Quick Facts
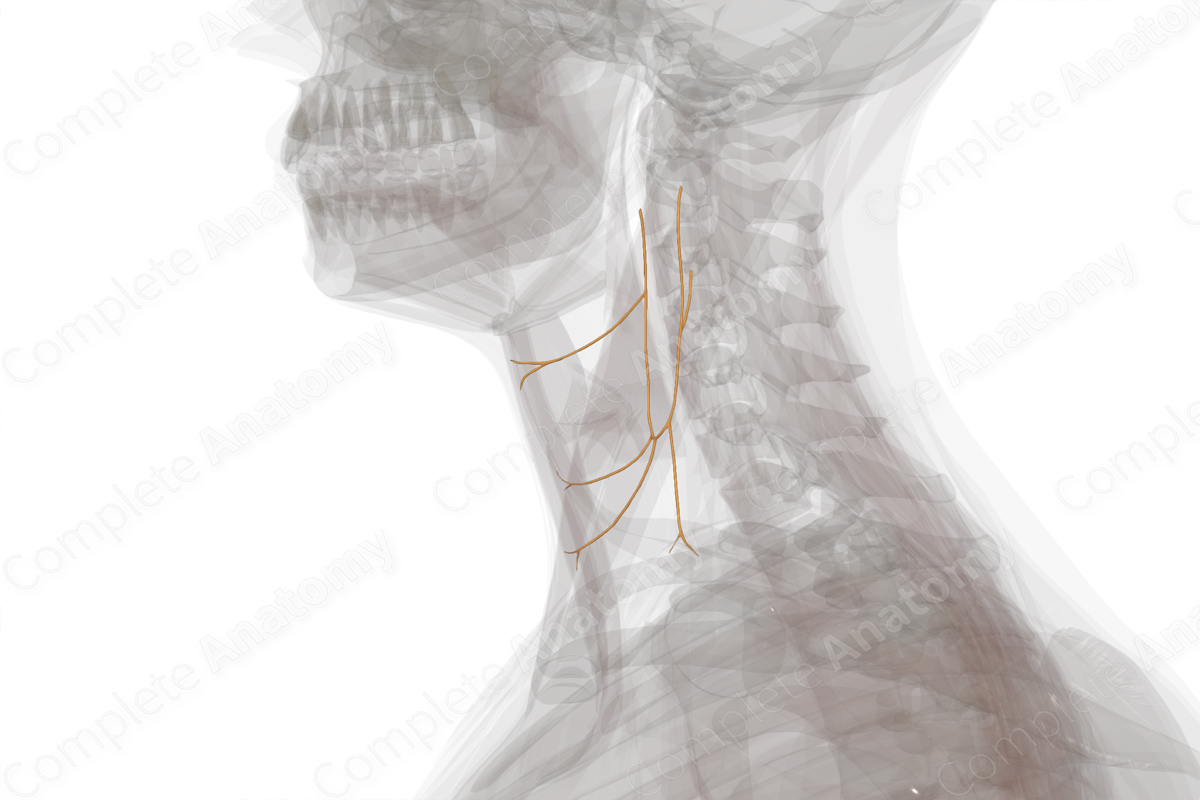
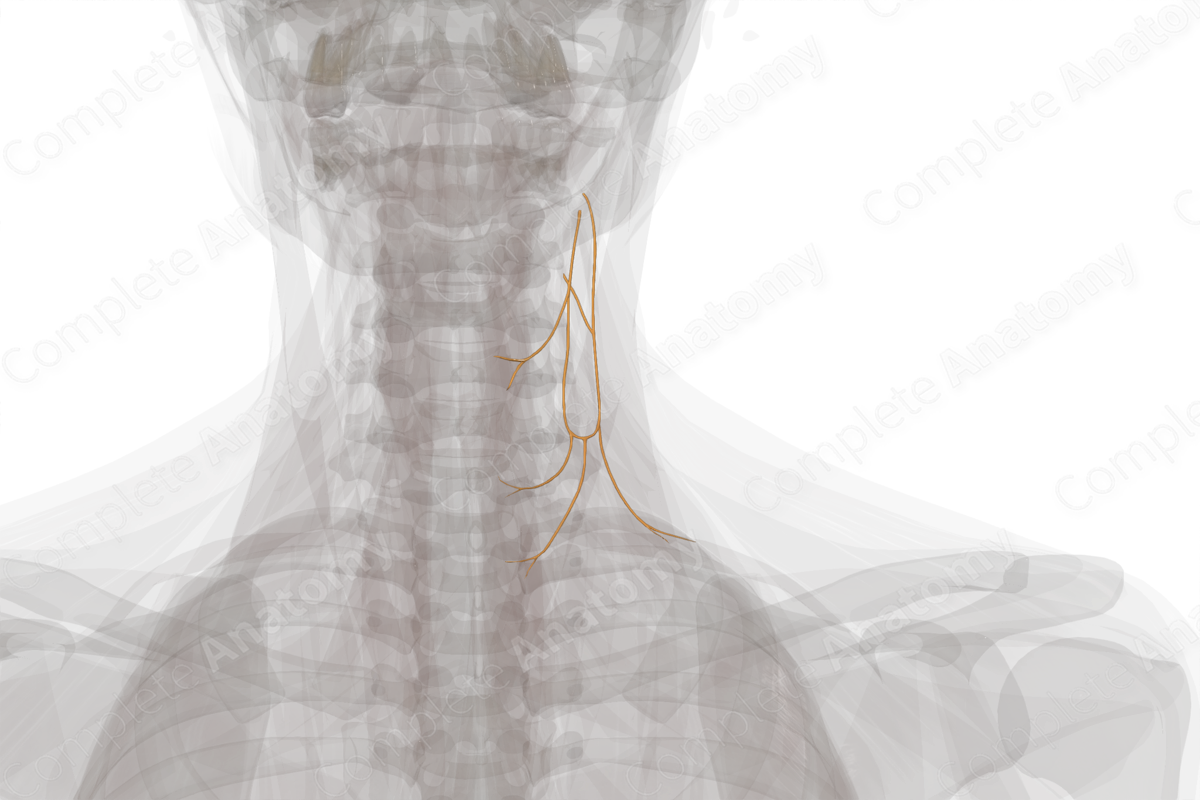
Origin: Anterior rami of first to third (sometimes fourth) cervical nerves.
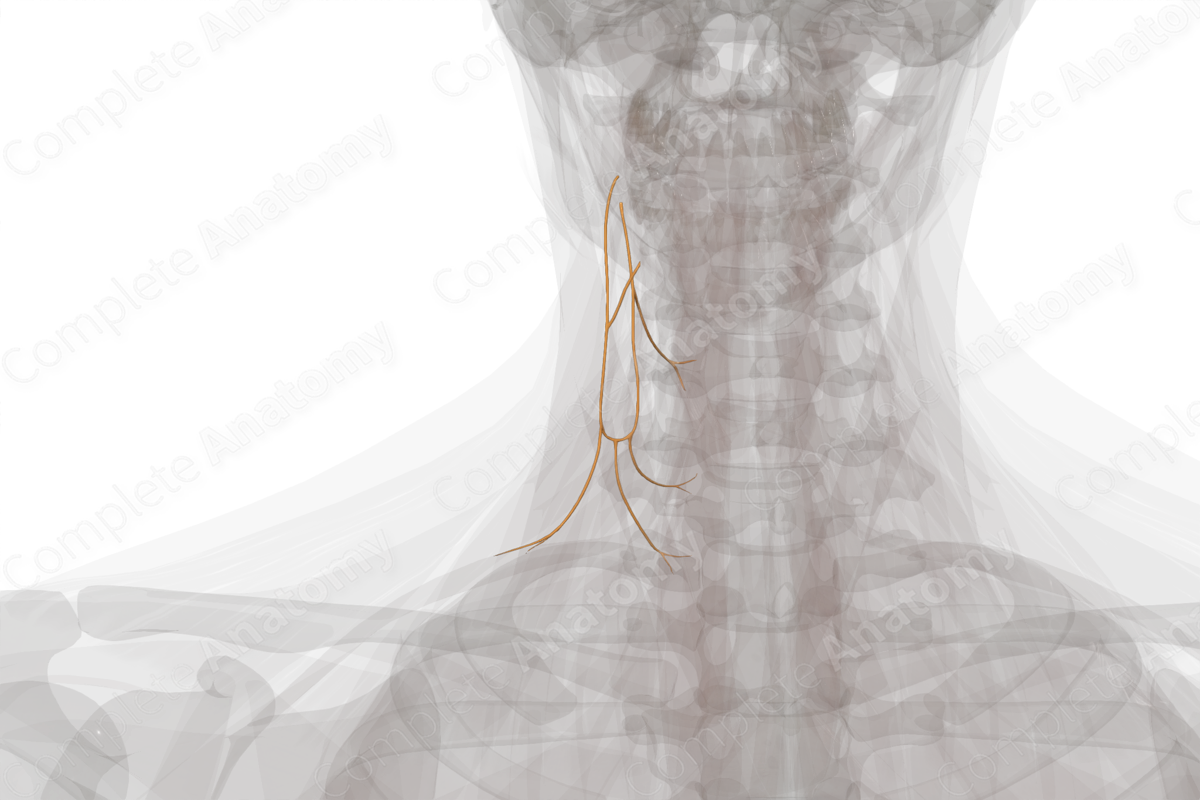
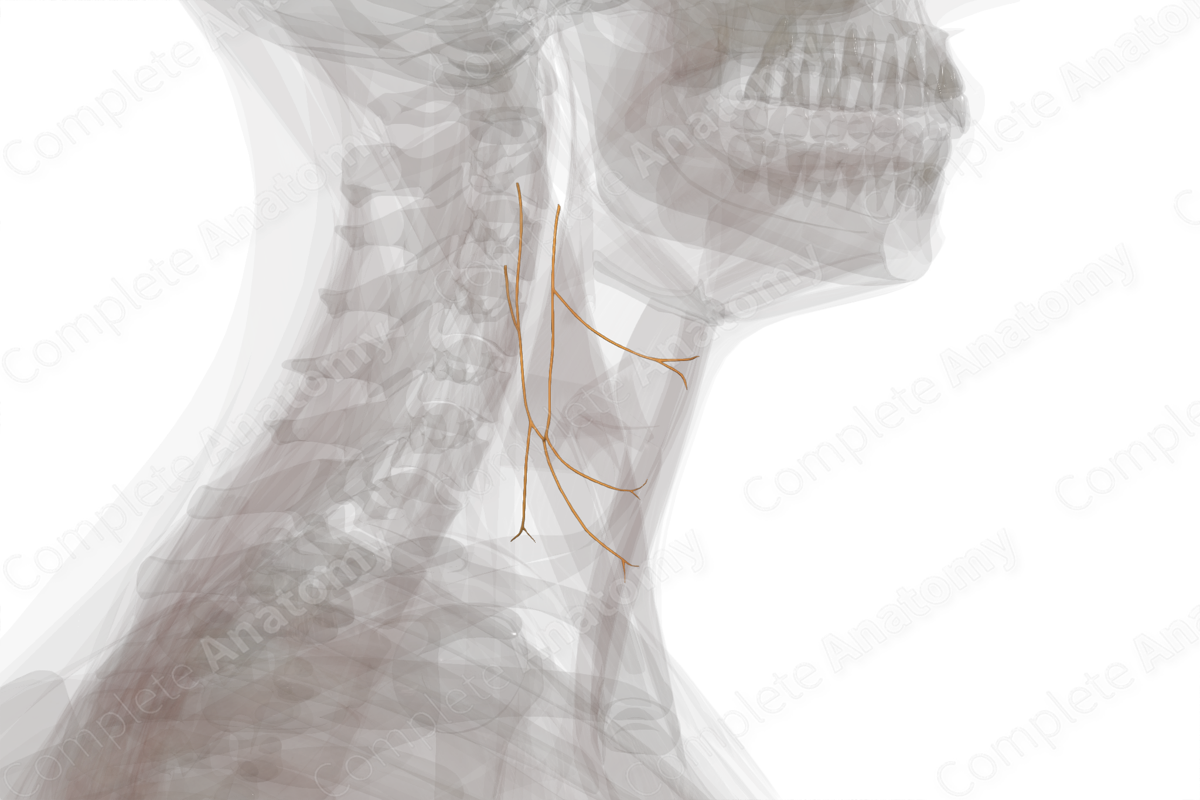
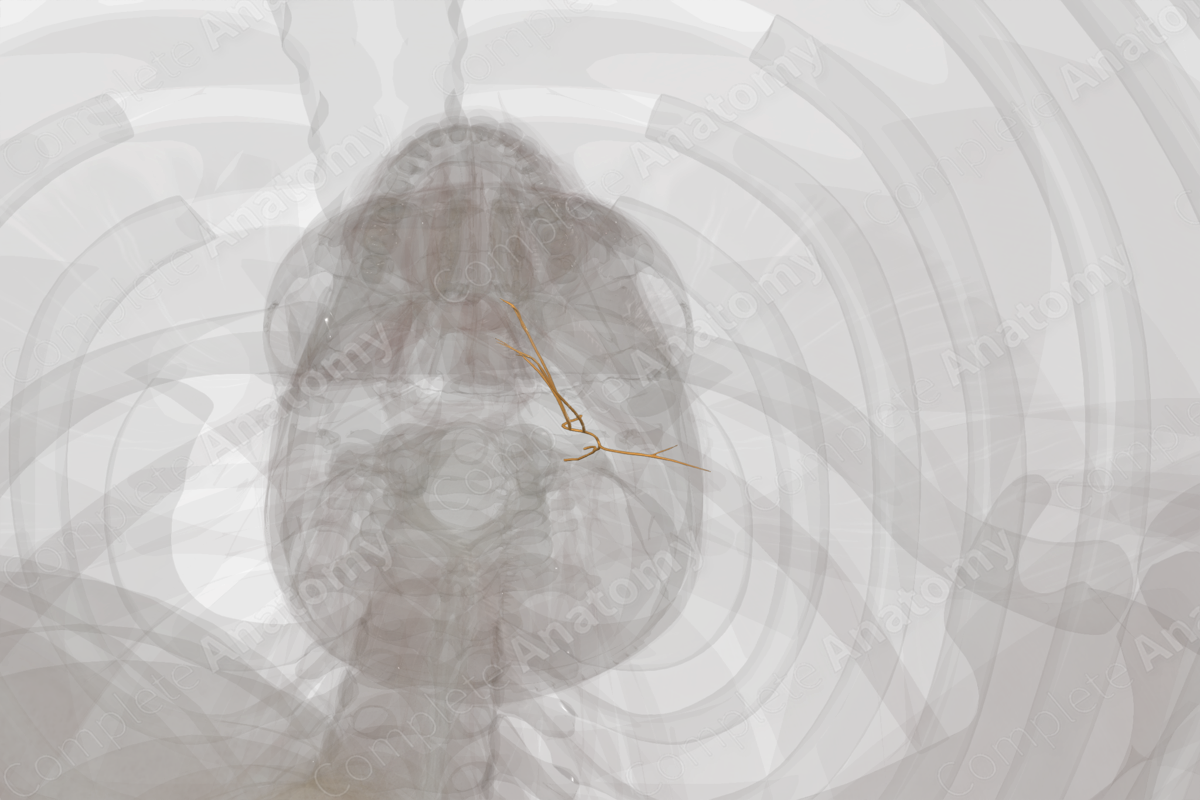
Course: The superior root leaves the hypoglossal nerve to descends between internal jugular vein and carotid arteries, while the inferior root descends medial or lateral to internal jugular vein. The two unite to form the ansa cervicalis.
Branches: Branches to infrahyoid muscles.
Supply: Infrahyoid muscles. Communicating branches to connect with cardiac and phrenic nerves.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ansa cervicalis is formed by the union of its superior and inferior roots, which contain neuronal fibers from the first to third cervical spinal segments. Communicating motor neuronal fibers emerge from the loop between C1 and C2 and travel through the hypoglossal nerve. Some of these fibers leave the nerve as a hypoglossal branch and contribute to the formation of the superior root of ansa cervicalis. The inferior root of the ansa cervicalis originates directly from the anterior rami of the second and third cervical nerves.
Course
The superior root of the ansa cervicalis, as it leaves the hypoglossal nerve, descends on the carotid sheath between the internal jugular vein and the carotid arteries. The inferior root descends in very close approximation to the internal jugular vein. The two roots united to form ansa cervicalis.
Branches
Both the superior and inferior roots of ansa cervicalis give muscular branches to infrahyoid muscles.
Supplied Structures
The ansa cervicalis innervates the infrahyoid muscle (omohyoid, sternothyroid, and sternohyoid), except the thyrohyoid muscle.