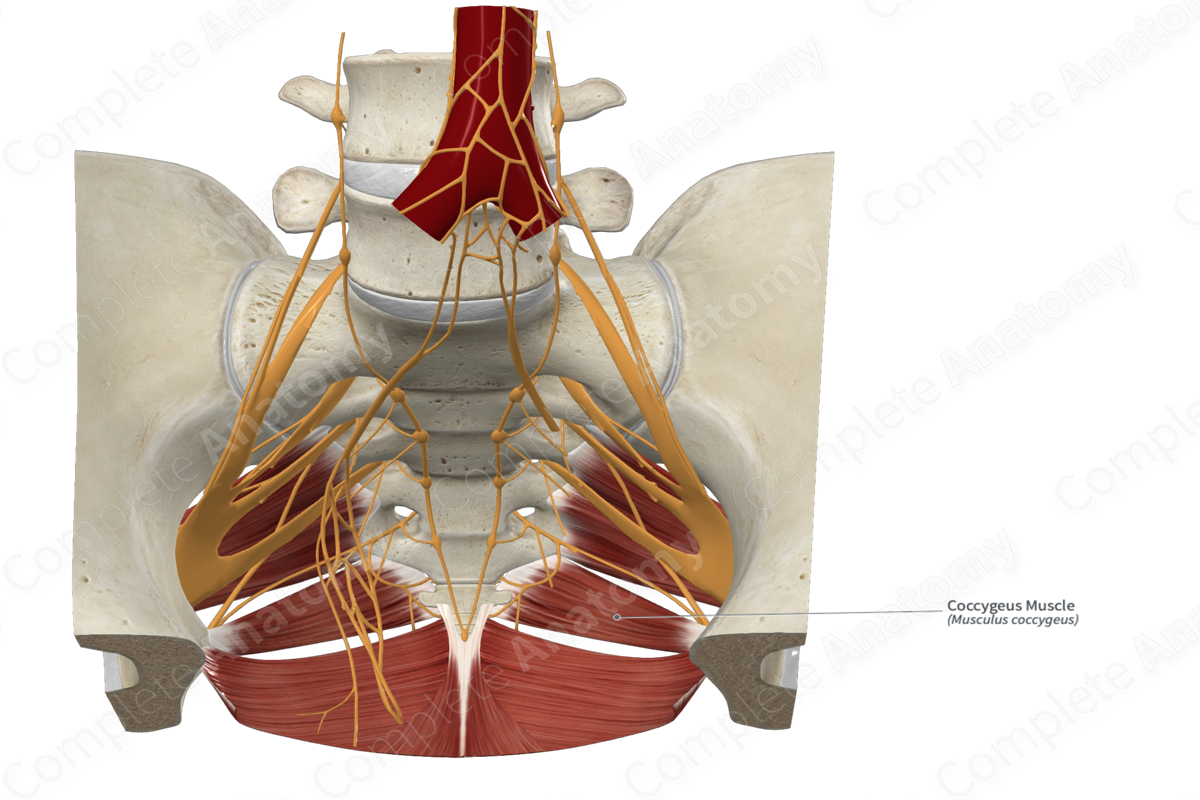
Quick Facts
Origin: Ischial spine.
Insertion: Anterolateral aspects of sacrum and coccyx.
Action: Provides structural support to adjacent pelvic structures.
Innervation: Anterior rami of fourth and fifth sacral nerves (S4-S5).
Arterial Supply: Inferior gluteal artery.
Origin
The coccygeus muscle originates from the ischial spine.
Insertion
The fibers of the coccygeus muscle travel posteromedially and insert, via a broad tendon, onto the:
- anterolateral aspect of the inferior area of the sacrum;
- anterolateral aspect of the superior area of the coccyx.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The coccygeus (ischiococcygeus) muscle is one of the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm. It is a flat, triangular skeletal muscle that forms the posterosuperior part of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located:
- anterior to the sacrospinous ligament, which it may also be attached to;
- superior to the iliococcygeus muscle of the levator ani;
- inferior to the piriformis muscle.
Actions
As part of the pelvic diaphragm, the coccygeus muscle provides structural support to adjacent pelvic structures (Sinnatamby, 2011).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Prolapse of pelvic viscera
- Urinary incontinence
- Fecal incontinence
References
Sinnatamby, C. S. (2011) Last's Anatomy: Regional and Applied. ClinicalKey 2012: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.
Actions
As part of the pelvic diaphragm, the coccygeus muscle provides structural support to adjacent pelvic structures (Sinnatamby, 2011).
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





