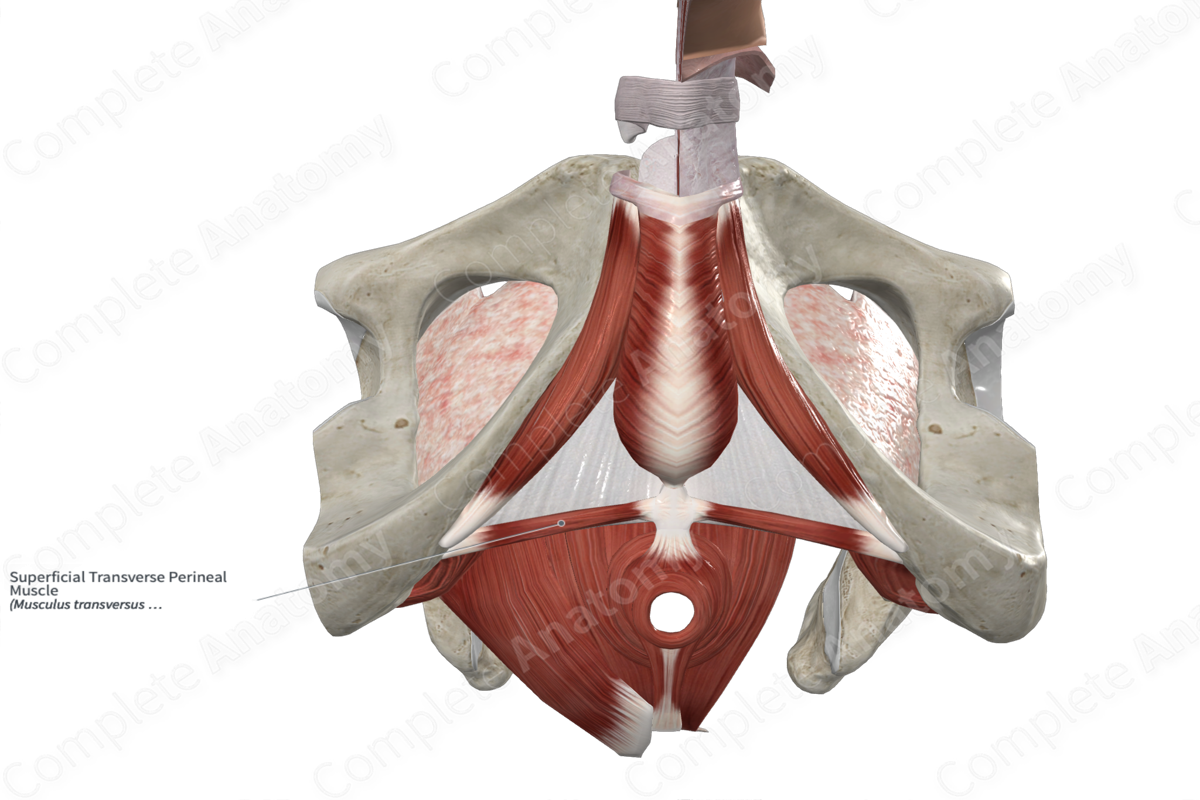
Superficial Transverse Perineal Muscle
Musculus transversus superficialis perinei
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Ischial tuberosity; ramus of ischium.
Insertion: Perineal body.
Action: Stabilizes perineal body; provides structural support to adjacent pelvic and perineal structures.
Innervation: Perineal nerve (S2-S4).
Arterial Supply: Perineal artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The superficial transverse perineal muscle originates from the:
- ischial tuberosity;
- ramus of ischium.
Insertion
The fibers of the superficial transverse perineal muscle travel medially and insert onto the perineal body.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
The superficial transverse perineal muscle is one of the muscles of the superficial perineal space, which itself is found in the urogenital triangle of the perineum. It is a short, thin skeletal muscle.
It is located:
- inferior to the perineal membrane and the deep transverse perineal muscle;
- medial to the ischium;
- lateral to the perineal body.
Actions
The superficial transverse perineal muscle stabilizes the perineal body and provides structural support to adjacent pelvic and perineal structures (Moore, Dalley and Agur, 2009).
References
Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F. and Agur, A. M. R. (2009) Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Actions
The superficial transverse perineal muscle stabilizes the perineal body and provides structural support to adjacent pelvic and perineal structures (Moore, Dalley and Agur, 2009).
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Perineum

The perineum is the space below the levator ani and includes the external genitalia, urethra, and anus.




