Quick Facts
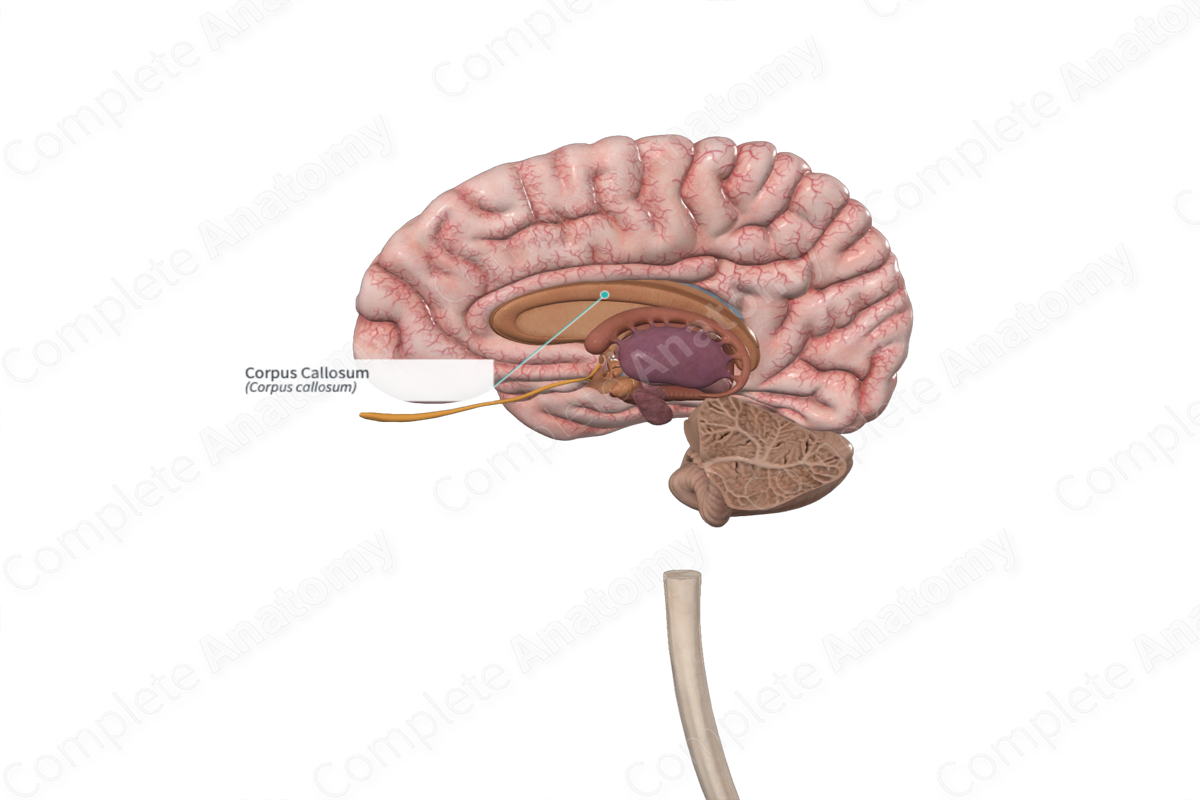
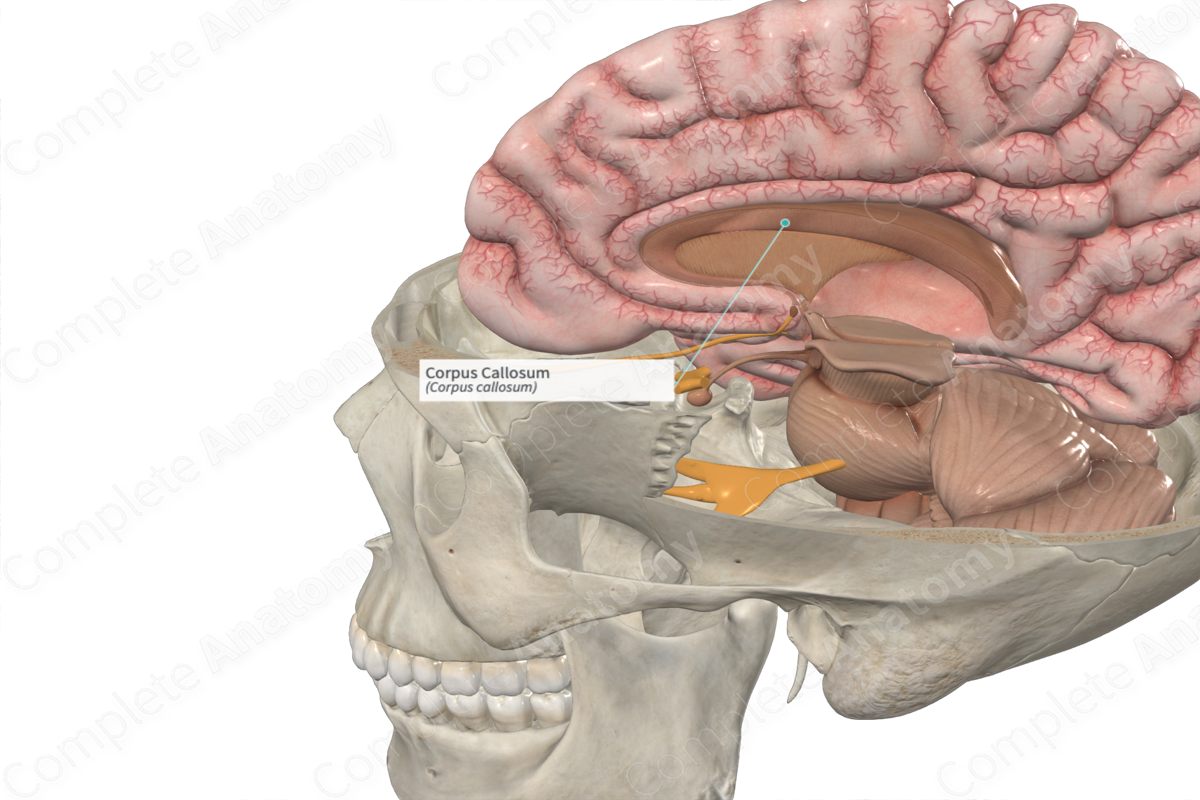
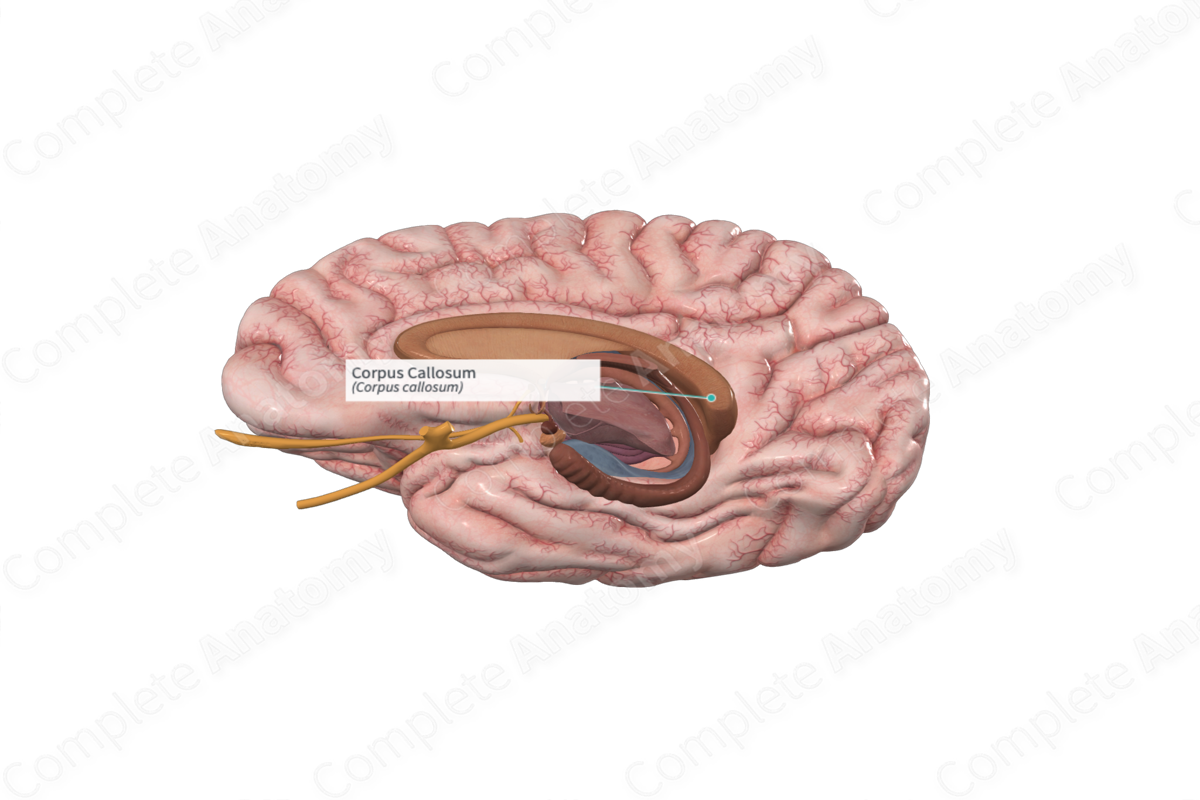
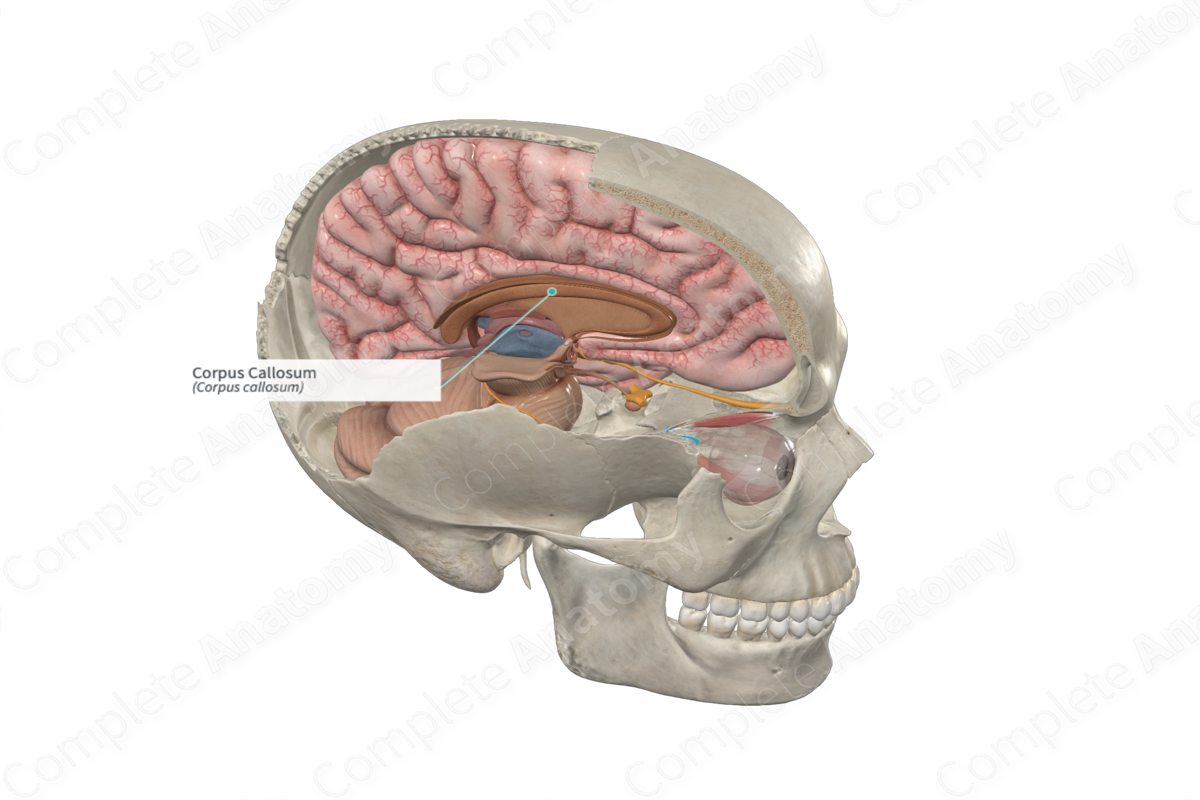
The corpus callosum (aka great cerebral commissure) forms a white matter bridge between the left and right cerebral hemispheres of the brain, allowing communication between them.
The posterior portion of the corpus callosum is called the splenium and the anterior portion the genu, with the body of the corpus callosum lying between these two portions.
Communication between the cerebral hemispheres may sometimes be severed in cases of epilepsy by separating the corpus callosum.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Corpus Callosum

The corpus callosum is a midline cerebral structure located at the superior margin of the cavum septum pellucidum (CSP), both of which develop from the commissural plate.
Corpus Callosum: What Is It, Location, Function, and More

The corpus callosum is a thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the two cerebral hemispheres, allowing them to communicate. It is also Learn with Osmosis