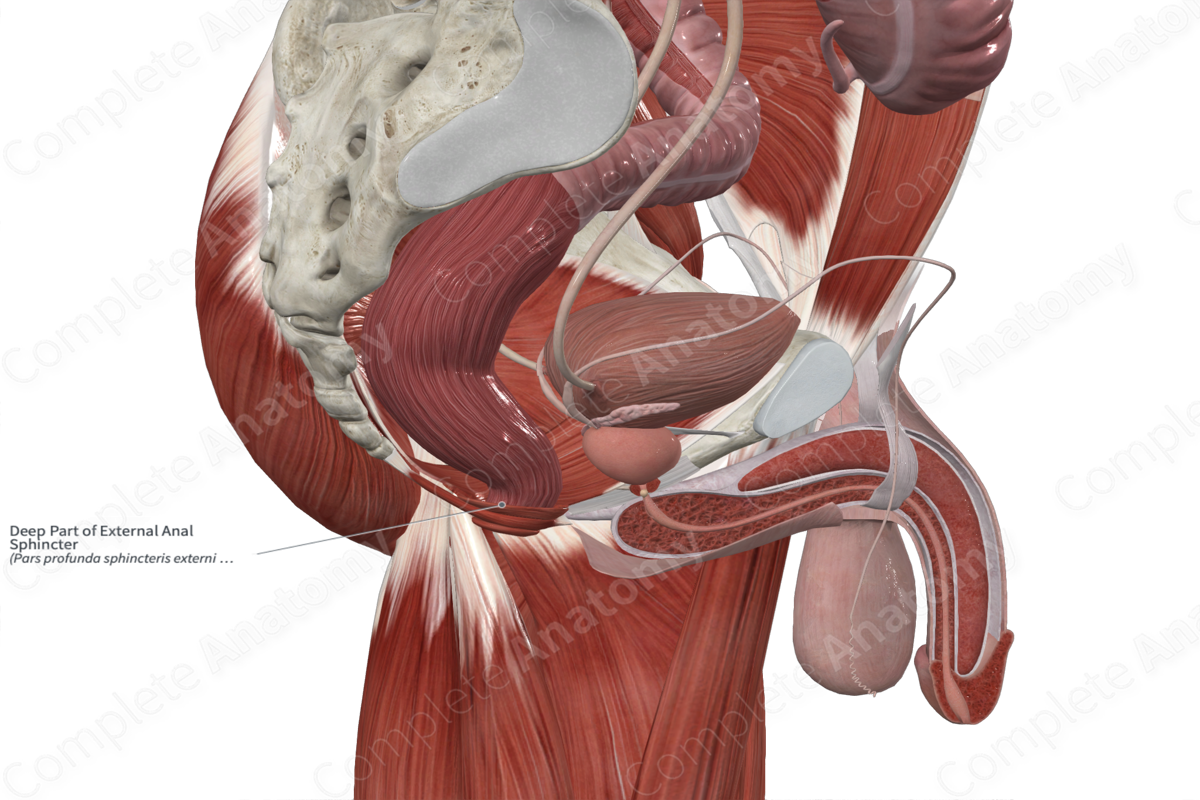
Quick Facts
Origin: Fibers of superficial part of external anal sphincter muscle.
Insertion: Fibers encircle anal canal.
Action: Constricts anal canal.
Innervation: Perineal and inferior anal nerves.
Arterial Supply: Inferior anorectal artery.
Origin
The fibers of the deep part of external anal sphincter muscle are continuous inferiorly with those of the superficial part.
Insertion
The fibers of the deep part of external anal sphincter muscle encircle the anal canal.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The external anal sphincter muscle is found in the anal triangle of the perineum. It is a large, voluntary, circular type of skeletal muscle that surrounds the anal canal.
For descriptive purposes, it is divided into three parts:
- a superiorly located deep part;
- a centrally located superficial part;
- an inferiorly located subcutaneous part.
The external anal sphincter muscle is located:
- anterior to the anococcygeal ligament;
- posterior to the perineal body and the superficial and deep transverse perineal muscles;
- superficial to the internal anal sphincter;
- inferior to the levator ani muscle.
Regarding the deep part of external anal sphincter muscle specifically:
- its fibers are continuous superiorly with those of the puboanalis muscle;
- it is located superficial to the internal anal sphincter.
Actions
The external anal sphincter muscle constricts the anal canal, keeping it closed and contributing to fecal continence. Its fibers are capable of maintaining a tonic contraction at rest, which relaxes during defecation (Moore, Dalley and Agur, 2009).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Fecal incontinence
References
Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F. and Agur, A. M. R. (2009) Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Actions
The external anal sphincter muscle constricts the anal canal, keeping it closed and contributing to fecal continence. Its fibers are capable of maintaining a tonic contraction at rest, which relaxes during defecation (Moore, Dalley and Agur, 2009).




