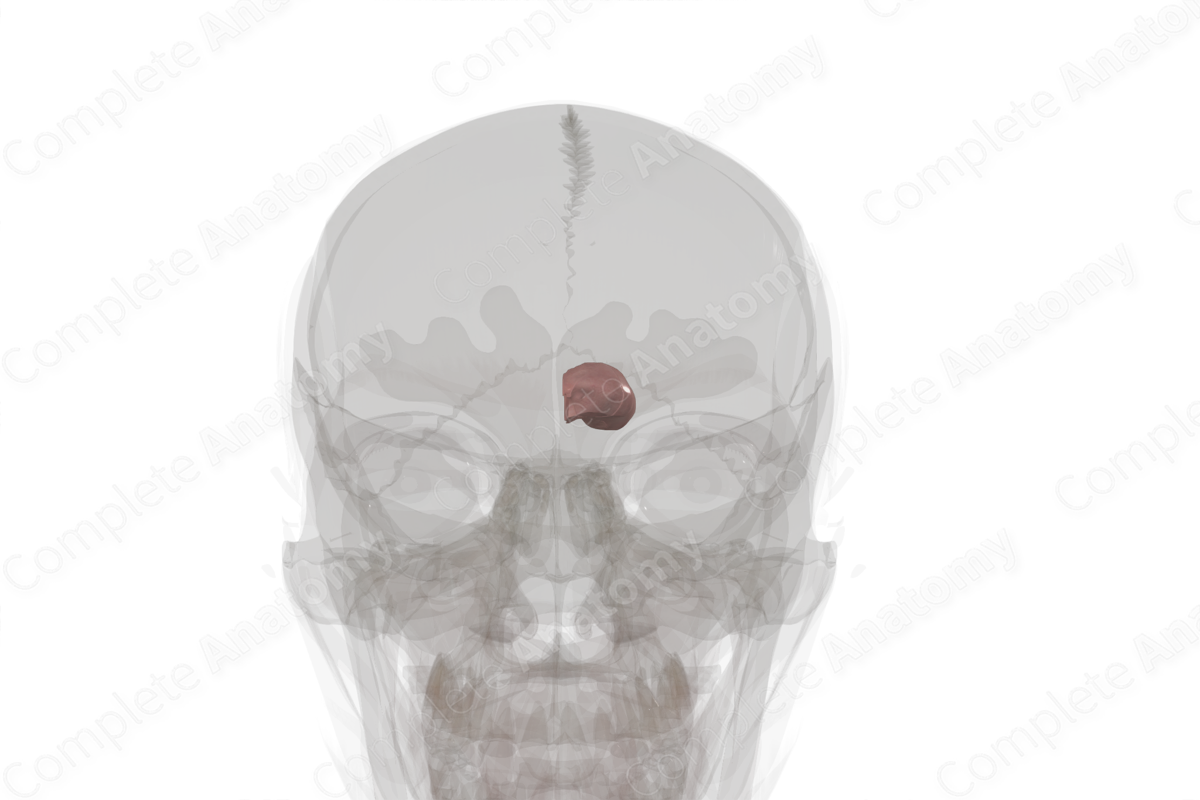
Thalamus (Left)
Quick Facts
This oval structure is the largest part of the diencephalon and borders the third ventricle. It is an important relay station for both motor and sensory fibers which leave and enter the brain. The thalamus also has a major role in the integration and processing of motor and sensory information to higher brain centers.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Thalamus: What Is It, Location, Function, and More

The thalamus, an egg-shaped structure made up of thalamic nuclei, is part of the brain that relays sensory and motor signals from various Learn with Osmosis





