Quick Facts
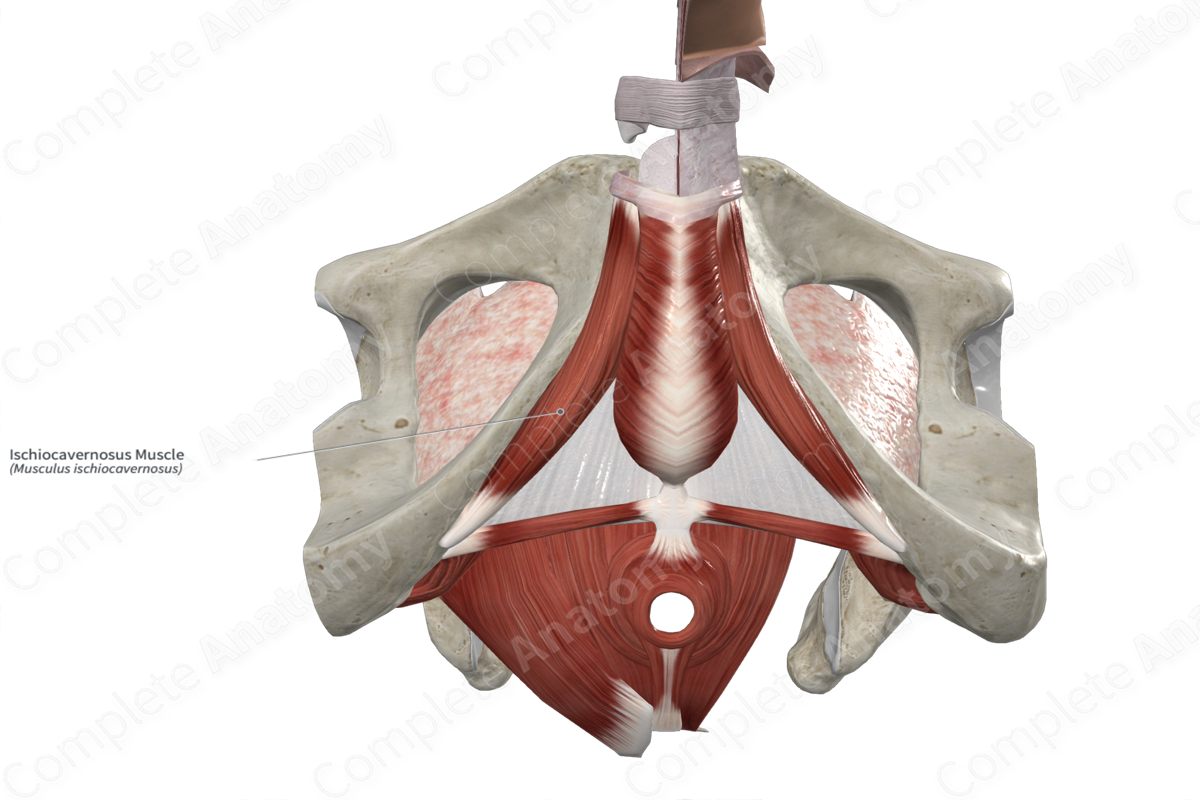
Origin: Ischial tuberosity and ramus of ischium.
Insertion: Female: crus of clitoris; Male: crus of penis.
Action: Assists in erection of clitoris in females and penis in males.
Innervation: Perineal nerve (S2-S4).
Arterial Supply: Female: posterior labial branches of perineal artery; Male: posterior scrotal branches of perineal artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ischiocavernosus muscle originates from the:
- ischial tuberosity;
- ramus of ischium.
Insertion
In females, the fibers of the ischiocavernosus muscle travel anteromedially and insert onto the inferior and medial aspects of the crus of clitoris.
In males, the fibers of the ischiocavernosus muscle travel anteromedially and insert onto the inferior and medial aspects of the crus of the penis.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The ischiocavernosus muscle is one of the muscles of the superficial perineal space, which itself is found in the urogenital triangle of the perineum. It is a short, thin skeletal muscle.
It is located:
- superficial to the crus of clitoris in the female and the crus of penis in the male;
- inferior to the perineal membrane;
- medial to the inferior pubic arch and ramus of ischium;
- lateral to the bulbospongiosus muscle.
Actions
The ischiocavernosus muscle assists in the erection of the clitoris in females and erection of the penis in males by compressing adjacent blood vessels (Standring, 2016).
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Actions
The ischiocavernosus muscle assists in the erection of the clitoris in females and erection of the penis in males by compressing adjacent blood vessels (Standring, 2016).
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Ischiocavernosus Muscle

The ischiocavernosus muscle extends from the ischial tuberosity to the clitoral crura, inserting on to the body of the clitoris (this muscle compresses the crura of the clitoris and delays the return of blood through the veins, contributing to maintain the erection).




