Quick Facts
Origin: Tendons of flexor digitorum profundus that travel to the ring and little fingers.
Insertion: Lateral aspect of extensor expansion of little finger.
Action: Simultaneously flexes metacarpophalangeal joint and extends interphalangeal joints of little finger.
Innervation: Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8-T1).
Arterial Supply: Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital and dorsal metacarpal arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
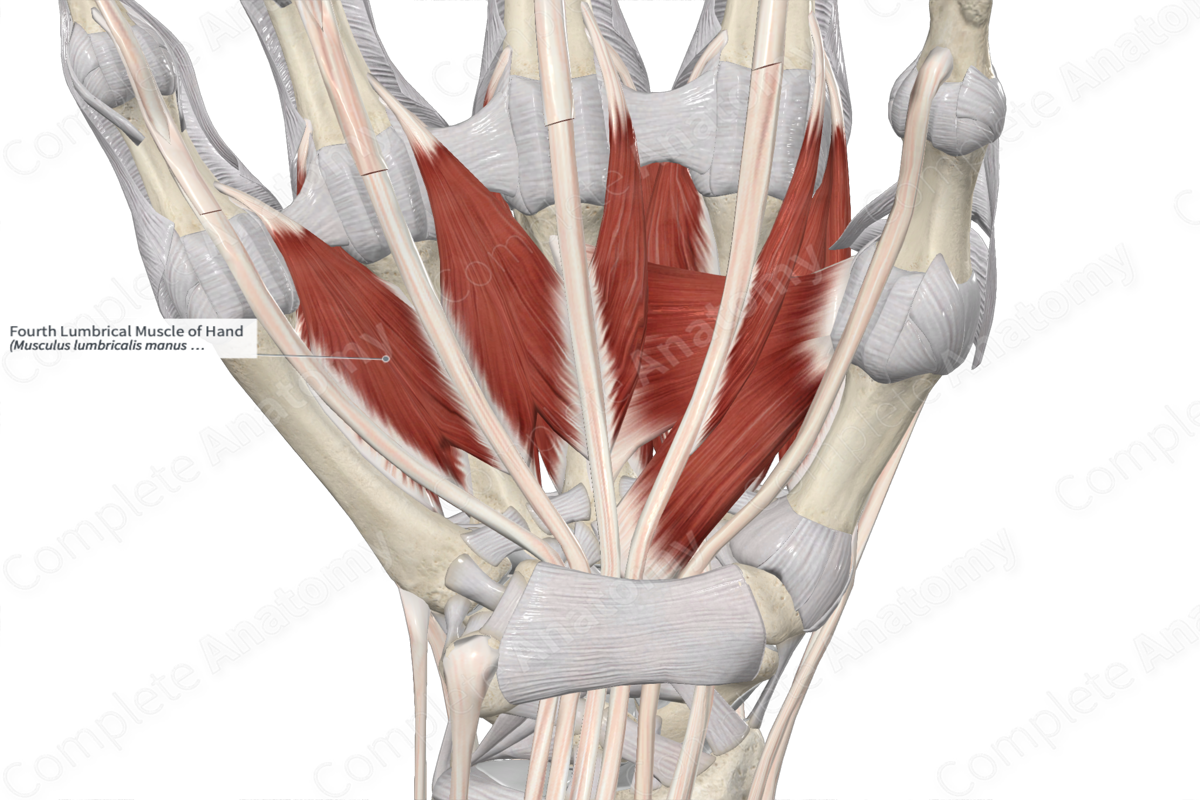
Origin
The fourth lumbrical muscle of hand consists of two heads:
- the lateral head, which originates from the medial aspect of the tendon of flexor digitorum profundus that travels to the ring finger;
- the medial head, which originates from the lateral aspect of the tendon of flexor digitorum profundus that travels to the little finger.
Insertion
The fibers of the fourth lumbrical muscle of hand travel inferiorly to the little finger and insert, via a short tendon, onto the lateral aspect of the extensor expansion of the little finger.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The fourth lumbrical muscle of hand is found in the central compartment of the hand. It is a short, wormlike, bipennate skeletal muscle. It is located:
- anterior to the third palmar and fourth dorsal interossei muscles of hand;
- posterior to the palmar aponeurosis;
- medial to the tendon of flexor digitorum profundus that travels to the ring finger;
- lateral to the tendon of flexor digitorum profundus that travels to the little finger.
Actions & Testing
The fourth lumbrical muscle of hand simultaneously flexes the fifth metacarpophalangeal joint and extends the interphalangeal joints of the little finger, which occurs when the third palmar interosseous muscle of hand contracts simultaneously with it.
The fourth lumbrical muscle of hand can be tested by simultaneously flexing the fifth metacarpophalangeal joint and extending the interphalangeal joints of the little finger. While holding this position, an examiner tries to either extend the metacarpophalangeal joint or flex the interphalangeal joints of the same finger (Sinnatamby, 2011).
References
Sinnatamby, C. S. (2011) Last's Anatomy: Regional and Applied. ClinicalKey 2012: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Hand Muscle

39,40 The lumbricals are a group of intrinsic hand muscles that originate on the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendons.

