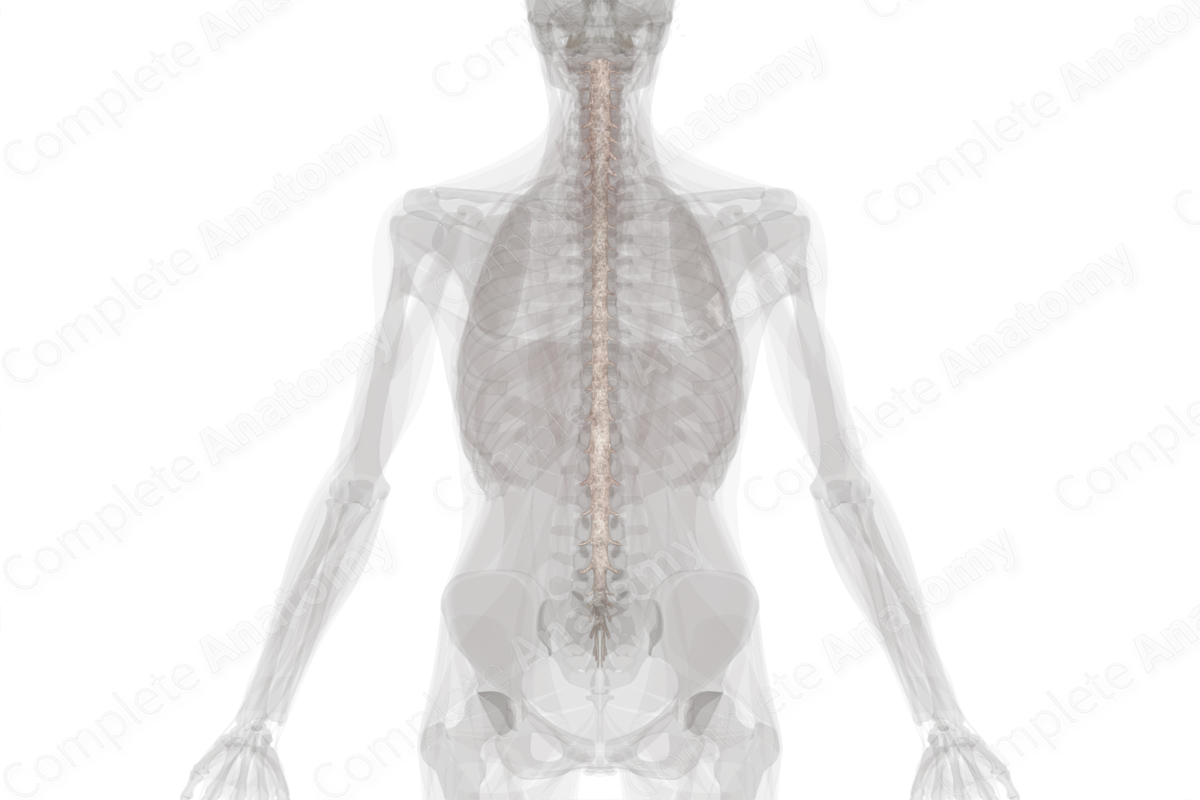
Spinal Arachnoid Structure
Arachnoid mater is a thin opaque layer that sends wispy fibers inward to the pia mater. This created the spider web appearance that gives the arachnoid mater its name. The spinal arachnoid mater has a similar function and appearance to the cranial arachnoid mater. It is the middle of the three meningeal layers.
Related parts of the anatomy
Spinal Arachnoid Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The arachnoid mater is located adjacent to the dura mater, separated from it by the potential subdural space. It is also separated from the spinal cord and pia mater by the presence of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space. At the level of the second sacral vertebra, the arachnoid mater fuses with the dura mater.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Spinal Arachnoid

Congenital or idiopathic spinal arachnoid cysts are diagnosed when there is no antecedent history of trauma or other etiologic factors and the intraoperative macroscopic and microscopic findings show a cyst wall composed of normal or slightly thickened arachnoid tissue.




