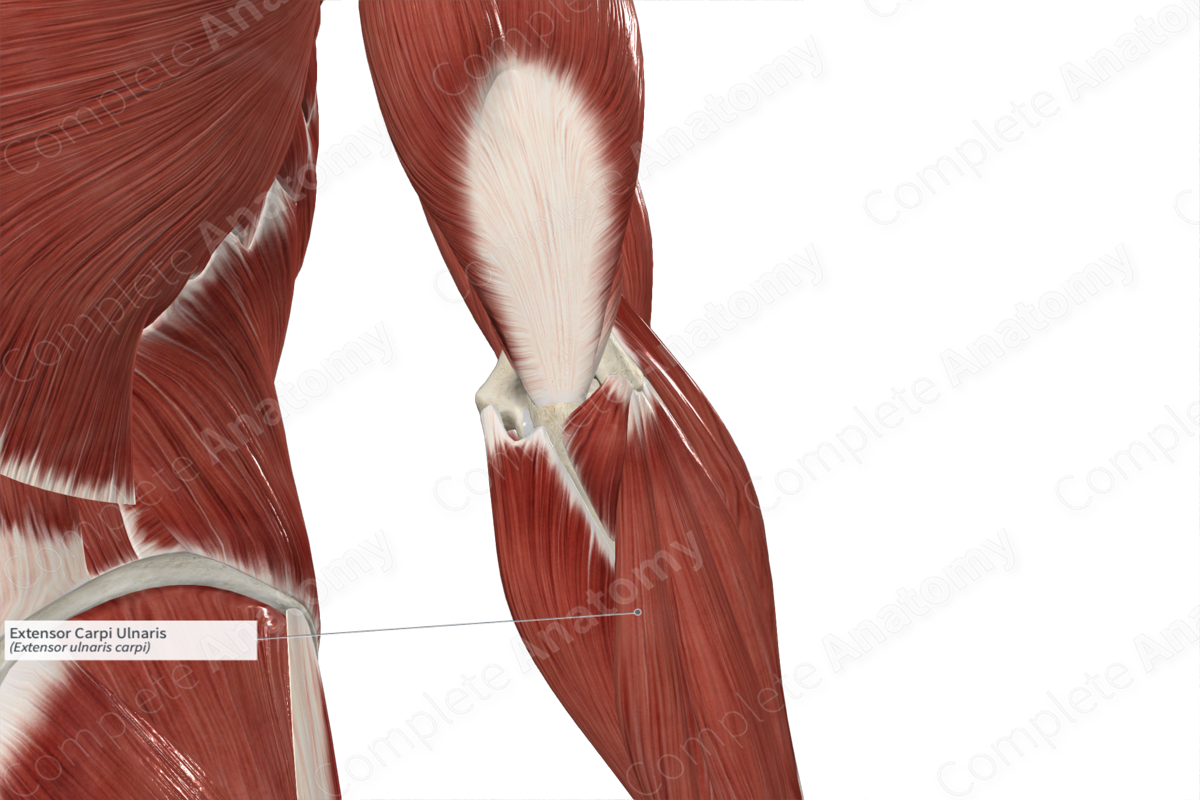
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle is one of the muscles of the superficial part of the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is a long fusiform type of skeletal muscle.
From its origin, the muscle belly travels inferomedially along the posterior aspect of the forearm. In the distal one third of the forearm, the muscle belly gives rise to a flat tendon, which travels inferiorly along a groove found on the medial aspect of the head of ulna. At the wrist, the tendon of the extensor carpi ulnaris travels deep to the extensor retinaculum of hand, where it passes through the tendinous sheath of extensor carpi ulnaris. Within the hand, the tendon then travels inferiorly to its insertion site.
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle is located:
- posterior (superficial) to the body of ulna;
- medial to the extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi muscles;
- lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris and anconeus muscles.
Actions & Testing
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle is involved in multiple actions:
- extends the hand at the radiocarpal (wrist) joint, which occurs when the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis contract simultaneously with it;
- adducts the hand at the radiocarpal joint, which occurs when the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle contracts simultaneously with it.
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle can be tested by adducting the hand at the radiocarpal joint against resistance while the forearm is held in the pronated position, during which it can be palpated (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.




